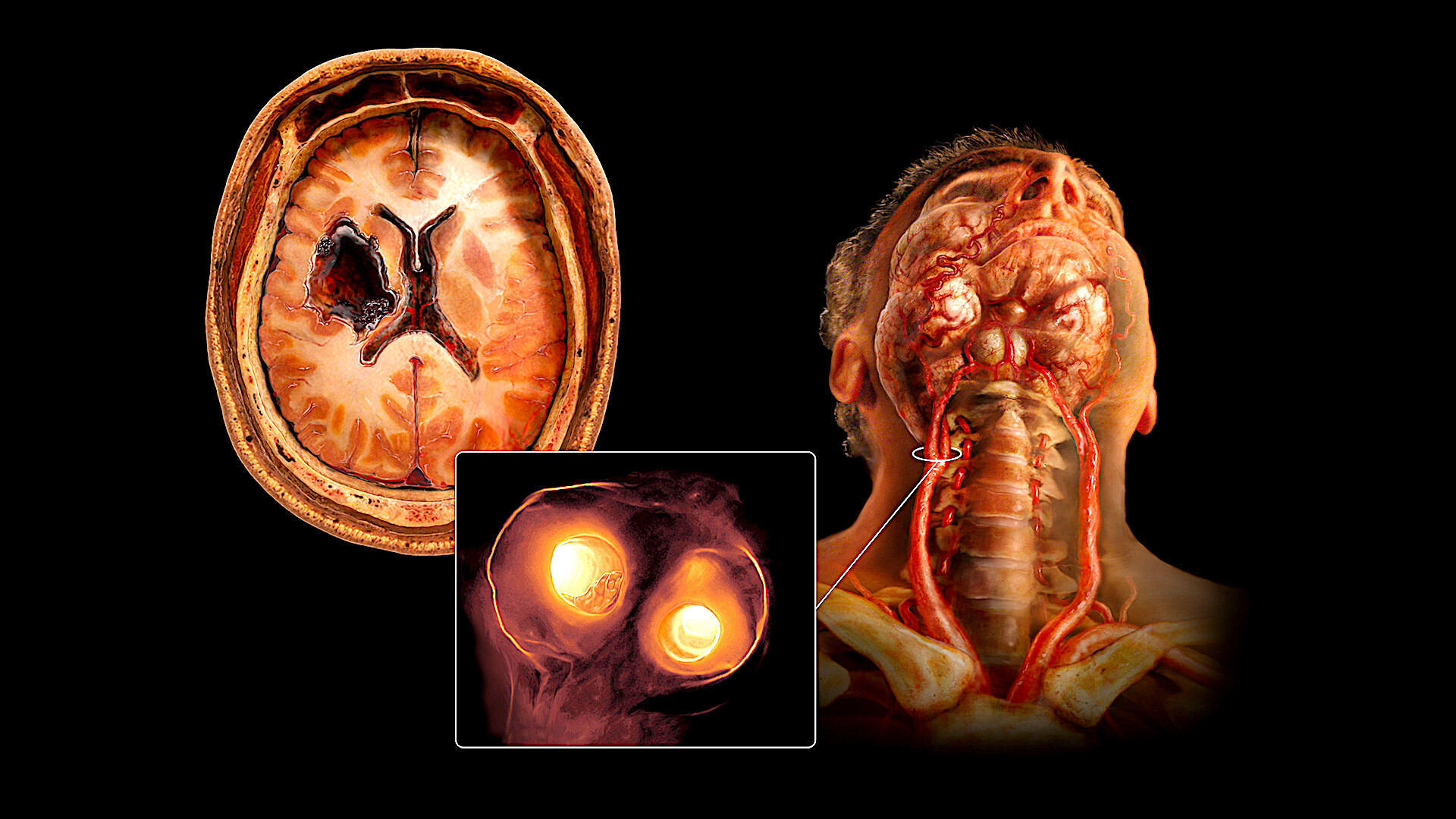
Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) is a rare condition that affects the arteries, causing them to narrow or bulge. This can lead to various health issues, including high blood pressure, stroke, and aneurysms. FMD primarily impacts women, though men can also be affected. The exact cause remains unknown, but genetics and hormones might play a role. Symptoms vary widely, making diagnosis tricky. Some people experience headaches, dizziness, or ringing in the ears, while others might have no symptoms at all. Understanding Fibromuscular Dysplasia is crucial for early detection and management. Let's dive into 40 facts that shed light on this mysterious condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) primarily affects women, causing abnormal cell growth in medium-sized arteries. It can lead to various symptoms and serious complications, requiring tailored treatment and ongoing monitoring.
- Diagnosis of FMD involves imaging techniques like angiography and blood tests to identify characteristic artery changes. Treatment options include medications, angioplasty, surgery, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
What is Fibromuscular Dysplasia?
Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) is a rare condition affecting the arteries. It causes abnormal cell growth in the walls of medium-sized arteries, leading to narrowing, beading, or aneurysms. This can affect blood flow and cause various symptoms.
-
FMD primarily affects women: About 90% of FMD patients are women, typically diagnosed between ages 40 and 60.
-
Not limited to one artery: FMD can affect multiple arteries, including those in the kidneys, brain, abdomen, and limbs.
-
Unknown cause: The exact cause of FMD remains unknown, though genetic and hormonal factors may play a role.
-
Different types: There are three main types of FMD: intimal, medial, and adventitial, each affecting different layers of the artery wall.
-
Medial FMD most common: The medial type, characterized by a "string of beads" appearance on imaging, is the most frequently diagnosed form.
Symptoms of Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Symptoms of FMD can vary widely depending on which arteries are affected. Some people may have no symptoms, while others experience severe complications.
-
High blood pressure: When FMD affects the renal arteries, it can lead to hypertension, which is often resistant to medication.
-
Headaches and dizziness: FMD in the carotid or vertebral arteries can cause headaches, dizziness, and even transient ischemic attacks (TIAs).
-
Abdominal pain: If the mesenteric arteries are involved, patients might experience abdominal pain, especially after eating.
-
Pulsatile tinnitus: A whooshing sound in the ears, known as pulsatile tinnitus, can occur if FMD affects the arteries near the ears.
-
Leg pain: FMD in the arteries of the legs can lead to pain, especially during exercise, due to reduced blood flow.
Diagnosis of Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Diagnosing FMD can be challenging due to its rarity and the variety of symptoms. Several imaging techniques are used to identify the characteristic changes in the arteries.
-
Angiography: This imaging technique uses X-rays and a contrast dye to visualize the arteries and detect the "string of beads" pattern.
-
Duplex ultrasound: A non-invasive test that uses sound waves to create images of blood flow in the arteries.
-
CT angiography: Combines a CT scan with an injected contrast dye to produce detailed images of the arteries.
-
MRI angiography: Uses magnetic fields and contrast dye to create detailed images of blood vessels.
-
Blood tests: While not diagnostic, blood tests can help rule out other conditions that might cause similar symptoms.
Treatment Options for Fibromuscular Dysplasia
There is no cure for FMD, but various treatments can help manage symptoms and prevent complications. Treatment plans are often tailored to the individual.
-
Medications: Blood pressure medications, such as ACE inhibitors or beta-blockers, are commonly prescribed.
-
Angioplasty: A procedure that involves inflating a small balloon inside the artery to widen it and improve blood flow.
-
Surgery: In severe cases, surgical options like arterial bypass or endarterectomy may be necessary.
-
Lifestyle changes: Patients are often advised to adopt a heart-healthy diet, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking.
-
Regular monitoring: Ongoing follow-up with a healthcare provider is crucial to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as needed.
Complications of Fibromuscular Dysplasia
FMD can lead to several serious complications if not properly managed. Understanding these risks is important for patients and healthcare providers.
-
Aneurysms: Abnormal bulges in the artery wall can form and potentially rupture, leading to life-threatening bleeding.
-
Dissections: Tears in the artery wall can occur, causing severe pain and potentially leading to stroke or organ damage.
-
Stroke: Reduced blood flow or artery dissections in the brain can increase the risk of stroke.
-
Kidney damage: Persistent high blood pressure due to renal artery involvement can lead to kidney damage over time.
-
Heart attack: FMD affecting the coronary arteries can increase the risk of heart attack.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand FMD and develop more effective treatments. Advances in genetics and imaging techniques hold promise for the future.
-
Genetic studies: Researchers are investigating potential genetic links to FMD to identify risk factors and develop targeted therapies.
-
New imaging techniques: Advances in imaging technology may improve the accuracy of FMD diagnosis and monitoring.
-
Clinical trials: Ongoing clinical trials are exploring new medications and treatment approaches for FMD.
-
Patient registries: Registries like the United States Registry for FMD collect data to improve understanding and management of the condition.
-
Awareness campaigns: Efforts to raise awareness among healthcare providers and the public aim to improve early diagnosis and treatment.
Living with Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Living with FMD can be challenging, but many patients lead full, active lives with proper management and support.
-
Support groups: Joining a support group can provide emotional support and practical advice from others living with FMD.
-
Education: Learning about the condition and staying informed about new developments can empower patients to take an active role in their care.
-
Advocacy: Patients and families can advocate for better research funding and healthcare policies to improve FMD care.
-
Mental health: Managing stress and mental health is important, as chronic illness can take a toll on emotional well-being.
-
Regular exercise: Staying active with appropriate exercise can help manage symptoms and improve overall health.
Famous Cases of Fibromuscular Dysplasia
While FMD is rare, some notable individuals have been diagnosed with the condition, bringing attention to this little-known disease.
-
Susan B. Anthony List President Marjorie Dannenfelser: Publicly shared her diagnosis to raise awareness about FMD.
-
Actress Sharon Stone: Suffered a stroke caused by FMD, highlighting the serious complications of the disease.
-
Author and advocate Karen Duffy: Uses her platform to educate others about living with FMD.
-
Olympic swimmer Dara Torres: Diagnosed with FMD, she continues to inspire others with her athletic achievements.
-
Journalist and author Jean Carper: Shares her experiences with FMD to help others understand the condition.
Final Thoughts on Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) is a rare condition that affects the arteries, causing them to narrow and potentially leading to serious health issues. Understanding the symptoms, such as high blood pressure, headaches, and dizziness, can help in early detection and treatment. While the exact cause remains unknown, genetic and hormonal factors may play a role. Treatment options vary from medication to surgical procedures, depending on the severity of the condition.
Staying informed about FMD is crucial for those affected and their loved ones. Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers can make a significant difference in managing the condition. Though living with FMD can be challenging, advancements in medical research continue to offer hope for better treatments and outcomes. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to managing health conditions like Fibromuscular Dysplasia.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
