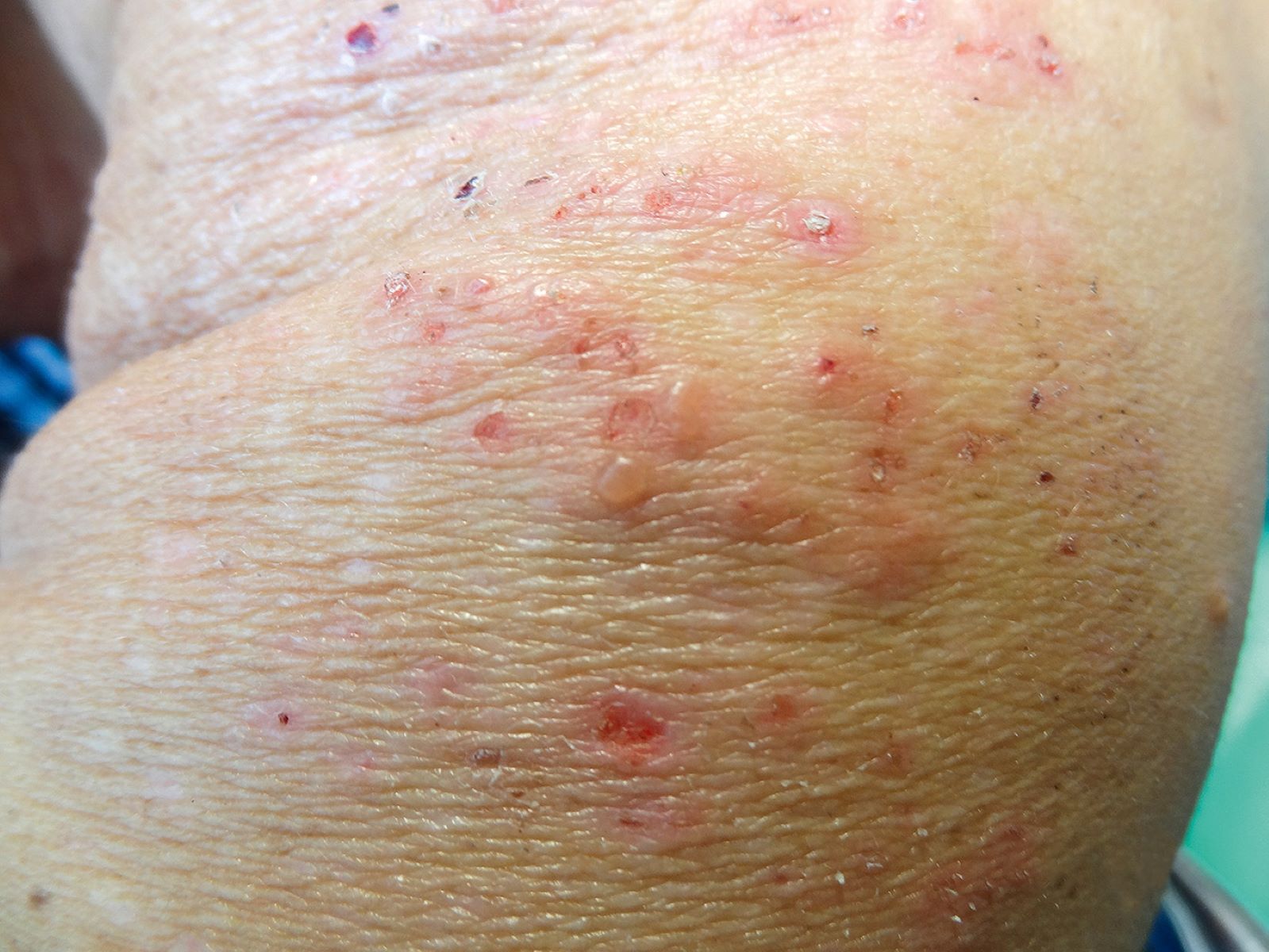
Duhring's Disease, also known as Dermatitis Herpetiformis, is a rare, chronic skin condition that causes intense itching and blistering. This autoimmune disorder is closely linked to celiac disease and is triggered by gluten ingestion. People with Duhring's Disease often experience clusters of small, itchy blisters and bumps, typically on elbows, knees, buttocks, and back. The exact cause remains unknown, but genetics and immune system malfunctions play significant roles. Diagnosis usually involves skin biopsies and blood tests. Treatment primarily focuses on a strict gluten-free diet and medications like dapsone to manage symptoms. Understanding Duhring's Disease can help those affected lead more comfortable lives.
Key Takeaways:
- Duhring's Disease, also known as Dermatitis Herpetiformis, causes itchy, blistering rashes and is linked to gluten sensitivity. Treatment involves a strict gluten-free diet and medication to manage symptoms.
- Living with Duhring's Disease can be challenging, but support groups, education, and a positive outlook can help manage the condition and improve quality of life.
What is Duhring's Disease?
Duhring's Disease, also known as Dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH), is a chronic skin condition. It causes itchy, blistering skin rashes. This disease is closely linked to gluten sensitivity and celiac disease.
- Duhring's Disease is named after Dr. Louis Adolphus Duhring, who first described it in 1884.
- Dermatitis Herpetiformis is often called the "gluten rash" because it is triggered by gluten consumption.
- Blisters and Itchiness are the main symptoms, appearing on elbows, knees, back, and buttocks.
- Celiac Disease Connection: Nearly all patients with DH have celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder.
- IgA Antibodies: The disease involves deposits of Immunoglobulin A (IgA) in the skin.
- Gluten-Free Diet: The primary treatment is a strict gluten-free diet.
- Dapsone Medication: Dapsone, an antibiotic, is often prescribed to control symptoms.
- Genetic Predisposition: It is more common in people with certain genetic markers, like HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8.
- Age of Onset: Typically appears in adults between 20 and 40 years old.
- Gender Prevalence: More common in men than women.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how Duhring's Disease is diagnosed can help in managing the condition effectively.
- Intense Itching: The itchiness can be severe, often leading to scratching and skin damage.
- Symmetrical Rash: The rash usually appears symmetrically on both sides of the body.
- Small Blisters: These blisters are filled with a clear fluid and can burst easily.
- Burning Sensation: Some patients experience a burning feeling before blisters appear.
- Skin Biopsy: A skin biopsy is used to diagnose DH, showing IgA deposits under the skin.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can detect antibodies associated with celiac disease.
- Misdiagnosis: DH is sometimes mistaken for eczema or other skin conditions.
- Delayed Diagnosis: Many patients experience a delay in diagnosis due to its rarity.
- Gluten Challenge: Sometimes, a gluten challenge is used to confirm the diagnosis.
- Dermatologist Consultation: Seeing a dermatologist is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment and Management
Managing Duhring's Disease involves both dietary changes and medication.
- Gluten-Free Diet: Eliminating gluten from the diet is essential for managing symptoms.
- Dapsone Side Effects: While effective, Dapsone can cause side effects like anemia and neuropathy.
- Regular Monitoring: Patients on Dapsone need regular blood tests to monitor for side effects.
- Alternative Medications: Sulfapyridine and other medications may be used if Dapsone is not tolerated.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Patients need to watch for deficiencies in iron, calcium, and vitamins.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional and practical support.
- Dietitian Consultation: Working with a dietitian can help ensure a balanced, gluten-free diet.
- Skin Care: Gentle skin care routines can help manage symptoms and prevent infections.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding other triggers, like iodine, can help reduce flare-ups.
- Long-Term Commitment: Managing DH requires a lifelong commitment to dietary changes.
Living with Duhring's Disease
Living with Duhring's Disease can be challenging, but understanding the condition can make it easier.
- Mental Health Impact: The chronic nature of DH can affect mental health, leading to anxiety or depression.
- Social Challenges: Eating out and social events can be difficult due to dietary restrictions.
- Education and Awareness: Educating friends and family about the condition can provide better support.
- Traveling Tips: Planning ahead for meals and snacks can make traveling easier.
- Label Reading: Learning to read food labels is crucial for avoiding gluten.
- Hidden Gluten: Gluten can be hidden in non-food items like medications and cosmetics.
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular medical check-ups are important to monitor the condition and overall health.
- Exercise and Fitness: Staying active can help improve overall well-being and reduce stress.
- Skin Protection: Protecting the skin from sun and injury can prevent worsening of symptoms.
- Positive Outlook: Maintaining a positive outlook and focusing on what can be controlled can improve quality of life.
Final Thoughts on Duhring's Disease
Duhring's Disease, also known as Dermatitis Herpetiformis, is a chronic skin condition linked to gluten sensitivity. It causes itchy, blistering skin rashes, often mistaken for other skin issues. Gluten-free diets can significantly reduce symptoms, making it crucial for those affected to avoid gluten. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing this condition effectively. While it can be challenging, understanding the triggers and maintaining a strict diet can lead to a better quality of life. If you suspect you have Duhring's Disease, consult a healthcare professional for proper testing and guidance. Remember, knowledge and proactive management are your best tools in dealing with this condition. Stay informed, stay healthy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
