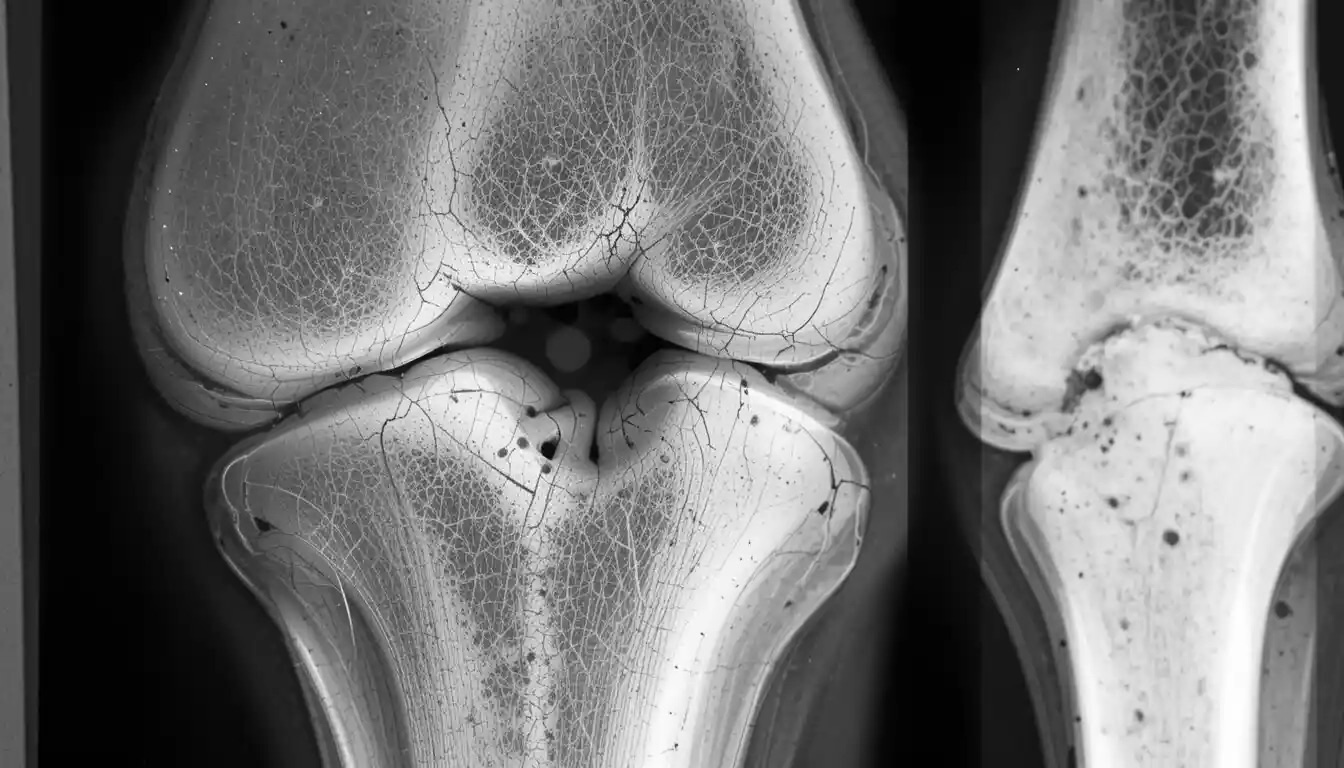
What is a Codman Triangle? A Codman Triangle is a type of periosteal reaction seen in radiology, often indicating an aggressive bone lesion. Named after American surgeon Ernest Amory Codman, this triangular area forms when a lesion lifts the periosteum away from the bone, creating a new bone formation. Common causes include osteosarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, and infections. Recognizing this pattern on X-rays can be crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the significance of a Codman Triangle helps medical professionals identify serious conditions quickly, potentially saving lives. Let's dive into 40 intriguing facts about this important radiological sign.
Key Takeaways:
- Codman Triangle is a radiographic sign linked to aggressive bone lesions, aiding in early diagnosis and treatment planning. It can appear in various conditions, including cancer and infections.
- Detecting a Codman Triangle involves imaging techniques like X-rays and MRI. Its presence guides biopsy, treatment planning, and can indicate the aggressiveness of the lesion.
What is Codman Triangle?
The Codman Triangle is a radiographic finding often associated with aggressive bone lesions. Named after Ernest Amory Codman, this triangular area forms when a periosteal reaction lifts the periosteum away from the bone. Here are some intriguing facts about this medical phenomenon.
-
Named After Ernest Codman: The Codman Triangle is named after Dr. Ernest Amory Codman, a pioneering American surgeon known for his work in bone pathology.
-
Indicative of Aggressive Lesions: This radiographic sign often suggests the presence of aggressive bone lesions, such as osteosarcoma or Ewing's sarcoma.
-
Periosteal Reaction: The triangle forms due to a periosteal reaction, where the periosteum (a layer covering the bone) gets lifted by a fast-growing lesion.
-
Common in Osteosarcoma: Osteosarcoma, a type of bone cancer, frequently shows the Codman Triangle on X-rays.
-
Not Exclusive to Cancer: While often linked to malignancies, the Codman Triangle can also appear in benign conditions like osteomyelitis (bone infection).
How is Codman Triangle Detected?
Detection of the Codman Triangle typically involves imaging techniques. Understanding these methods can help in early diagnosis and treatment.
-
X-rays: The most common method for detecting a Codman Triangle is through plain radiographs or X-rays.
-
CT Scans: Computed Tomography (CT) scans provide a more detailed view, helping to confirm the presence of the triangle.
-
MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can also be used, especially to assess the extent of soft tissue involvement.
-
Bone Scans: Bone scintigraphy can help in identifying the activity of the lesion, which might show a Codman Triangle.
-
Ultrasound: Though less common, ultrasound can sometimes detect periosteal reactions in superficial bones.
Clinical Significance of Codman Triangle
The presence of a Codman Triangle has significant clinical implications. It often guides the diagnosis and management of bone lesions.
-
Early Diagnosis: Detecting a Codman Triangle can lead to early diagnosis of aggressive bone lesions, improving treatment outcomes.
-
Guides Biopsy: The presence of this sign can help in deciding the site for a biopsy, ensuring accurate sampling.
-
Treatment Planning: Recognizing a Codman Triangle aids in planning the appropriate treatment, whether surgical or medical.
-
Prognostic Indicator: The appearance of a Codman Triangle can sometimes indicate the aggressiveness of the lesion, influencing prognosis.
-
Differential Diagnosis: It helps in differentiating between various types of bone lesions, both benign and malignant.
Historical Context of Codman Triangle
Understanding the historical context of the Codman Triangle provides insight into its significance in medical history.
-
First Described in 1934: Dr. Ernest Codman first described this radiographic sign in 1934.
-
Pioneering Work: Codman's work laid the foundation for modern bone pathology and radiology.
-
Legacy in Medicine: The Codman Triangle remains a crucial concept in orthopedic and oncologic radiology.
-
Educational Tool: It is widely used in medical education to teach about periosteal reactions and bone lesions.
-
Influence on Research: Codman's findings have influenced numerous research studies in bone pathology.
Codman Triangle in Different Conditions
The Codman Triangle can appear in various medical conditions, each with unique characteristics.
-
Osteosarcoma: This primary bone cancer often shows a Codman Triangle due to rapid periosteal elevation.
-
Ewing's Sarcoma: Another aggressive bone tumor, Ewing's Sarcoma, frequently presents with this radiographic sign.
-
Osteomyelitis: Infections like osteomyelitis can cause a periosteal reaction, forming a Codman Triangle.
-
Metastatic Lesions: Secondary bone cancers can also lead to the appearance of this triangle on X-rays.
-
Benign Bone Lesions: Conditions like aneurysmal bone cysts and giant cell tumors might show a Codman Triangle.
Codman Triangle in Pediatric Patients
Children can also present with a Codman Triangle, often indicating different underlying conditions compared to adults.
-
Common in Children: Pediatric patients with bone lesions often show a Codman Triangle due to their active periosteum.
-
Juvenile Osteosarcoma: This type of osteosarcoma in children frequently presents with a Codman Triangle.
-
Ewing's Sarcoma in Kids: Ewing's Sarcoma is more common in children and adolescents, often showing this radiographic sign.
-
Bone Infections: Pediatric osteomyelitis can cause a periosteal reaction, forming a Codman Triangle.
-
Growth Plate Involvement: In children, lesions involving the growth plate can lead to the appearance of a Codman Triangle.
Imaging Techniques for Codman Triangle
Various imaging techniques are employed to detect and analyze the Codman Triangle, each offering unique advantages.
-
Digital Radiography: Modern digital X-rays provide high-resolution images, making it easier to spot a Codman Triangle.
-
3D CT Scans: Three-dimensional CT scans offer a detailed view of the bone and periosteal reaction.
-
Contrast-Enhanced MRI: Using contrast agents in MRI can highlight the extent of the lesion and periosteal elevation.
-
PET Scans: Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans can assess the metabolic activity of the lesion, often correlating with the presence of a Codman Triangle.
-
Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA): Though primarily used for bone density, DEXA scans can sometimes detect periosteal reactions.
Future Research on Codman Triangle
Ongoing research continues to explore the implications and applications of the Codman Triangle in medical science.
-
Genetic Studies: Research is being conducted to understand the genetic factors associated with lesions showing a Codman Triangle.
-
Advanced Imaging: Development of new imaging technologies aims to improve the detection and analysis of periosteal reactions.
-
Targeted Therapies: Studies are exploring targeted therapies for lesions presenting with a Codman Triangle, aiming for better outcomes.
-
Artificial Intelligence: AI and machine learning are being used to enhance the detection and interpretation of Codman Triangles in radiographic images.
-
Clinical Trials: Ongoing clinical trials are investigating new treatments for conditions associated with the Codman Triangle, aiming to improve patient care.
Final Thoughts on Codman Triangle
Understanding the Codman Triangle can be crucial for anyone interested in radiology or orthopedics. This triangular area on X-rays often indicates aggressive bone lesions like osteosarcoma. Recognizing it early can lead to quicker diagnosis and treatment, potentially improving patient outcomes. While not always a sign of cancer, it’s a red flag that should prompt further investigation.
Learning about these medical signs helps demystify complex topics, making them more accessible. Whether you're a student, a healthcare professional, or just curious, knowing about the Codman Triangle adds to your knowledge toolkit.
Thanks for sticking with us through this exploration. Keep learning, stay curious, and remember, knowledge is power.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
