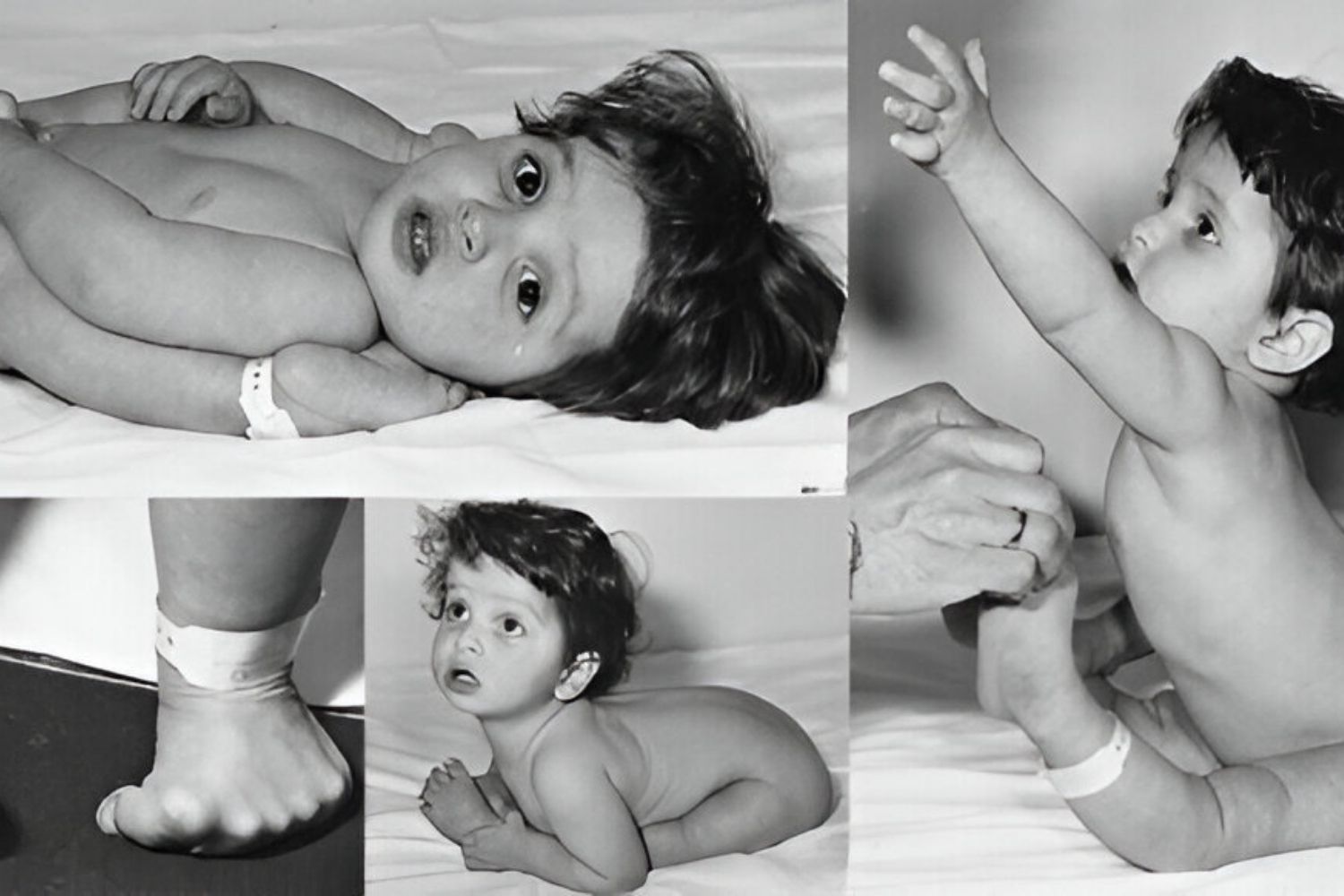
Arthrochalasia Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (aEDS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects connective tissues, leading to joint hypermobility, skin that bruises easily, and other systemic issues. Characterized by mutations in the COL1A1 and COL1A2 genes, this condition disrupts the normal production of collagen, a crucial protein for skin, bones, and other tissues. Symptoms often appear early in life, with infants showing signs of joint dislocations and fragile skin. Managing aEDS requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving geneticists, orthopedists, and physical therapists to address the diverse symptoms. Understanding the complexities of aEDS can help those affected lead healthier lives and raise awareness for better research and treatment options.
Key Takeaways:
- Arthrochalasia Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (aEDS) is a rare genetic disorder causing joint hypermobility, skin issues, and chronic pain due to collagen deficiency. Early diagnosis and personalized care can improve quality of life.
- Living with aEDS requires support from healthcare professionals, adaptive equipment, and strong emotional support networks. Despite challenges, individuals with aEDS show resilience and lead fulfilling lives.
What is Arthrochalasia Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome?
Arthrochalasia Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (aEDS) is a rare genetic disorder affecting connective tissues. This condition leads to joint hypermobility, skin abnormalities, and other systemic issues. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about aEDS.
-
Genetic Mutation: aEDS results from mutations in the COL1A1 or COL1A2 genes, which are crucial for collagen production.
-
Collagen Deficiency: Collagen, a protein that provides structure and strength to connective tissues, is deficient in individuals with aEDS.
-
Joint Hyperlaxity: People with aEDS often experience extreme joint hypermobility, making their joints unusually flexible.
-
Frequent Dislocations: Due to hypermobility, joint dislocations are common and can occur with minimal trauma.
-
Skin Elasticity: The skin of those with aEDS is often highly elastic and can stretch more than usual.
-
Easy Bruising: Fragile blood vessels lead to easy bruising, even from minor bumps or pressure.
-
Delayed Motor Skills: Children with aEDS may experience delays in motor skill development, such as walking or grasping objects.
-
Scoliosis: Spinal curvature, or scoliosis, is a frequent complication in individuals with aEDS.
-
Muscle Hypotonia: Reduced muscle tone, known as hypotonia, is common and can affect overall strength and coordination.
-
Chronic Pain: Joint and muscle pain are persistent issues for many with aEDS, often requiring pain management strategies.
Diagnosis and Symptoms
Diagnosing aEDS involves a combination of genetic testing and clinical evaluation. Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to better management.
-
Genetic Testing: Confirming aEDS typically requires genetic testing to identify mutations in the COL1A1 or COL1A2 genes.
-
Family History: A detailed family history can provide clues, as aEDS is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
-
Skin Biopsy: Sometimes, a skin biopsy is performed to examine the collagen structure under a microscope.
-
Joint Hypermobility Score: The Beighton score is used to assess the degree of joint hypermobility.
-
Skin Fragility: Thin, fragile skin that tears easily is a hallmark symptom of aEDS.
-
Wound Healing: Poor wound healing and the formation of atrophic scars are common in aEDS patients.
-
Dental Issues: Dental problems, including fragile teeth and gum disease, can occur due to collagen deficiencies.
-
Eye Problems: Some individuals may experience eye issues, such as myopia or retinal detachment.
-
Heart Valve Issues: Mitral valve prolapse and other heart valve abnormalities can be associated with aEDS.
-
Hernias: Hernias, particularly inguinal hernias, are more frequent due to weakened connective tissues.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for aEDS, various treatments and management strategies can improve quality of life.
-
Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy helps maintain joint function and muscle strength.
-
Pain Management: Pain relief can be achieved through medications, physical therapy, and other interventions.
-
Bracing: Joint braces or supports can help stabilize hypermobile joints and prevent dislocations.
-
Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to correct joint dislocations or other complications.
-
Skin Care: Gentle skin care routines and avoiding trauma can help manage skin fragility.
-
Dental Care: Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene are essential to prevent dental issues.
-
Cardiac Monitoring: Regular heart check-ups are important to monitor and manage any heart valve issues.
-
Nutritional Support: A balanced diet and possibly supplements can support overall health and well-being.
-
Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy can assist with daily activities and improve quality of life.
-
Psychological Support: Counseling or support groups can help individuals and families cope with the emotional aspects of aEDS.
Living with Arthrochalasia Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Living with aEDS requires adapting to various challenges, but with the right support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives.
-
Education: Educating patients, families, and caregivers about aEDS is crucial for effective management.
-
Support Networks: Connecting with support groups and communities can provide emotional and practical support.
-
Adaptive Equipment: Using adaptive equipment, such as mobility aids, can enhance independence.
-
Regular Monitoring: Ongoing medical monitoring helps manage symptoms and prevent complications.
-
Lifestyle Adjustments: Making lifestyle adjustments, such as avoiding high-impact activities, can reduce injury risk.
-
Emergency Preparedness: Having a plan in place for medical emergencies is important for individuals with aEDS.
-
Advocacy: Advocating for awareness and research can help improve understanding and treatment of aEDS.
-
Genetic Counseling: Genetic counseling can provide information and support for family planning decisions.
-
Personalized Care: Each individual with aEDS may require a personalized care plan tailored to their specific needs.
-
Hope and Resilience: Despite the challenges, many individuals with aEDS demonstrate remarkable resilience and lead meaningful lives.
Final Thoughts on Arthrochalasia Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Arthrochalasia Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (aEDS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects connective tissues, leading to joint hypermobility, skin elasticity, and fragile tissues. Understanding aEDS can help those affected manage symptoms better and seek appropriate medical care. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and improving quality of life. Genetic counseling can provide valuable insights for families dealing with this condition.
Living with aEDS requires a multidisciplinary approach, including physical therapy, pain management, and regular monitoring by healthcare professionals. Awareness and education about aEDS can foster a supportive community, reducing the stigma and isolation often felt by those affected. By staying informed and proactive, individuals with aEDS can lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by this condition. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to managing rare disorders like aEDS.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
