Sneddon's Syndrome is a rare, mysterious condition that often leaves people scratching their heads. But what exactly is it? Sneddon's Syndrome is a disorder that affects blood vessels, leading to a mix of skin and neurological symptoms. Imagine having a condition where your skin shows a net-like pattern, and you might also experience strokes or other brain issues. Sounds confusing, right? This syndrome primarily affects young to middle-aged adults, and its exact cause remains unknown. However, researchers believe it could be linked to autoimmune or blood clotting disorders. Understanding Sneddon's Syndrome can help those affected manage symptoms better and seek appropriate medical care. Ready to dive into 35 intriguing facts about this puzzling condition? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Sneddon's Syndrome is a rare disorder affecting blood vessels, causing skin discoloration and neurological symptoms. Early diagnosis and proper management are crucial for those affected.
- Treatment for Sneddon's Syndrome focuses on managing symptoms and reducing complications. Regular medical check-ups, lifestyle changes, and emotional support can improve the quality of life for patients.
What is Sneddon's Syndrome?
Sneddon's Syndrome is a rare, progressive disorder affecting blood vessels. It primarily impacts the skin and brain, leading to a variety of symptoms. Understanding this condition can help those affected manage their health better.
- Sneddon's Syndrome is named after Dr. Ian Sneddon, who first described it in 1965.
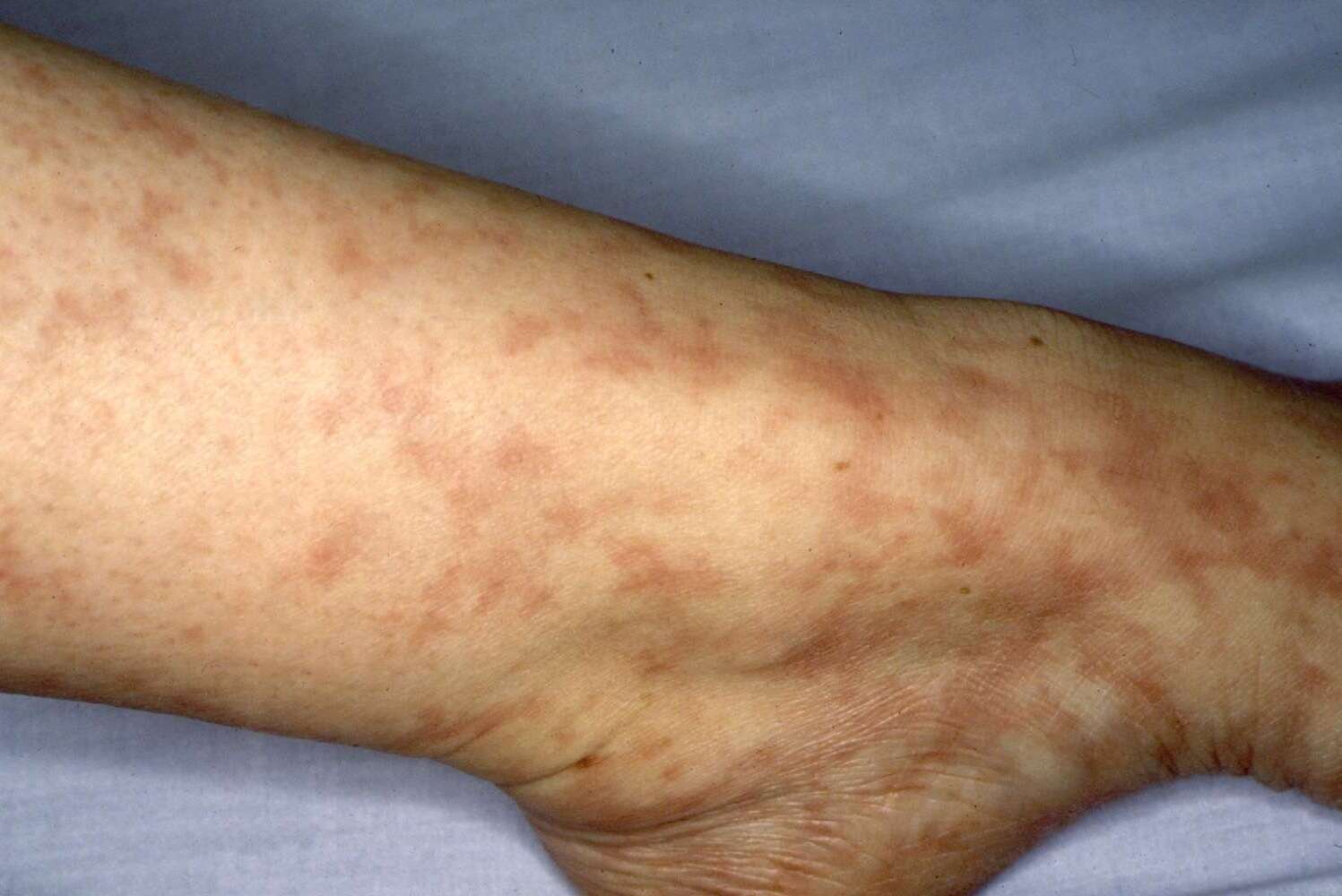
- It is characterized by a combination of livedo reticularis (a mottled purplish skin discoloration) and cerebrovascular disease.
- The exact cause of Sneddon's Syndrome remains unknown, though it is believed to involve autoimmune mechanisms.
- It predominantly affects young to middle-aged adults, with a higher prevalence in women.
- Symptoms often begin with skin changes before neurological symptoms appear.
Symptoms of Sneddon's Syndrome
The symptoms of Sneddon's Syndrome can vary widely among individuals. They often involve both dermatological and neurological manifestations.
- Livedo reticularis is the most common skin symptom, presenting as a net-like pattern of reddish-blue skin discoloration.
- Patients may experience transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), which are temporary episodes of stroke-like symptoms.
- Strokes are a significant risk, leading to permanent neurological damage in some cases.
- Headaches, particularly migraines, are frequently reported by those with Sneddon's Syndrome.
- Cognitive impairments, including memory loss and difficulty concentrating, can occur as the disease progresses.
Diagnosis of Sneddon's Syndrome
Diagnosing Sneddon's Syndrome can be challenging due to its rarity and the variability of symptoms. A combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests is often required.
- Dermatologists and neurologists typically collaborate to diagnose Sneddon's Syndrome.
- Skin biopsy can reveal characteristic changes in blood vessels, aiding in diagnosis.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain may show evidence of past strokes or other abnormalities.
- Blood tests can help rule out other conditions with similar symptoms, such as antiphospholipid syndrome.
- A thorough patient history and physical examination are crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Sneddon's Syndrome
While there is no cure for Sneddon's Syndrome, various treatments can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
- Anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin, are often prescribed to prevent blood clots.
- Antiplatelet drugs, like aspirin, may also be used to reduce stroke risk.
- Immunosuppressive therapies can be beneficial for patients with an autoimmune component.
- Regular monitoring and follow-up with healthcare providers are essential for managing the condition.
- Lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet and regular exercise, can improve overall health and reduce symptom severity.
Complications Associated with Sneddon's Syndrome
Sneddon's Syndrome can lead to various complications, particularly if not managed effectively. Awareness of these potential issues is important for patients and caregivers.
- Recurrent strokes are a major complication, potentially leading to significant disability.
- Chronic headaches and migraines can severely impact quality of life.
- Cognitive decline may progress over time, affecting daily functioning.
- Skin ulcers and other dermatological issues can develop in some patients.
- Cardiovascular problems, such as hypertension, are more common in individuals with Sneddon's Syndrome.
Living with Sneddon's Syndrome
Living with Sneddon's Syndrome requires ongoing management and support. Patients can take several steps to improve their quality of life.
- Regular medical check-ups are essential to monitor disease progression and adjust treatments as needed.
- Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Educating family and friends about the condition can foster a supportive environment.
- Stress management techniques, such as meditation and yoga, can help reduce symptom flare-ups.
- Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand Sneddon's Syndrome and develop more effective treatments. Advances in medical science offer hope for improved outcomes.
- Genetic studies are exploring potential hereditary factors contributing to the syndrome.
- New imaging techniques may enhance early diagnosis and monitoring of disease progression.
- Clinical trials are investigating novel therapies, including targeted immunosuppressive drugs.
- Collaborative research efforts are essential for advancing knowledge and treatment of this rare condition.
- Increased awareness and education about Sneddon's Syndrome can lead to earlier diagnosis and better patient outcomes.
Final Thoughts on Sneddon's Syndrome
Sneddon's Syndrome, a rare and complex condition, intertwines skin and neurological symptoms. Understanding its symptoms like livedo reticularis and strokes can lead to early diagnosis and better management. Though no cure exists, treatments focus on controlling symptoms and preventing complications. Anticoagulants and immunosuppressants often play a role in managing this syndrome.
Awareness and research are crucial for improving patient outcomes. If you or someone you know shows signs of Sneddon's Syndrome, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation. Staying informed and proactive can make a significant difference in managing this condition.
Remember, while Sneddon's Syndrome may be rare, support and resources are available. Stay connected with medical communities and support groups to navigate this journey effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
