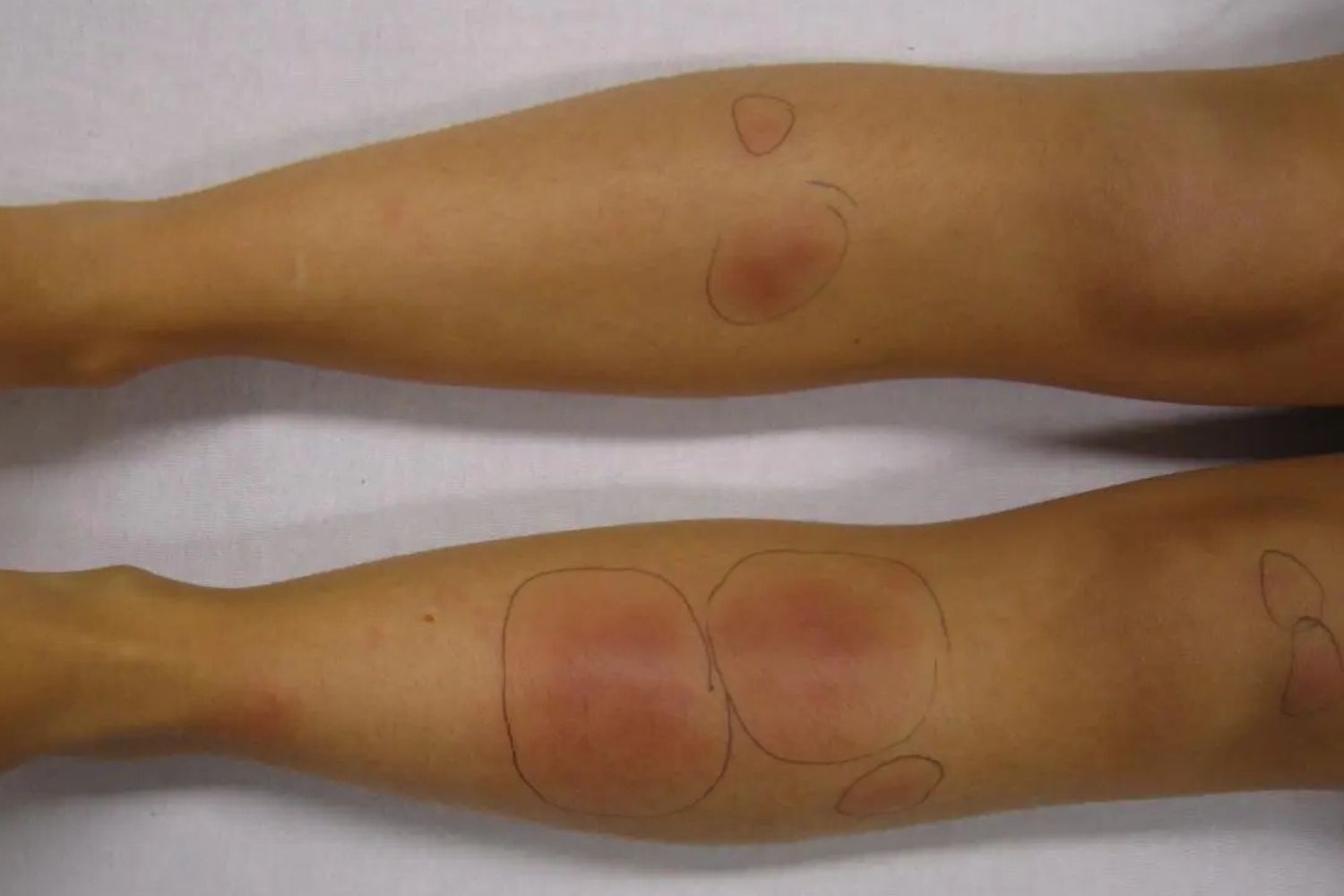
Weber–Christian Disease, also known as relapsing febrile nodular panniculitis, is a rare inflammatory condition. It primarily affects the skin and subcutaneous fat, leading to painful nodules. These nodules can appear anywhere on the body but are most common on the legs and arms. Symptoms often include fever, fatigue, and weight loss. The exact cause remains unknown, but it is believed to involve an abnormal immune response. Diagnosis typically requires a biopsy of the affected tissue. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and may include medications like corticosteroids. Understanding this disease can help those affected manage their condition better.
Key Takeaways:
- Weber-Christian Disease causes painful nodules, fever, fatigue, and weight loss. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve the prognosis, but ongoing management and support are essential for quality of life.
- Ongoing research into genetic factors and new therapies aims to better understand and treat Weber-Christian Disease, offering hope for improved patient outcomes in the future.
What is Weber–Christian Disease?
Weber–Christian Disease, also known as relapsing febrile nodular nonsuppurative panniculitis, is a rare inflammatory condition. It primarily affects the subcutaneous fat tissue, leading to painful nodules and systemic symptoms. Here are some intriguing facts about this uncommon disease.
Symptoms of Weber–Christian Disease
Understanding the symptoms can help in early detection and management. Here are some key symptoms associated with Weber–Christian Disease:
- Painful Nodules: Patients often develop painful, red nodules under the skin, usually on the legs and arms.
- Fever: Recurrent fevers are common, often accompanying the appearance of new nodules.
- Fatigue: Chronic fatigue and general malaise are frequent complaints among those affected.
- Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss can occur due to the body's inflammatory response.
- Joint Pain: Some patients experience joint pain, adding to their discomfort.
- Muscle Pain: Muscle aches and pains are also reported, contributing to overall weakness.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause remains unknown, several factors may contribute to the development of Weber–Christian Disease. Here are some potential causes and risk factors:
- Autoimmune Response: The disease may be linked to an abnormal immune response, where the body attacks its own fat tissue.
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of autoimmune diseases might increase the risk.
- Infections: Certain infections could trigger the onset of symptoms in susceptible individuals.
- Medications: Some drugs, particularly those affecting the immune system, might play a role.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, especially in women, could be a contributing factor.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain environmental triggers might exacerbate the condition.
Diagnosis of Weber–Christian Disease
Diagnosing Weber–Christian Disease can be challenging due to its rarity and nonspecific symptoms. Here are some methods used for diagnosis:
- Clinical Examination: A thorough physical examination to identify characteristic nodules.
- Biopsy: A biopsy of the affected tissue can confirm the diagnosis by revealing inflammation in the fat tissue.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests to check for markers of inflammation and rule out other conditions.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging techniques like MRI or ultrasound may help visualize the extent of inflammation.
- Patient History: Detailed patient history to identify any potential triggers or risk factors.
Treatment Options
Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and reducing inflammation. Here are some common treatment approaches:
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory drugs are often the first line of treatment.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications that suppress the immune system can help control symptoms.
- Pain Relief: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs to manage pain and discomfort.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can improve overall well-being.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy to maintain mobility and reduce muscle pain.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor the disease's progression and adjust treatment as needed.
Prognosis and Complications
The prognosis for Weber–Christian Disease varies. Here are some factors that can influence the outcome:
- Early Diagnosis: Early detection and treatment can improve the prognosis.
- Response to Treatment: How well a patient responds to treatment plays a significant role.
- Chronic Nature: The disease can be chronic, with periods of remission and flare-ups.
- Complications: Potential complications include infections, organ involvement, and severe weight loss.
- Quality of Life: The impact on quality of life can be significant, requiring ongoing management and support.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand Weber–Christian Disease and develop more effective treatments. Here are some areas of focus:
- Genetic Studies: Research into genetic factors that may predispose individuals to the disease.
- New Therapies: Development of new medications and treatment approaches to improve patient outcomes.
Final Thoughts on Weber–Christian Disease
Weber–Christian Disease, also known as relapsing febrile nodular nonsuppurative panniculitis, is a rare condition that affects the fatty layer under the skin. It causes painful nodules, fever, and other systemic symptoms. Though the exact cause remains unknown, it’s often linked to autoimmune responses. Diagnosis can be tricky due to its similarity to other diseases, but a biopsy usually confirms it. Treatment typically involves corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for better outcomes. If you or someone you know shows signs of this disease, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management. Staying informed and proactive can make a significant difference in managing this rare condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
