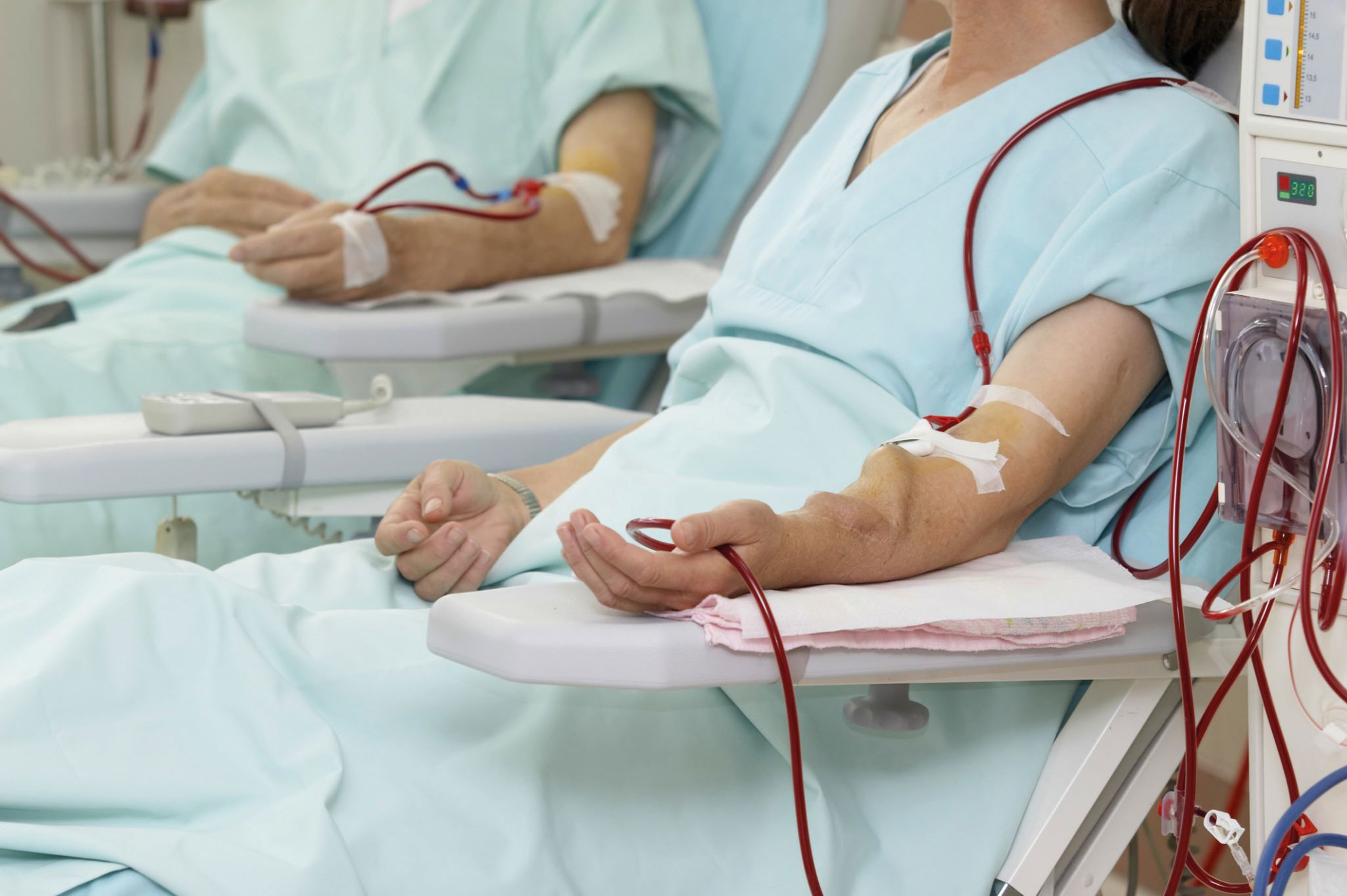
Vascular Access Steal Syndrome (VASS) is a condition that can occur after creating a vascular access for hemodialysis. This condition happens when blood flow is diverted away from the hand, leading to symptoms like pain, numbness, or even tissue damage. Understanding VASS is crucial for patients undergoing dialysis, as early detection and treatment can prevent severe complications. This article will provide 30 facts about VASS, covering its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Whether you're a patient, caregiver, or healthcare professional, these facts will help you grasp the essentials of this condition and how to manage it effectively.
Key Takeaways:
- Vascular Access Steal Syndrome (VASS) primarily affects dialysis patients with arteriovenous fistulas or grafts, causing pain, coldness, and tissue damage. Early detection and management are crucial for preventing severe complications.
- Prevention and management of VASS involve regular monitoring, controlling diabetes, maintaining vascular health, and educating patients. Addressing both physical and emotional aspects can significantly improve a patient's quality of life.
What is Vascular Access Steal Syndrome?
Vascular Access Steal Syndrome (VASS) is a condition affecting patients with arteriovenous fistulas or grafts, commonly used for hemodialysis. This syndrome occurs when blood flow is diverted from the distal extremity, leading to ischemia. Understanding VASS is crucial for those undergoing dialysis and their caregivers.
-
VASS primarily affects dialysis patients. Those with arteriovenous fistulas or grafts are at risk because these access points can divert blood flow.
-
Symptoms include pain and coldness. Patients often experience pain, coldness, or numbness in the affected limb due to reduced blood flow.
-
Can lead to tissue damage. If untreated, VASS can cause severe tissue damage, including ulcers and gangrene.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of VASS. Knowing these can help in early detection and prevention.
-
High-flow fistulas increase risk. Fistulas with high blood flow rates are more likely to cause steal syndrome.
-
Diabetes is a significant risk factor. Diabetic patients are more susceptible due to compromised blood vessels.
-
Older age contributes to higher risk. Elderly patients have a higher incidence of VASS due to age-related vascular changes.
-
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) exacerbates the condition. PAD can worsen the symptoms and severity of VASS.
Diagnosis and Detection
Early diagnosis is key to managing VASS effectively. Various methods are used to identify this condition.
-
Physical examination is the first step. Doctors check for signs like coldness, pallor, and weak pulses in the affected limb.
-
Doppler ultrasound aids in diagnosis. This imaging technique helps assess blood flow and detect abnormalities.
-
Angiography provides detailed images. It offers a clear view of blood vessels, helping to pinpoint the exact location of the problem.
-
Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is highly accurate. DSA is considered the gold standard for diagnosing VASS.
Treatment Options
Several treatment options are available, ranging from conservative measures to surgical interventions.
-
Banding the fistula can reduce symptoms. This procedure narrows the fistula, decreasing blood flow and alleviating symptoms.
-
Ligation is a more drastic measure. In severe cases, the fistula or graft may be tied off to stop the steal.
-
Revascularization restores blood flow. Surgical procedures can redirect blood flow to the affected limb.
-
Endovascular techniques offer less invasive options. These include angioplasty and stenting to improve blood flow.
Prevention and Management
Preventing VASS involves careful monitoring and management of risk factors.
-
Regular monitoring is essential. Frequent check-ups can help detect early signs of VASS.
-
Controlling diabetes reduces risk. Proper management of blood sugar levels can lower the chances of developing VASS.
-
Maintaining vascular health is crucial. Healthy lifestyle choices, like quitting smoking and exercising, can improve vascular health.
-
Educating patients is vital. Patients should be aware of the symptoms and seek medical attention promptly.
Impact on Quality of Life
VASS can significantly affect a patient's quality of life, making it important to address both physical and emotional aspects.
-
Pain management is a priority. Effective pain relief strategies can improve daily functioning.
-
Psychological support is beneficial. Counseling and support groups can help patients cope with the emotional impact.
-
Physical therapy aids recovery. Exercises can improve circulation and strengthen the affected limb.
-
Nutritional support enhances overall health. A balanced diet can support vascular health and aid recovery.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of VASS.
-
New diagnostic tools are being developed. Advances in imaging technology promise earlier and more accurate detection.
-
Innovative treatments are on the horizon. Research into new surgical techniques and medications offers hope for better outcomes.
-
Patient-centered care models are emerging. These approaches focus on individualized treatment plans and holistic care.
-
Telemedicine is expanding access to care. Remote monitoring and consultations can help manage VASS more effectively.
Case Studies and Real-Life Examples
Real-life examples illustrate the challenges and successes in managing VASS.
-
Case studies highlight diverse experiences. Each patient's journey with VASS is unique, offering valuable insights.
-
Success stories inspire hope. Patients who have overcome VASS provide encouragement and motivation.
-
Lessons learned guide future care. Understanding what works and what doesn't can improve treatment strategies for others.
Final Thoughts on Vascular Access Steal Syndrome
Vascular Access Steal Syndrome (VASS) can be a serious condition, especially for those undergoing hemodialysis. Understanding the symptoms, such as cold hands, pain, and numbness, helps in early detection. Quick intervention can prevent complications. Treatments range from simple banding procedures to more complex surgeries, depending on severity. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers ensure any issues are caught early. Awareness and education about VASS are crucial for patients and caregivers alike. By staying informed, you can take proactive steps to manage and mitigate the risks associated with this condition. Always consult with medical professionals if you suspect any symptoms. Knowledge is power when it comes to health, and being vigilant can make a significant difference in outcomes. Stay proactive, stay informed, and prioritize your vascular health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
