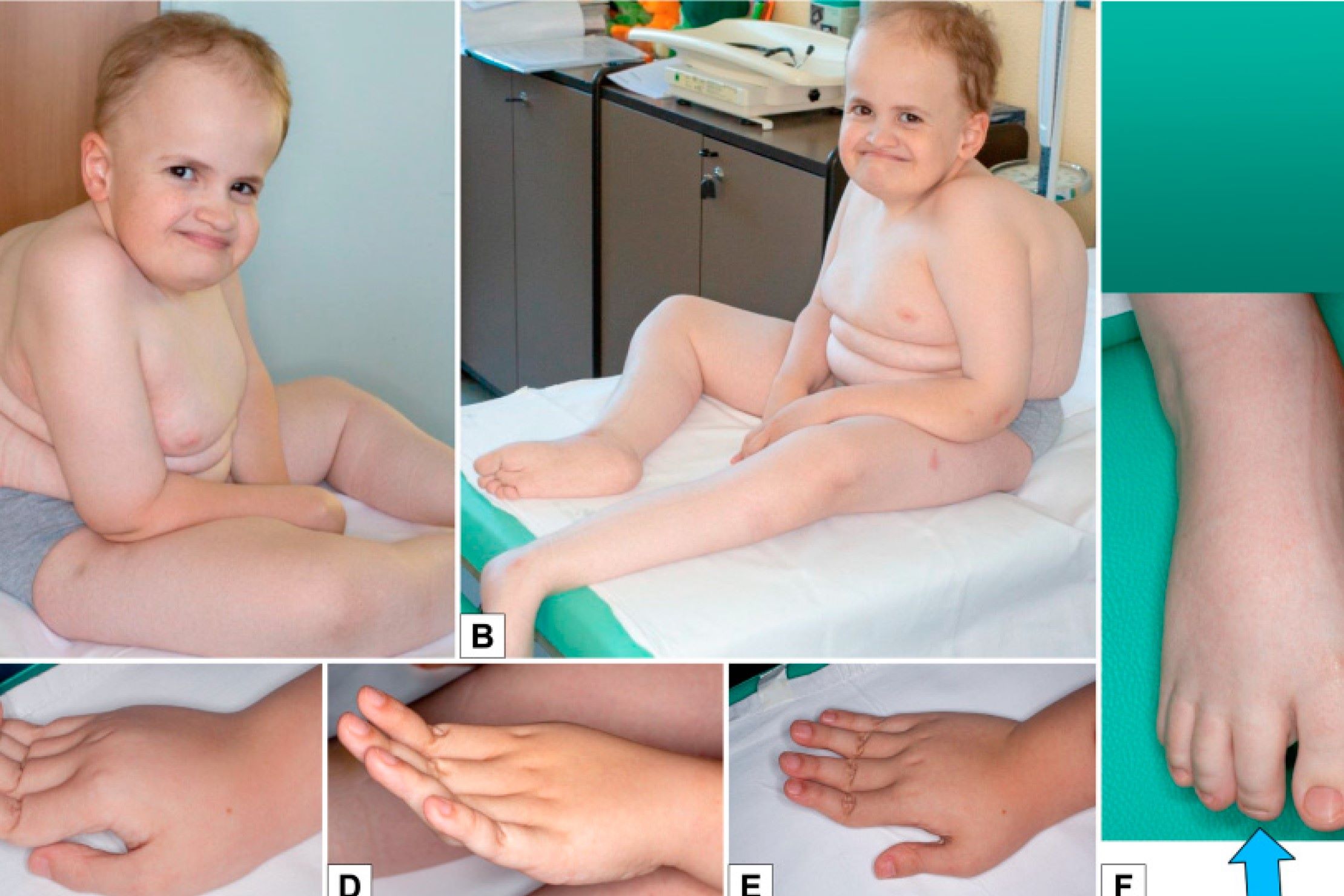
Spondylodysplastic Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (spEDS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects connective tissues, leading to a range of symptoms. This condition can cause joint hypermobility, skin that bruises easily, and skeletal abnormalities. spEDS is caused by mutations in specific genes, which disrupt the normal production of collagen, a crucial protein for connective tissues. People with this syndrome may experience muscle weakness, spinal deformities, and other complications. Understanding spEDS is vital for early diagnosis and management, improving the quality of life for those affected. Here, we present 30 intriguing facts about Spondylodysplastic Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome to shed light on this complex condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Spondylodysplastic Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (spEDS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the spine and skeletal system, causing symptoms like joint hypermobility, skin abnormalities, and delayed motor development.
- Diagnosis of spEDS involves clinical evaluation, genetic testing, and family history analysis, while treatment focuses on physical therapy, orthopedic interventions, pain management, and regular monitoring for a balanced and fulfilling life.
What is Spondylodysplastic Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome?
Spondylodysplastic Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (spEDS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects connective tissues. It is one of the many types of Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes (EDS), each characterized by unique symptoms and genetic causes. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this condition.
-
spEDS is a subtype of Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes. There are 13 different types of EDS, and spEDS is one of them, specifically affecting the spine and skeletal system.
-
It is caused by genetic mutations. Mutations in the B4GALT7, B3GALT6, and SLC39A13 genes are responsible for spEDS.
-
Symptoms often appear in childhood. Children with spEDS may show signs like short stature, muscle weakness, and spinal deformities early in life.
-
Joint hypermobility is common. People with spEDS often have joints that move beyond the normal range, leading to frequent dislocations and pain.
-
Skin abnormalities are a hallmark. Thin, translucent skin that bruises easily is a typical feature of spEDS.
-
Delayed motor development is frequent. Many children with spEDS experience delays in reaching motor milestones like walking and sitting.
-
Muscle hypotonia is prevalent. Reduced muscle tone, or hypotonia, is a common symptom, making muscles appear floppy.
-
Spinal deformities are significant. Conditions like scoliosis and kyphosis are often seen in individuals with spEDS.
-
Osteopenia and osteoporosis are risks. Reduced bone density can lead to brittle bones and fractures.
-
Dental issues are frequent. Problems like crowded teeth and gum disease are common in spEDS patients.
How is spEDS Diagnosed?
Diagnosing spEDS involves a combination of clinical evaluation, genetic testing, and family history analysis. Here are some key facts about the diagnostic process.
-
Clinical evaluation is the first step. Doctors look for physical signs like joint hypermobility, skin abnormalities, and spinal deformities.
-
Genetic testing confirms the diagnosis. Identifying mutations in the B4GALT7, B3GALT6, or SLC39A13 genes can confirm spEDS.
-
Family history is crucial. A detailed family history helps identify inherited patterns of the disorder.
-
Radiographic imaging is used. X-rays and MRIs can reveal skeletal abnormalities associated with spEDS.
-
Skin biopsy may be performed. Examining skin tissue under a microscope can show characteristic changes in connective tissue.
-
Blood tests are sometimes needed. These can help rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
-
Multidisciplinary approach is essential. Diagnosis often involves a team of specialists, including geneticists, orthopedists, and dermatologists.
Treatment and Management of spEDS
While there is no cure for spEDS, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some important facts about treatment options.
-
Physical therapy is beneficial. Regular physical therapy helps strengthen muscles and improve joint stability.
-
Orthopedic interventions are common. Braces, splints, and sometimes surgery are used to manage skeletal deformities.
-
Pain management is crucial. Medications and other therapies help control chronic pain associated with spEDS.
-
Regular monitoring is needed. Frequent check-ups with healthcare providers ensure timely management of complications.
-
Nutritional support is important. A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D supports bone health.
-
Dental care is essential. Regular dental visits help manage oral health issues common in spEDS.
-
Occupational therapy aids daily living. This therapy helps individuals adapt to daily activities and maintain independence.
-
Psychological support is valuable. Counseling and support groups provide emotional support for patients and families.
Living with spEDS
Living with spEDS presents unique challenges, but with proper management, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some insights into daily life with spEDS.
-
Education and awareness are key. Understanding the condition helps patients and families manage symptoms effectively.
-
Adaptive devices can help. Tools like grab bars, special utensils, and mobility aids improve daily functioning.
-
Support networks are vital. Connecting with others who have spEDS provides emotional and practical support.
-
Regular exercise is beneficial. Low-impact activities like swimming and yoga help maintain muscle strength and flexibility.
-
Advocacy is important. Raising awareness about spEDS helps drive research and improve care for those affected.
Final Thoughts on Spondylodysplastic Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Spondylodysplastic Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (spEDS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects connective tissues, leading to symptoms like joint hypermobility, skin abnormalities, and skeletal issues. Understanding spEDS can help those affected manage their symptoms better and seek appropriate medical care. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and improving quality of life. Genetic counseling can provide valuable insights for families dealing with spEDS. While there's no cure, supportive therapies like physical therapy, pain management, and lifestyle adjustments can make a significant difference. Staying informed and connected with support groups can offer emotional and practical assistance. Remember, knowledge is power when dealing with rare conditions like spEDS. Keep advocating for yourself or your loved ones, and never hesitate to reach out for help.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
