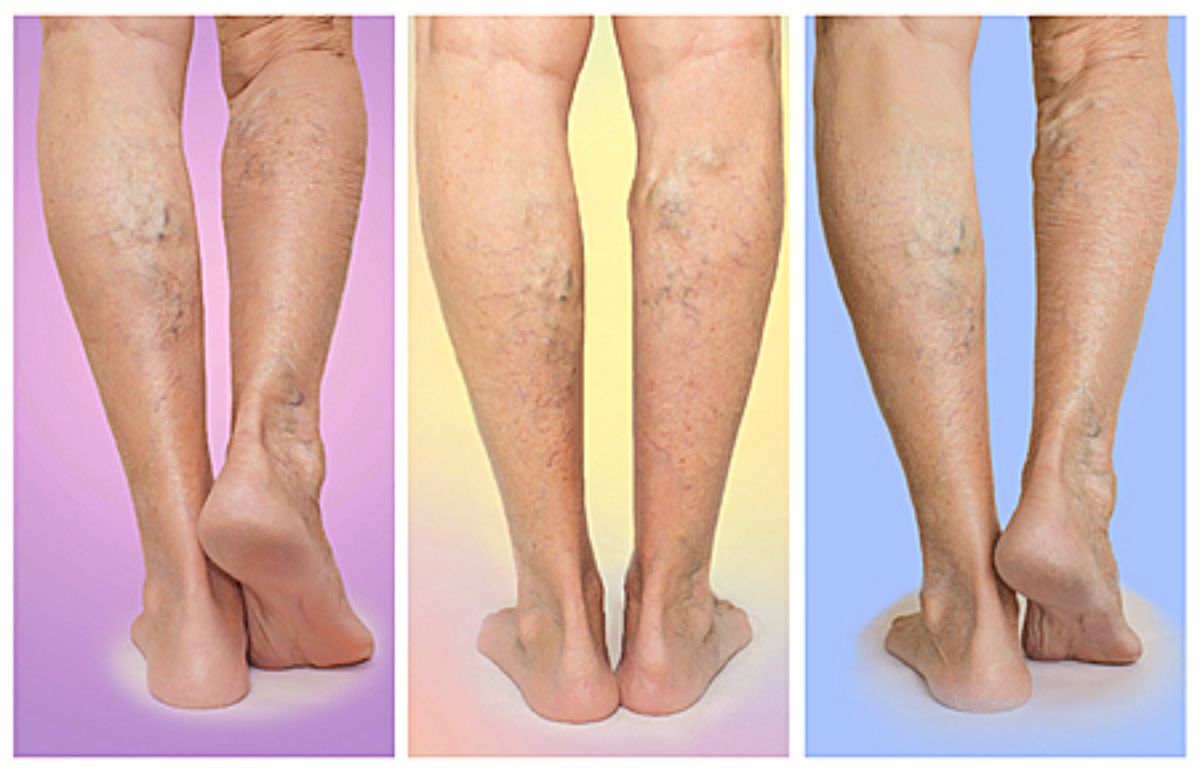
Peripheral Blood Vessel Disorder affects millions worldwide, causing discomfort and serious health issues. This condition involves the narrowing or blockage of blood vessels outside the heart and brain. Symptoms can range from leg pain and numbness to more severe complications like ulcers or gangrene. Understanding this disorder is crucial for early detection and management. Risk factors include smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and avoiding tobacco can help manage and prevent this condition. Treatments vary from lifestyle changes to medications and, in severe cases, surgery. Stay informed to protect your vascular health.
Key Takeaways:
- Peripheral Blood Vessel Disorder (PBVD) affects arteries outside the heart and brain, leading to leg pain and potential tissue damage. Lifestyle changes, regular check-ups, and early treatment can improve outcomes and quality of life.
- Smoking, diabetes, and high cholesterol increase the risk of PBVD. Symptoms include leg pain, slow-healing wounds, and numbness. Regular exercise, healthy eating, and managing diabetes effectively can help prevent and manage PBVD.
Understanding Peripheral Blood Vessel Disorder
Peripheral Blood Vessel Disorder (PBVD) affects the blood vessels outside the heart and brain. It can lead to serious health issues if not managed properly. Here are some intriguing facts about PBVD.
-
PBVD is also known as Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD). This condition primarily affects arteries, reducing blood flow to limbs.
-
Smoking is a major risk factor. Smokers are at a significantly higher risk of developing PBVD compared to non-smokers.
-
Diabetes increases the risk. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, making diabetics more susceptible to PBVD.
-
Symptoms often include leg pain. Many people experience cramping or pain in their legs while walking, known as claudication.
-
PBVD can lead to gangrene. Severe cases may result in tissue death, potentially requiring amputation.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes PBVD and the associated risk factors can help in prevention and early detection.
-
High cholesterol is a culprit. Excess cholesterol can build up in blood vessel walls, narrowing them and restricting blood flow.
-
Hypertension contributes to PBVD. High blood pressure can damage arteries, making them more prone to narrowing.
-
Age is a factor. The risk of PBVD increases with age, particularly after 50.
-
Family history matters. A family history of cardiovascular diseases can increase the likelihood of developing PBVD.
-
Obesity is linked to PBVD. Excess weight puts additional strain on blood vessels, increasing the risk.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding how PBVD is diagnosed can lead to timely treatment.
-
Cold feet and toes. Reduced blood flow can make extremities feel unusually cold.
-
Slow-healing wounds. Cuts or sores on the legs and feet may heal slowly due to poor circulation.
-
Numbness or weakness. Some people experience numbness or weakness in their legs.
-
Color changes in the skin. Affected areas may appear pale or bluish.
-
Ultrasound is a common diagnostic tool. Doctors often use ultrasound to visualize blood flow in the arteries.
Treatment Options
Various treatments are available to manage PBVD and improve quality of life.
-
Lifestyle changes are crucial. Quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet can significantly improve symptoms.
-
Medications can help. Drugs to lower cholesterol, control blood pressure, and prevent blood clots are often prescribed.
-
Angioplasty is a treatment option. This procedure involves widening narrowed arteries using a balloon catheter.
-
Stents may be used. Small mesh tubes called stents can be placed in arteries to keep them open.
-
Bypass surgery is sometimes necessary. In severe cases, surgeons may create a new pathway for blood flow around a blocked artery.
Prevention and Management
Preventing PBVD and managing its symptoms can lead to a healthier life.
-
Regular exercise is beneficial. Walking and other forms of exercise can improve circulation and reduce symptoms.
-
Healthy eating is important. A diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol can help prevent artery narrowing.
-
Monitoring blood pressure. Keeping blood pressure under control can reduce the risk of PBVD.
-
Managing diabetes effectively. Controlling blood sugar levels can prevent damage to blood vessels.
-
Regular check-ups are essential. Routine medical exams can help detect PBVD early and manage it effectively.
Complications and Prognosis
Understanding potential complications and the long-term outlook for PBVD patients is important.
-
Heart attack risk increases. PBVD patients are at higher risk for heart attacks due to shared risk factors.
-
Stroke is a concern. Reduced blood flow can also affect the brain, increasing the risk of stroke.
-
Critical limb ischemia. This severe form of PBVD can cause severe pain and skin ulcers due to extremely reduced blood flow.
-
Quality of life can be affected. Chronic pain and mobility issues can impact daily activities and overall well-being.
-
Early treatment improves outcomes. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the prognosis for PBVD patients.
Key Takeaways on Peripheral Blood Vessel Disorder
Peripheral Blood Vessel Disorder (PBVD) affects millions worldwide, causing symptoms like pain, numbness, and swelling. Early detection is crucial for managing the condition effectively. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking can help reduce risks. Medications and surgical options are available for severe cases. Knowing the symptoms and seeking medical advice early can prevent complications.
Understanding PBVD empowers individuals to take proactive steps in maintaining vascular health. Staying informed about treatment options and lifestyle changes can make a significant difference. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
By staying vigilant and adopting healthy habits, you can manage PBVD and improve your quality of life. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to health. Stay proactive, stay healthy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
