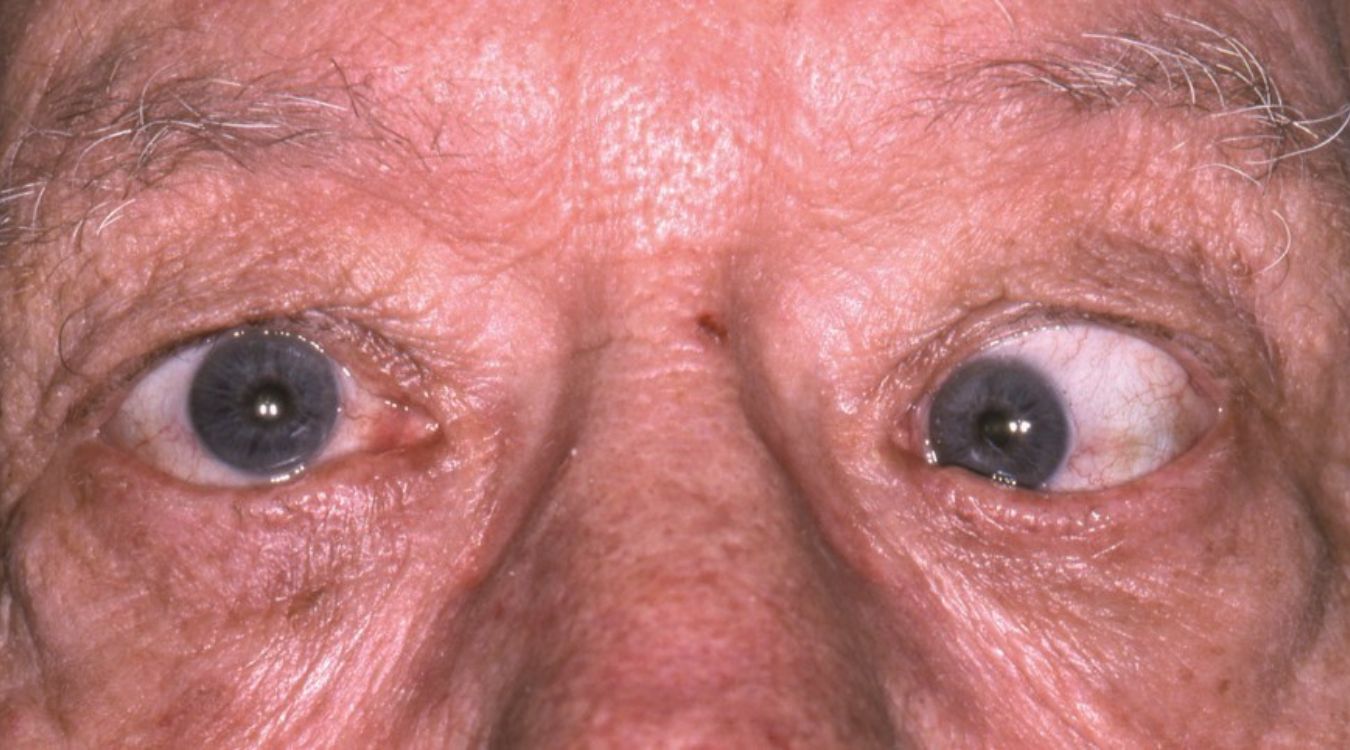
Ocular motility disorders affect how eyes move and work together. These conditions can cause double vision, misalignment, or difficulty focusing. Common disorders include strabismus, nystagmus, and cranial nerve palsies. Strabismus involves eyes not aligning properly, leading to crossed or wandering eyes. Nystagmus causes involuntary eye movements, making it hard to see clearly. Cranial nerve palsies impact the nerves controlling eye muscles, resulting in limited movement. Understanding these disorders helps in recognizing symptoms and seeking treatment. Early diagnosis and intervention can improve quality of life. Let's dive into 30 intriguing facts about these eye conditions.
Key Takeaways:
- Ocular motility disorders affect eye movement and can cause misalignment, double vision, and difficulty focusing. Early detection and treatment are crucial for managing these conditions effectively.
- Symptoms of ocular motility disorders include eye misalignment, blurred vision, headaches, and difficulty reading. Seeking timely medical advice and exploring treatment options can help individuals lead fulfilling lives despite these challenges.
What Are Ocular Motility Disorders?
Ocular motility disorders affect the movement of the eyes. These conditions can cause misalignment, difficulty focusing, and other visual problems. Understanding these disorders helps in managing and treating them effectively.
-
Strabismus is a common ocular motility disorder where the eyes do not align properly. One eye may turn in, out, up, or down while the other looks straight ahead.
-
Nystagmus involves involuntary, rapid eye movements. This can affect vision and depth perception, making daily tasks challenging.
-
Amblyopia, also known as lazy eye, occurs when one eye becomes weaker than the other. This usually happens because the brain favors the stronger eye.
-
Diplopia, or double vision, happens when the eyes do not work together properly. This can result from muscle imbalances or nerve issues.
-
Convergence Insufficiency is when the eyes struggle to work together while focusing on a close object. This can cause headaches, eye strain, and difficulty reading.
Causes of Ocular Motility Disorders
Various factors can lead to ocular motility disorders. Knowing these causes can aid in early detection and treatment.
-
Genetics play a significant role. Many ocular motility disorders run in families, indicating a hereditary component.
-
Neurological Conditions such as multiple sclerosis or stroke can disrupt the nerves controlling eye muscles, leading to motility issues.
-
Trauma to the head or eyes can damage muscles or nerves, causing misalignment or movement problems.
-
Infections like meningitis can affect the brain and nerves, leading to ocular motility disorders.
-
Thyroid Eye Disease can cause inflammation and swelling of the eye muscles, leading to misalignment and movement issues.
Symptoms of Ocular Motility Disorders
Recognizing symptoms early can help in seeking timely medical advice. Symptoms vary depending on the specific disorder.
-
Eye Misalignment is a visible sign where one or both eyes do not look in the same direction.
-
Blurred Vision can occur when the eyes do not focus together properly.
-
Headaches are common, especially with convergence insufficiency, due to the strain of trying to focus.
-
Eye Strain happens when the eyes work harder to compensate for misalignment or movement issues.
-
Difficulty Reading can result from convergence insufficiency or other motility disorders, making it hard to focus on text.
Diagnosing Ocular Motility Disorders
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Various tests and examinations help in identifying these disorders.
-
Eye Exams by an ophthalmologist or optometrist can detect misalignment and other issues.
-
Cover Test involves covering one eye at a time to see how the uncovered eye moves, helping to identify misalignment.
-
Prism Testing uses prisms to measure the degree of eye misalignment.
-
Neurological Exams may be necessary if a neurological condition is suspected as the cause.
-
Imaging Tests like MRI or CT scans can help identify structural or nerve issues affecting eye movement.
Treatment Options for Ocular Motility Disorders
Various treatments can help manage and correct ocular motility disorders. The choice of treatment depends on the specific condition and its severity.
-
Glasses or Contact Lenses can help correct vision problems associated with some motility disorders.
-
Prism Lenses are special glasses that can help align the eyes and reduce double vision.
-
Vision Therapy involves exercises to strengthen eye muscles and improve coordination.
-
Surgery may be necessary to correct severe misalignment or other structural issues.
-
Botox Injections can temporarily weaken overactive eye muscles, helping to improve alignment.
Living with Ocular Motility Disorders
Managing daily life with an ocular motility disorder can be challenging. However, with the right strategies, individuals can lead a fulfilling life.
-
Regular Eye Exams are essential to monitor the condition and adjust treatments as needed.
-
Adaptive Techniques like using larger print or audio books can help with reading difficulties.
-
Ergonomic Adjustments such as proper lighting and screen positioning can reduce eye strain.
-
Support Groups provide emotional support and practical advice from others with similar conditions.
-
Education and Awareness about the disorder can help individuals advocate for themselves and seek appropriate accommodations.
Final Thoughts on Ocular Motility Disorders
Understanding ocular motility disorders can make a big difference in recognizing symptoms early and seeking proper treatment. These conditions affect how the eyes move, leading to issues like double vision, misalignment, and difficulty focusing. Knowing the facts helps in identifying problems and discussing them with healthcare professionals.
Early diagnosis and treatment can improve quality of life. Treatments range from glasses and eye exercises to surgery, depending on the severity. Regular eye exams are crucial for catching these disorders early.
Remember, eye health is vital for overall well-being. If you notice any changes in your vision or eye movement, consult an eye specialist. Staying informed empowers you to take control of your eye health and seek the best care possible. Keep these facts in mind and prioritize your vision.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
