Neuronal Intranuclear Hyaline Inclusion Disease (NIHID) is a rare, progressive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects the brain and spinal cord. This condition is characterized by the presence of abnormal protein deposits, known as hyaline inclusions, within the nuclei of neurons. Symptoms often include cognitive decline, movement disorders, and psychiatric issues, which can vary widely among individuals. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and sometimes genetic testing. While there is no cure for NIHID, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Understanding this disease can help in recognizing its impact and the importance of ongoing research.
Key Takeaways:
- Neuronal Intranuclear Hyaline Inclusion Disease (NIHID) is a rare neurodegenerative disorder characterized by protein accumulation in the brain, leading to cognitive decline, movement disorders, and seizures.
- Currently, there is no cure for NIHID, but treatments focus on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Research is ongoing to find potential treatments and better understand the disease.
What is Neuronal Intranuclear Hyaline Inclusion Disease?
Neuronal Intranuclear Hyaline Inclusion Disease (NIHID) is a rare, progressive neurodegenerative disorder. It primarily affects the nervous system, leading to various neurological symptoms. Understanding this disease can help in recognizing its impact on patients and their families.
- NIHID is characterized by the presence of hyaline inclusions within the nuclei of neurons.
- These inclusions are made up of proteins that abnormally accumulate inside the cell nucleus.
- The disease was first identified in the 1980s, making it a relatively recent discovery in medical history.
Symptoms of NIHID
The symptoms of NIHID can vary widely among patients. They often depend on which parts of the nervous system are affected.
- Common symptoms include cognitive decline, similar to dementia.
- Patients may experience movement disorders, such as tremors or difficulty walking.
- Seizures are also a frequent symptom in those with NIHID.
- Some individuals may have psychiatric symptoms, including depression or anxiety.
- Speech and language difficulties can arise as the disease progresses.
Causes and Genetics
The exact cause of NIHID remains unknown. However, researchers have identified some genetic factors that may contribute to the disease.
- NIHID is often inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
- Mutations in the gene encoding the protein ubiquitin-like with PHD and ring finger domains 1 (UHRF1) have been linked to NIHID.
- Not all cases of NIHID are inherited; some may occur sporadically without a family history.
Diagnosis of NIHID
Diagnosing NIHID can be challenging due to its rarity and the variability of symptoms. Several methods are used to confirm the diagnosis.
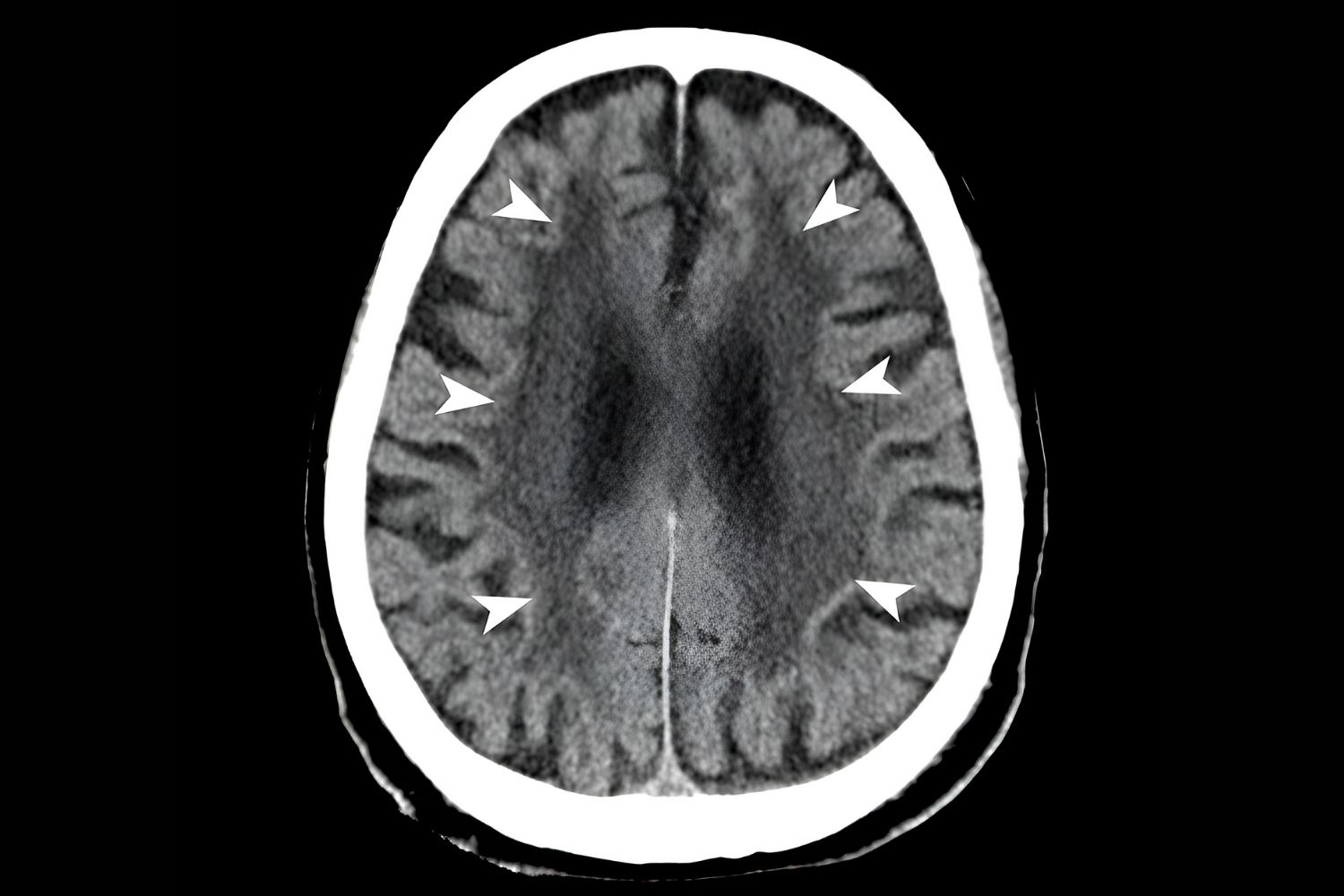
- MRI scans can reveal brain abnormalities associated with NIHID.
- A definitive diagnosis often requires a brain biopsy to identify the characteristic hyaline inclusions.
- Genetic testing can help identify mutations linked to the disease.
- Neurological examinations and patient history are crucial in the diagnostic process.
Treatment and Management
Currently, there is no cure for NIHID. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving the quality of life for patients.
- Medications can help control seizures and psychiatric symptoms.
- Physical therapy may assist with movement disorders and improve mobility.
- Speech therapy can be beneficial for those with language difficulties.
- Supportive care, including counseling and social support, is essential for patients and their families.
- Research is ongoing to find potential treatments and better understand the disease.
Prognosis and Life Expectancy
The prognosis for individuals with NIHID varies. It largely depends on the severity of symptoms and the rate of disease progression.
- NIHID is a progressive disease, meaning symptoms worsen over time.
- Life expectancy can be significantly reduced, with many patients living only a few years after diagnosis.
- Early diagnosis and symptom management can improve the quality of life for patients.
Research and Future Directions
Research into NIHID is crucial for developing better diagnostic tools and treatments. Scientists are exploring various avenues to understand and combat this disease.
- Studies are investigating the role of protein accumulation in the development of NIHID.
- Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment option.
- Animal models are being used to study the disease and test new therapies.
- Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and patient advocacy groups is essential for advancing NIHID research.
Living with NIHID
Living with NIHID can be challenging for patients and their families. Support and resources are available to help navigate these difficulties.
- Patient support groups can provide emotional and practical assistance.
- Educational resources can help families understand the disease and its management.
- Advocacy organizations work to raise awareness and fund research for NIHID.
Understanding Neuronal Intranuclear Hyaline Inclusion Disease is vital for improving the lives of those affected by this rare condition. Through continued research and support, there is hope for better treatments and outcomes in the future.
Final Thoughts on Neuronal Intranuclear Hyaline Inclusion Disease
Neuronal Intranuclear Hyaline Inclusion Disease (NIHID) remains a rare, complex condition. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and current research is crucial for those affected. Symptoms often include cognitive decline, movement disorders, and seizures. Genetic mutations, particularly in the ubiquitin-proteasome system, play a significant role in its development.
Research continues to explore potential treatments and therapies. While no cure exists, early diagnosis and supportive care can improve quality of life. Staying informed about the latest advancements and participating in clinical trials may offer hope for patients and families.
NIHID highlights the importance of ongoing medical research and awareness. By sharing knowledge and supporting scientific efforts, we can contribute to better outcomes for those living with this challenging disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
