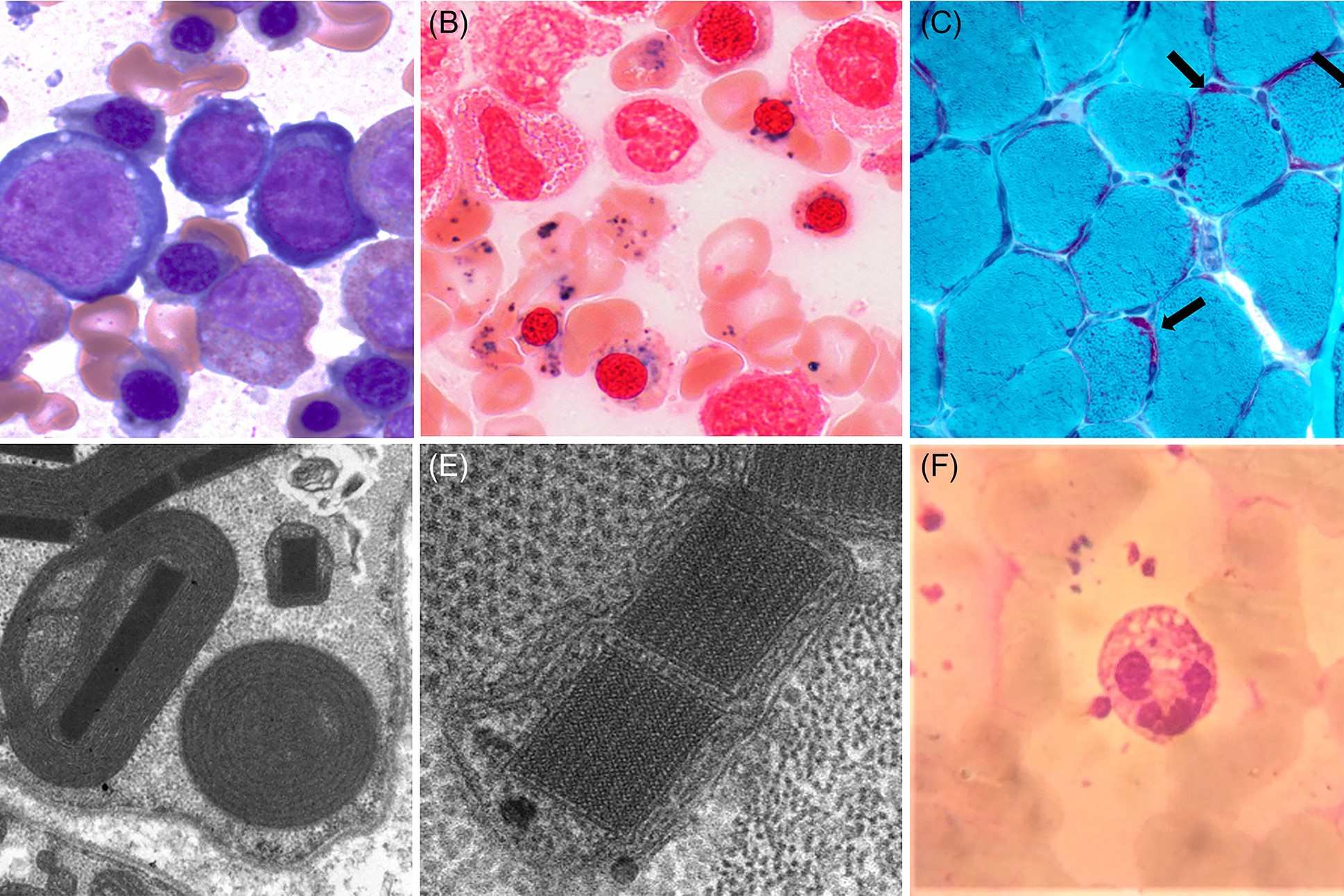
Myopathy with lactic acidosis and sideroblastic anemia is a rare genetic disorder that affects muscles, blood, and energy production. This condition can cause muscle weakness, fatigue, and difficulty breathing. Lactic acidosis occurs when lactic acid builds up in the body, leading to nausea, vomiting, and rapid breathing. Sideroblastic anemia is characterized by the body's inability to properly incorporate iron into hemoglobin, causing fatigue and pale skin. Understanding this complex condition involves looking at its genetic roots, symptoms, and treatment options. Here are 30 facts that will help you grasp the essentials of myopathy with lactic acidosis and sideroblastic anemia.
Key Takeaways:
- Myopathy with Lactic Acidosis and Sideroblastic Anemia (MLASA) is a rare genetic disorder affecting muscles, blood, and energy production, causing symptoms like muscle weakness, fatigue, and anemia in children.
- MLASA has no cure, but treatments focus on managing symptoms and complications. Research is ongoing, exploring gene therapy, new drugs, and better diagnostic tools to improve diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Myopathy with Lactic Acidosis and Sideroblastic Anemia
Myopathy with lactic acidosis and sideroblastic anemia (MLASA) is a rare genetic disorder. It affects muscles, blood, and energy production. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
MLASA is a mitochondrial disorder. Mitochondria are the powerhouses of cells. In MLASA, these powerhouses don't work properly, leading to energy production issues.
-
The disorder is inherited. MLASA is passed down through families. It follows an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning both parents must carry the gene.
-
Symptoms often appear in childhood. Kids with MLASA may show signs early on. Muscle weakness, fatigue, and anemia are common.
-
Lactic acidosis is a key feature. High levels of lactic acid build up in the blood. This can cause muscle pain, cramps, and fatigue.
-
Sideroblastic anemia affects red blood cells. In MLASA, red blood cells can't use iron properly. This leads to anemia, causing fatigue and weakness.
Genetic Causes and Diagnosis
Understanding the genetic basis of MLASA helps in diagnosis and management. Here are some facts about its genetic causes and how it's diagnosed.
-
Mutations in the YARS2 gene are common. The YARS2 gene provides instructions for making an enzyme involved in protein synthesis. Mutations disrupt this process.
-
Genetic testing confirms the diagnosis. Doctors use genetic tests to identify mutations in the YARS2 gene. This helps confirm MLASA.
-
Family history is important. Knowing if relatives have MLASA can aid diagnosis. Genetic counseling is often recommended for families.
-
Biochemical tests can detect lactic acidosis. Blood tests measure lactic acid levels. High levels suggest lactic acidosis, a hallmark of MLASA.
-
Bone marrow biopsy may be needed. This test can show ringed sideroblasts, abnormal red blood cells seen in sideroblastic anemia.
Symptoms and Complications
MLASA presents with a variety of symptoms and potential complications. Here are some key points to understand.
-
Muscle weakness is a primary symptom. Affected individuals often experience muscle weakness, especially in the arms and legs.
-
Exercise intolerance is common. People with MLASA may struggle with physical activity. They tire quickly and may experience muscle pain.
-
Fatigue is a major issue. Chronic fatigue affects daily life. It can be debilitating and impact quality of life.
-
Heart problems can occur. Some individuals develop cardiomyopathy, a disease of the heart muscle. This can lead to heart failure.
-
Breathing difficulties may arise. Weak respiratory muscles can cause breathing problems. Some may need respiratory support.
Treatment and Management
Managing MLASA involves addressing symptoms and improving quality of life. Here are some facts about treatment and management strategies.
-
No cure exists for MLASA. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and complications. Regular monitoring is essential.
-
Physical therapy can help. Exercise programs tailored to individual needs can improve muscle strength and function.
-
Medications may be prescribed. Drugs to manage lactic acidosis, anemia, and heart problems are often used.
-
Nutritional support is important. A balanced diet can help manage symptoms. Some may need supplements to address deficiencies.
-
Regular follow-ups are crucial. Ongoing medical care helps monitor the condition and adjust treatments as needed.
Research and Future Directions
Research on MLASA is ongoing. Scientists are exploring new treatments and ways to improve diagnosis. Here are some exciting developments.
-
Gene therapy holds promise. Researchers are investigating gene therapy as a potential treatment. This approach aims to correct the underlying genetic defect.
-
New drugs are being tested. Clinical trials are underway to find effective treatments. These drugs target specific symptoms and complications.
-
Better diagnostic tools are in development. Advances in genetic testing and imaging may improve diagnosis. Early detection can lead to better outcomes.
-
Patient registries are valuable. Collecting data on individuals with MLASA helps researchers understand the condition. This can lead to new insights and treatments.
-
Collaboration is key. Scientists, doctors, and patients are working together. Collaborative efforts drive progress in understanding and treating MLASA.
Living with MLASA
Living with MLASA presents challenges, but support and resources are available. Here are some facts about daily life with this condition.
-
Support groups can be helpful. Connecting with others who have MLASA provides emotional support. Sharing experiences can be comforting.
-
Education is important. Learning about MLASA helps individuals and families manage the condition. Knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions.
-
Adaptive devices can improve mobility. Tools like wheelchairs and braces can aid movement. These devices enhance independence.
-
Mental health support is crucial. Coping with a chronic condition can be stressful. Counseling and therapy can provide emotional support.
-
Advocacy makes a difference. Raising awareness about MLASA can lead to better resources and support. Advocacy efforts can drive research and policy changes.
Final Thoughts on Myopathy With Lactic Acidosis And Sideroblastic Anemia
Understanding myopathy with lactic acidosis and sideroblastic anemia can be challenging, but knowing the facts helps. This rare condition affects muscles, energy production, and red blood cells. Symptoms like muscle weakness, fatigue, and anemia can impact daily life. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Genetic testing, blood tests, and muscle biopsies aid in diagnosis. Treatment often includes vitamin B6 supplements, physical therapy, and managing lactic acidosis. While there's no cure, ongoing research offers hope for better treatments. Staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers can make a significant difference. Remember, you're not alone—support groups and resources are available. Keep advocating for your health and stay hopeful for advancements in medical science.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
