Metastatic insulinoma is a rare type of pancreatic tumor that spreads to other parts of the body. These tumors produce excessive amounts of insulin, leading to dangerously low blood sugar levels. Understanding this condition is crucial for those affected and their loved ones. In this blog post, we'll explore 30 facts about metastatic insulinoma to help you grasp its complexities. From symptoms and diagnosis to treatment options and survival rates, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview. Whether you're a patient, caregiver, or just curious, these facts will offer valuable insights into this challenging medical condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Metastatic insulinoma is a rare pancreatic tumor that spreads to other parts of the body, causing low blood sugar. It's diagnosed through blood tests and imaging, and treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy.
- Symptoms of metastatic insulinoma include confusion, sweating, and rapid heartbeat due to low blood sugar. Treatment involves surgery, chemotherapy, and emerging therapies like peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) and somatostatin analogs.
What is Metastatic Insulinoma?
Metastatic insulinoma is a rare type of pancreatic tumor that spreads to other parts of the body. These tumors produce excessive amounts of insulin, leading to low blood sugar levels. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition:
- Metastatic insulinomas are extremely rare, with an incidence of about 1 in 1 million people per year.
- These tumors originate from the beta cells in the pancreas, which are responsible for insulin production.
- Unlike other pancreatic tumors, insulinomas are usually benign, but around 10% can become malignant and metastasize.
- The liver is the most common site for metastasis in insulinoma cases.
- Symptoms often include confusion, sweating, and rapid heartbeat due to hypoglycemia.
- Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to measure insulin and glucose levels, along with imaging studies.
- A 72-hour fasting test is often used to diagnose insulinoma, as it triggers hypoglycemia in affected individuals.
- Surgery is the primary treatment for localized insulinomas, aiming to remove the tumor completely.
- For metastatic cases, treatment options may include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and radiofrequency ablation.
- Everolimus, a targeted therapy drug, has shown promise in treating metastatic insulinoma.
- Insulinomas are more common in adults aged 40-60, but they can occur at any age.
- Genetic conditions like Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) increase the risk of developing insulinomas.
- The Whipple triad is a classic diagnostic criterion for insulinoma, involving symptoms of hypoglycemia, low blood glucose levels, and relief of symptoms after glucose intake.
- Insulinomas can be challenging to locate due to their small size, often less than 2 cm in diameter.
- Endoscopic ultrasound is a valuable tool for detecting small insulinomas that might be missed by other imaging techniques.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and diagnostic methods for metastatic insulinoma can help in early detection and treatment. Here are some key points:
- Symptoms of insulinoma can mimic other conditions, making diagnosis tricky.
- Common symptoms include dizziness, blurred vision, and irritability, all related to low blood sugar.
- Some patients experience weight gain due to frequent eating to counteract hypoglycemia.
- Seizures and loss of consciousness can occur in severe cases of hypoglycemia.
- Blood tests measuring insulin, proinsulin, and C-peptide levels are crucial for diagnosis.
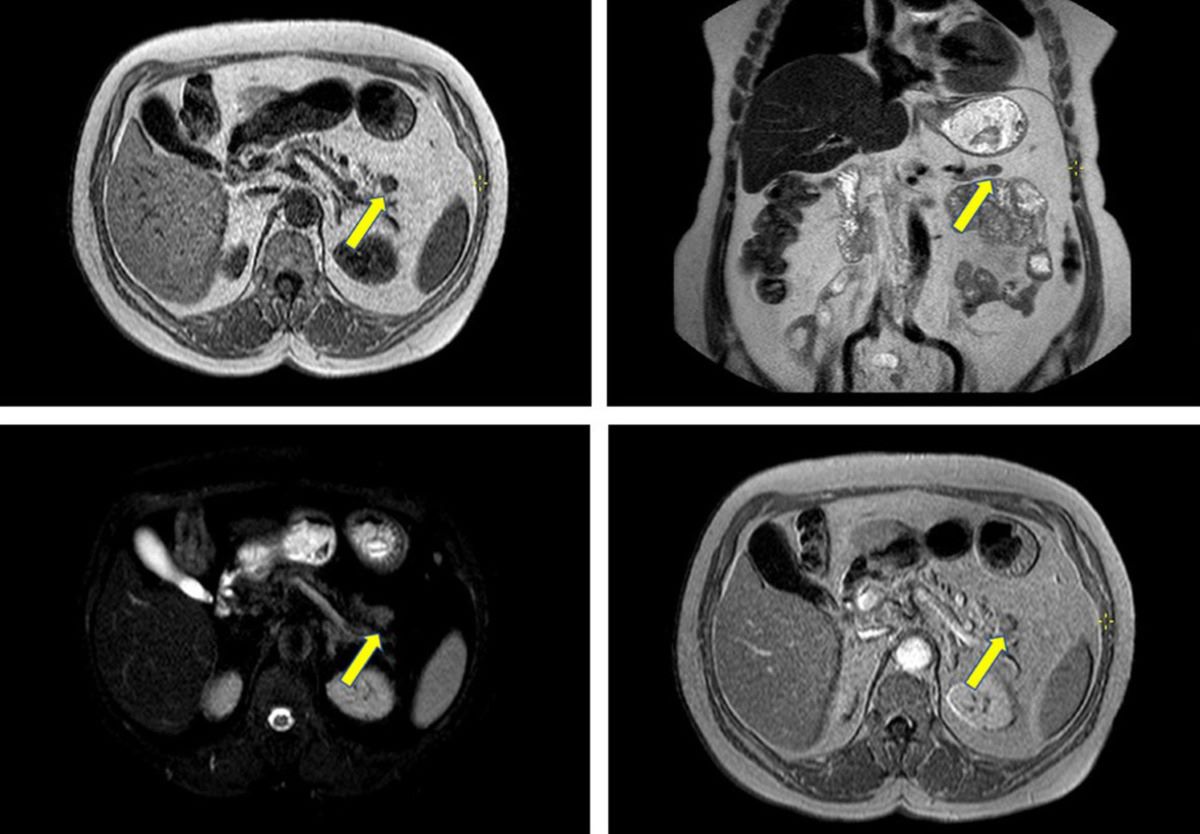
- Imaging studies like CT scans, MRI, and PET scans help locate the primary tumor and metastases.
- Selective arterial calcium stimulation with hepatic venous sampling (SACST) is a specialized test to localize insulinomas.
- Genetic testing may be recommended for patients with a family history of MEN1 or other genetic syndromes.
Treatment Options
Treating metastatic insulinoma involves a combination of surgical and medical approaches. Here are some treatment facts:
- Surgical resection is the preferred treatment for localized insulinomas and can be curative.
- For metastatic cases, debulking surgery may be performed to reduce tumor burden.
- Chemotherapy regimens often include drugs like streptozocin and doxorubicin.
- Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) is an emerging treatment that targets tumor cells with radioactive peptides.
- Somatostatin analogs, such as octreotide, can help control symptoms by inhibiting insulin release.
- Liver-directed therapies, including embolization and ablation, are used for liver metastases.
- Clinical trials are ongoing to explore new treatments and improve outcomes for patients with metastatic insulinoma.
Final Thoughts on Metastatic Insulinoma
Metastatic insulinoma, though rare, presents unique challenges. Understanding its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options can make a significant difference. Early detection remains crucial. Symptoms like frequent hypoglycemia, confusion, and sweating shouldn't be ignored. Diagnostic tools such as blood tests, imaging, and biopsies play a vital role. Treatment varies from surgery to medications, depending on the stage and spread. Patients need a strong support system, including healthcare professionals and loved ones. Staying informed and proactive can improve outcomes. Remember, every case is unique, so personalized care is essential. By spreading awareness and knowledge, we can help those affected navigate this complex condition. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and support those battling metastatic insulinoma.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
