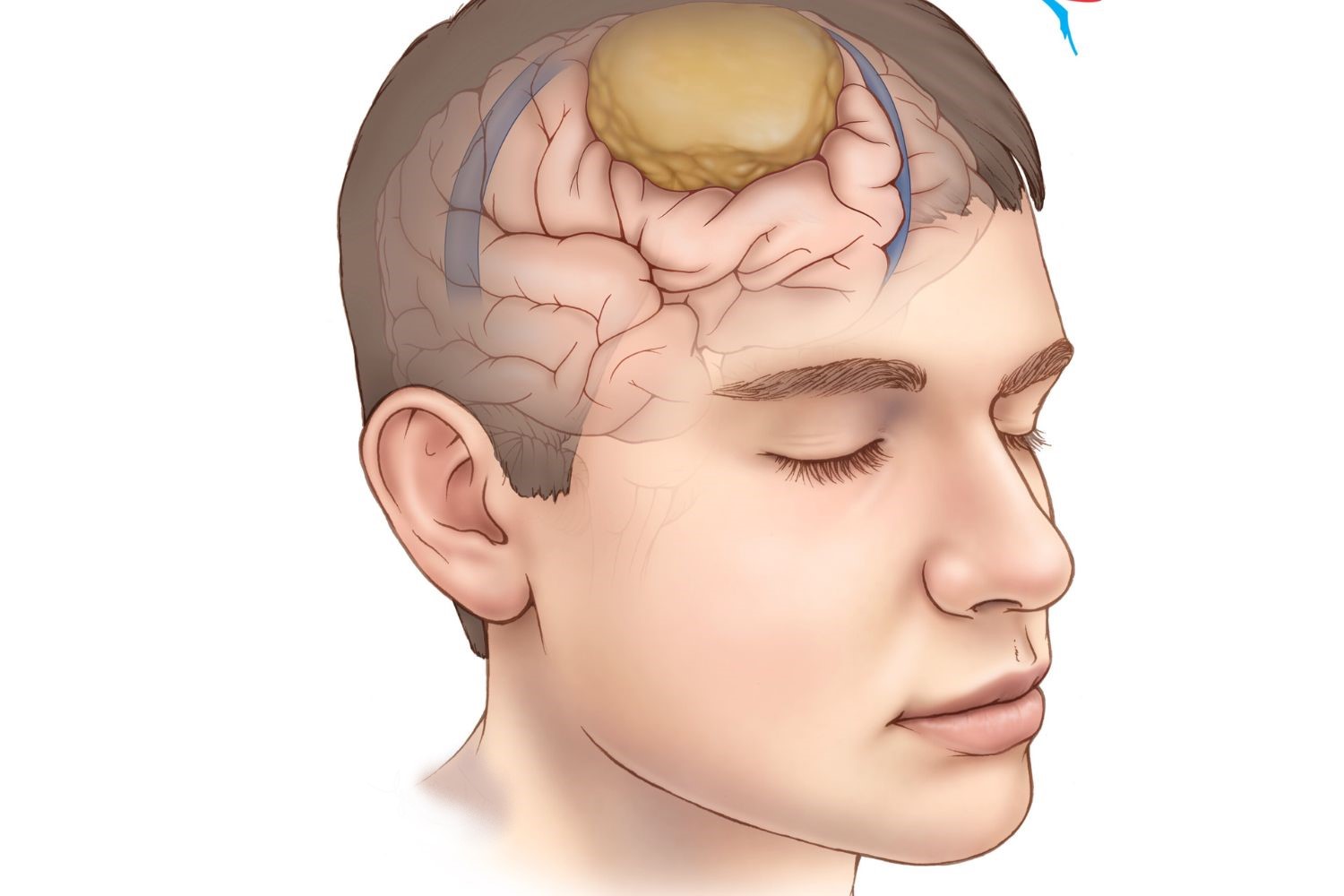
Meningioma is a type of tumor that forms on the meninges, the protective layers covering the brain and spinal cord. These tumors are usually benign, meaning they aren't cancerous, but they can still cause serious health issues due to their location. Did you know that meningiomas account for about 30% of all brain tumors? They are more common in women than men, especially in those aged 40 to 70. Symptoms can vary widely, from headaches and vision problems to seizures and changes in personality. Early detection and treatment are crucial for managing this condition effectively. Let's dive into 30 intriguing facts about meningioma that will help you understand this medical condition better.
Key Takeaways:
- Meningiomas are the most common type of primary brain tumor, often benign but sometimes malignant. They can cause symptoms like headaches, seizures, and vision problems, and are more common in women.
- Diagnosis and treatment involve imaging tests, biopsies, surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Regular monitoring and healthy lifestyle choices may help lower the risk of developing meningiomas.
What is Meningioma?
Meningioma is a type of tumor that forms on the meninges, the protective layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord. These tumors are usually benign but can sometimes be malignant. Here are some fascinating facts about meningioma.
- Meningiomas account for about 30% of all brain tumors, making them the most common type of primary brain tumor.
- They are more common in women than men, with a ratio of about 2:1.
- The exact cause of meningiomas is unknown, but genetic factors and radiation exposure are considered risk factors.
- Most meningiomas grow slowly and may not cause symptoms for years.
- Symptoms can include headaches, seizures, vision problems, and changes in personality or behavior.
- Meningiomas are often discovered incidentally during imaging tests for other conditions.
- They can occur at any age but are most commonly diagnosed in people between 40 and 70 years old.
- There are three grades of meningiomas: Grade I (benign), Grade II (atypical), and Grade III (anaplastic or malignant).
- Grade I meningiomas are the most common, accounting for about 80% of cases.
- Grade II and III meningiomas are more aggressive and have a higher risk of recurrence after treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing and treating meningiomas involves a combination of imaging tests, biopsies, and various treatment options. Understanding these processes can help in managing the condition effectively.
- MRI is the most common imaging test used to diagnose meningiomas.
- CT scans can also be used, especially if MRI is not available.
- A biopsy may be performed to determine the grade of the tumor.
- Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and, in some cases, chemotherapy.
- Surgery is often the first line of treatment, especially for accessible tumors.
- Complete surgical removal of the tumor can lead to a cure in many cases.
- Radiation therapy is used when the tumor cannot be completely removed or if it recurs.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery is a type of radiation therapy that delivers a high dose of radiation to the tumor while sparing surrounding tissue.
- Chemotherapy is rarely used but may be considered for aggressive or recurrent meningiomas.
- Regular follow-up with imaging tests is essential to monitor for recurrence.
Risk Factors and Prevention
While the exact cause of meningiomas remains unclear, certain risk factors have been identified. Knowing these can help in early detection and possibly prevention.
- Exposure to ionizing radiation, especially to the head, increases the risk of developing meningiomas.
- Genetic conditions like neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) are associated with a higher risk.
- Hormonal factors may play a role, as meningiomas are more common in women and can grow during pregnancy.
- Obesity has been linked to an increased risk of meningiomas.
- There is no known way to prevent meningiomas, but reducing exposure to radiation and maintaining a healthy lifestyle may help lower the risk.
Living with Meningioma
Living with a meningioma diagnosis can be challenging, but many people lead full, active lives with proper management and support.
- Regular monitoring and follow-up care are crucial for managing the condition.
- Support groups and counseling can help patients and their families cope with the emotional impact of the diagnosis.
- Rehabilitation therapies, such as physical, occupational, and speech therapy, may be needed to address symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Advances in medical research are continually improving the understanding and treatment of meningiomas.
- Many people with meningiomas live long, healthy lives, especially when the tumor is detected early and managed effectively.
Final Thoughts on Meningioma
Meningiomas, though often benign, can still pose significant health challenges. Understanding symptoms like headaches, vision problems, and seizures helps in early detection. Regular check-ups and imaging tests are crucial for those at risk. Treatments range from surgery to radiation therapy, depending on the tumor's size and location. Advances in medical technology have improved outcomes for many patients. However, ongoing research is essential for better treatment options and early diagnosis. Staying informed and proactive about your health can make a big difference. If you or a loved one experiences any concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Knowledge is power, and being aware of the facts about meningiomas can lead to better health decisions. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and prioritize your well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
