May–Hegglin Anomaly is a rare genetic disorder that affects blood cells, causing a unique set of symptoms. Ever wondered what makes this condition so special? May–Hegglin Anomaly is characterized by large platelets, low platelet count, and distinctive white blood cell inclusions called Döhle-like bodies. These features can lead to easy bruising, nosebleeds, and other bleeding issues. Despite its rarity, understanding this condition is crucial for those affected and their families. This article will dive into 30 intriguing facts about May–Hegglin Anomaly, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and management. Get ready to learn more about this fascinating medical condition!
Key Takeaways:
- May–Hegglin Anomaly is a rare genetic disorder affecting blood cells, causing platelet and white blood cell abnormalities, leading to bleeding tendencies and potential hearing loss.
- Diagnosis involves blood tests, genetic analysis, and family history evaluation. Treatment focuses on symptom management, regular monitoring, and genetic counseling for affected individuals and their families.
What is May–Hegglin Anomaly?
May–Hegglin Anomaly (MHA) is a rare genetic disorder affecting blood cells. It involves abnormalities in platelets, white blood cells, and sometimes bleeding tendencies. Here are some fascinating facts about this condition.
-
Genetic Origin: MHA is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning only one copy of the mutated gene is needed to cause the disorder.
-
MYH9 Gene Mutation: The condition is caused by mutations in the MYH9 gene, which provides instructions for making a protein called non-muscle myosin heavy chain IIA.
-
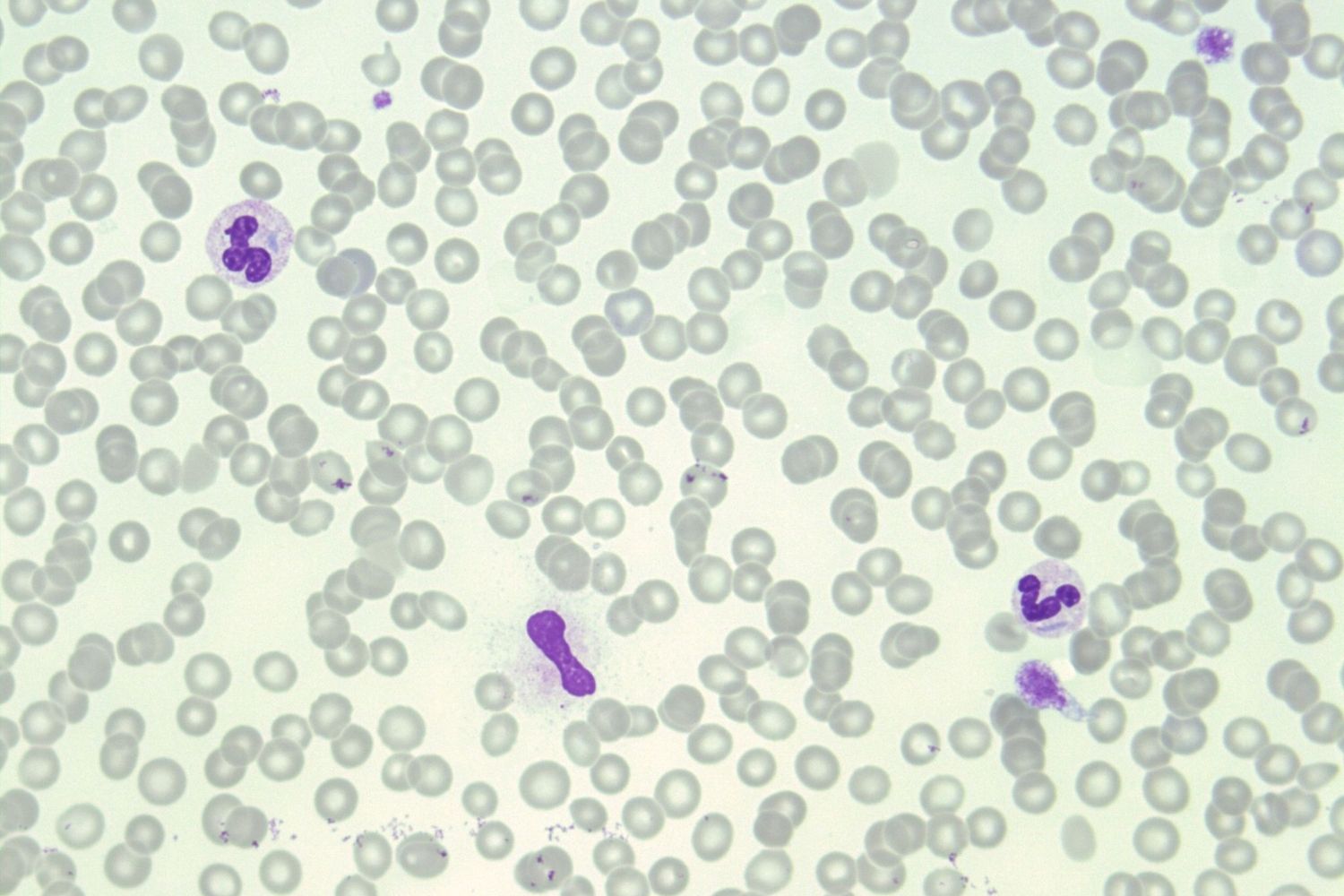
Platelet Abnormalities: Individuals with MHA have larger-than-normal platelets, known as macrothrombocytes.
-
Bleeding Tendencies: Due to the abnormal platelets, people with MHA may experience easy bruising and prolonged bleeding.
-
Leukocyte Inclusions: White blood cells in MHA patients often contain distinctive inclusions called Döhle-like bodies.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosis typically involves blood tests, genetic testing, and examination of blood smears under a microscope.
-
Symptoms Variability: Symptoms can vary widely among individuals, even within the same family.
-
Thrombocytopenia: Many individuals with MHA have a lower-than-normal number of platelets, a condition known as thrombocytopenia.
-
Non-Muscle Myosin: The MYH9 gene mutation affects non-muscle myosin, which plays a role in cell shape and movement.
-
Hearing Loss: Some individuals with MHA may experience sensorineural hearing loss.
How is May–Hegglin Anomaly Diagnosed?
Diagnosing MHA involves a combination of clinical evaluation, blood tests, and genetic analysis. Here are some key points about the diagnostic process.
-
Blood Smear Examination: A blood smear can reveal large platelets and Döhle-like bodies in white blood cells.
-
Genetic Testing: Confirmatory diagnosis often requires genetic testing to identify mutations in the MYH9 gene.
-
Family History: A detailed family history can provide clues, as MHA is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
-
Platelet Count: Blood tests typically show a reduced platelet count, which helps in the diagnosis.
-
Bone Marrow Examination: In some cases, a bone marrow biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions.
-
Hearing Tests: Audiometric tests may be conducted to check for hearing loss associated with MHA.
-
Differential Diagnosis: It's important to differentiate MHA from other conditions with similar symptoms, such as other MYH9-related disorders.
Treatment and Management of May–Hegglin Anomaly
While there is no cure for MHA, various treatments and management strategies can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular blood tests and check-ups are essential to monitor platelet levels and overall health.
-
Bleeding Precautions: Individuals with MHA should take precautions to avoid injuries that could lead to bleeding.
-
Hearing Aids: For those with hearing loss, hearing aids or other assistive devices can be beneficial.
-
Genetic Counseling: Genetic counseling can help affected individuals and their families understand the condition and its inheritance pattern.
-
Avoiding Certain Medications: Some medications that affect platelet function should be avoided to reduce bleeding risk.
-
Platelet Transfusions: In severe cases, platelet transfusions may be necessary to manage bleeding episodes.
-
Education and Awareness: Educating patients and their families about MHA is crucial for effective management.
Interesting Facts and Research on May–Hegglin Anomaly
Research on MHA continues to uncover new insights and potential treatments. Here are some interesting facts and recent findings.
-
Rare Condition: MHA is extremely rare, with only a few hundred cases reported worldwide.
-
Research Advances: Advances in genetic research are helping to better understand the underlying mechanisms of MHA.
-
Animal Models: Researchers are developing animal models to study MHA and test potential treatments.
-
Potential Therapies: Studies are exploring gene therapy and other innovative treatments for MHA.
-
Patient Registries: Patient registries and databases are being established to collect data and improve understanding of MHA.
-
Support Groups: Support groups and online communities provide valuable resources and support for individuals with MHA and their families.
Final Thoughts on May–Hegglin Anomaly
May–Hegglin Anomaly (MHA) is a rare genetic disorder that affects blood cells, leading to distinct physical characteristics and medical challenges. Understanding MHA helps in managing symptoms and improving quality of life for those affected. Early diagnosis and regular monitoring are key to addressing potential complications like bleeding issues or infections. Genetic counseling can provide valuable insights for families with a history of MHA, helping them make informed decisions about their health. While there's no cure, treatments focus on symptom management and preventive care. Staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers ensures the best possible outcomes for individuals with MHA. Remember, knowledge is power when dealing with rare conditions like May–Hegglin Anomaly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
