Mansonelliasis might sound like a tongue-twister, but it's a serious parasitic disease caused by tiny worms called filariae. Found mainly in tropical regions, this illness spreads through bites from infected midges or blackflies. Symptoms can range from mild to severe, including itching, joint pain, and skin rashes. Despite its impact, many people have never heard of it. Why? Because it's often overshadowed by more well-known diseases like malaria or dengue fever. Understanding mansonelliasis is crucial for those living in or traveling to affected areas. Let's dive into 30 facts that will shed light on this lesser-known but significant health issue.
Key Takeaways:
- Mansonelliasis is a parasitic disease transmitted by tiny worms through insect bites, causing symptoms like itching and joint pain. Prevention includes using insect repellent and wearing protective clothing.
- Treatment for Mansonelliasis involves antiparasitic drugs and supportive care. Public health initiatives and ongoing research are crucial for controlling the disease and improving diagnosis and treatment methods.
What is Mansonelliasis?
Mansonelliasis is a parasitic disease caused by tiny worms called filariae. These worms are transmitted to humans through the bites of infected midges or blackflies. The disease is prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, particularly in Africa and South America.
- Mansonelliasis is caused by three species of filarial worms: Mansonella perstans, Mansonella ozzardi, and Mansonella streptocerca.
- The disease is primarily transmitted by biting midges of the genus Culicoides and blackflies of the genus Simulium.
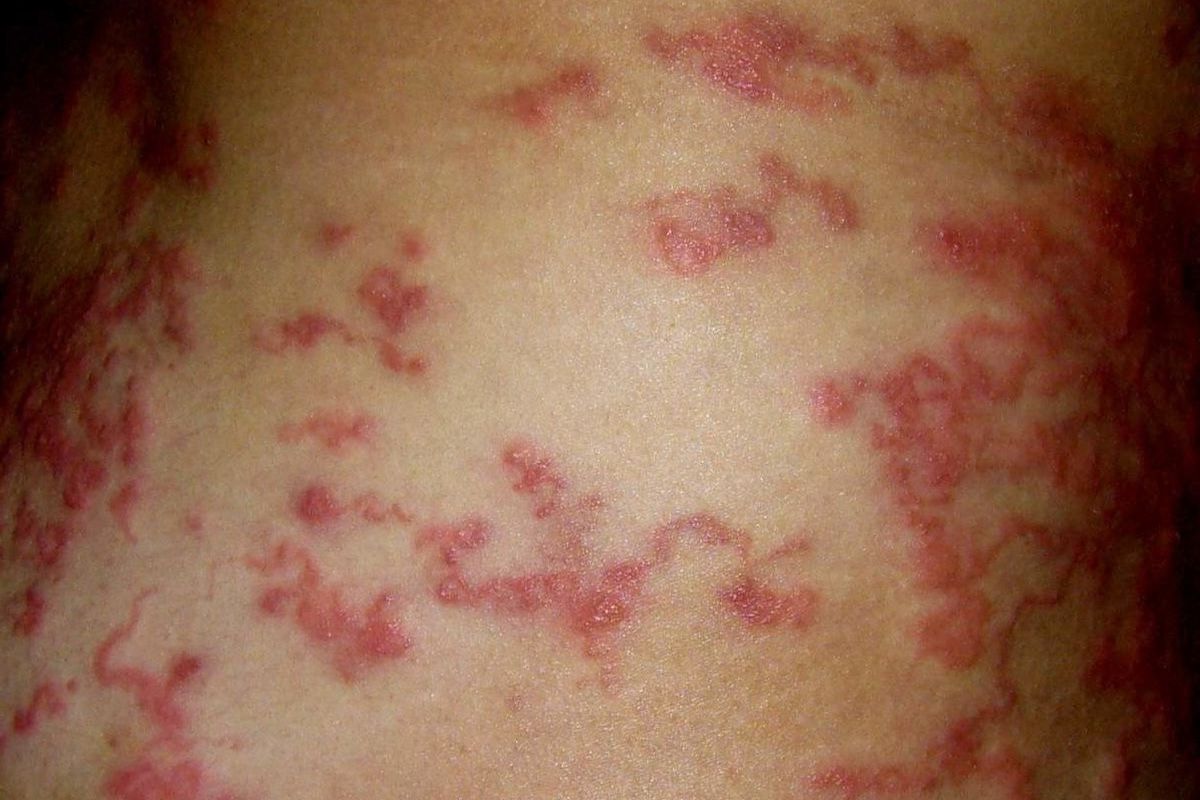
- Symptoms can vary widely, from mild to severe, and may include itching, skin rashes, and joint pain.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how to diagnose Mansonelliasis is crucial for effective treatment. Here are some key points to consider.
- Many infected individuals remain asymptomatic, meaning they show no symptoms at all.
- When symptoms do occur, they often include fever, headache, and muscle pain.
- Skin manifestations such as rashes and itching are common in symptomatic cases.
- Diagnosis typically involves microscopic examination of blood samples to detect the presence of microfilariae.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) tests can also be used for more accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Treating Mansonelliasis involves a combination of medications and supportive care. Here are some treatment facts.
- The primary treatment for Mansonelliasis is the use of antiparasitic drugs like Ivermectin and Albendazole.
- In some cases, a combination of medications may be required to effectively eliminate the parasites.
- Supportive care, including pain relief and anti-inflammatory medications, can help manage symptoms.
- Regular follow-up is essential to ensure the complete eradication of the parasites.
Geographic Distribution
Mansonelliasis is not evenly distributed around the world. Its prevalence is higher in certain regions.
- The disease is most commonly found in sub-Saharan Africa, Central and South America, and the Caribbean.
- In Africa, countries like Uganda, Cameroon, and the Democratic Republic of Congo report high infection rates.
- In South America, Brazil and Venezuela are among the countries with significant cases.
- The disease is less common in Asia and Europe, although cases have been reported in travelers returning from endemic regions.
Prevention and Control
Preventing Mansonelliasis involves reducing exposure to the vectors that transmit the disease. Here are some preventive measures.
- Using insect repellent can help reduce the risk of bites from infected midges and blackflies.
- Wearing long sleeves and pants can provide a physical barrier against bites.
- Sleeping under insecticide-treated bed nets is another effective preventive measure.
- Community-wide vector control programs, including insecticide spraying, can help reduce the population of biting midges and blackflies.
Impact on Public Health
Mansonelliasis has significant implications for public health, particularly in endemic regions.
- The disease can lead to chronic health issues, affecting the quality of life of those infected.
- In endemic areas, Mansonelliasis can place a considerable burden on healthcare systems.
- Public health initiatives aimed at controlling the disease can help reduce its prevalence and impact.
- Education and awareness campaigns are crucial for informing communities about the risks and prevention methods.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is essential for better understanding and controlling Mansonelliasis. Here are some recent developments.
- Scientists are exploring new diagnostic methods to improve the accuracy and speed of detection.
- Research is being conducted to develop more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
- Studies are also focusing on understanding the life cycle of the filarial worms to identify potential intervention points.
- Vaccine development is in the early stages, with the hope of providing long-term protection against the disease.
- International collaborations are crucial for advancing research and implementing control measures in endemic regions.
- Increased funding and resources are needed to support ongoing research and public health initiatives aimed at combating Mansonelliasis.
Final Thoughts on Mansonelliasis
Mansonelliasis, though not as well-known as other parasitic diseases, poses significant health risks in affected regions. Understanding its transmission, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for managing and preventing outbreaks. Public health initiatives focusing on education, vector control, and improved diagnostic methods can make a big difference in combating this disease.
Increased awareness and research funding are essential for developing better treatments and vaccines. By staying informed and supporting global health efforts, we can help reduce the impact of mansonelliasis on vulnerable populations.
Remember, knowledge is power. The more we know about mansonelliasis, the better equipped we are to fight it. Stay curious, stay informed, and contribute to the global effort to eradicate this parasitic threat.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
