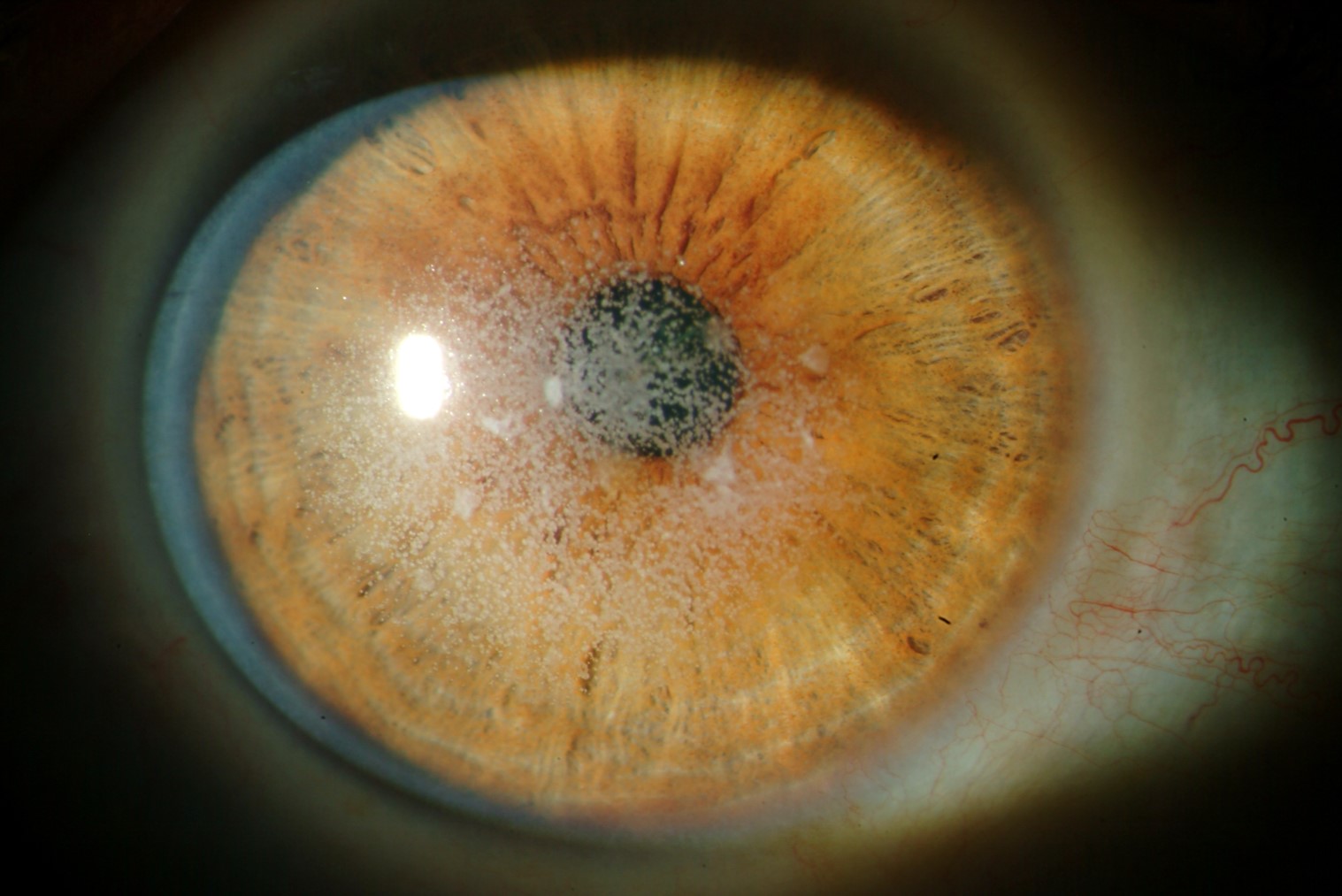
Lattice Corneal Dystrophy Type 2 is a rare genetic eye disorder that affects the cornea, leading to vision problems. This condition is characterized by the presence of lattice-like deposits in the cornea, which can cause cloudiness and vision impairment. Symptoms often include blurry vision, eye pain, and sensitivity to light. Caused by mutations in the TGFBI gene, this disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning only one copy of the altered gene is needed to cause the condition. Treatment options are limited but may include corneal transplants or laser surgery to improve vision. Understanding the genetic basis and symptoms of Lattice Corneal Dystrophy Type 2 can help in managing and treating this condition effectively.
Key Takeaways:
- Lattice Corneal Dystrophy Type 2 (LCD2) is a rare genetic eye disorder that can cause blurry vision, light sensitivity, and eye pain. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- While there is no cure for LCD2, treatments like lubricating eye drops, bandage contact lenses, and corneal transplants can help manage symptoms. Research into gene therapy and stem cell therapy offers hope for future treatments.
What is Lattice Corneal Dystrophy Type 2?
Lattice Corneal Dystrophy Type 2 (LCD2) is a rare genetic eye disorder. It affects the cornea, the clear front surface of the eye. This condition can lead to vision problems and discomfort.
-
Genetic Origin: LCD2 is caused by mutations in the TGFBI gene. This gene provides instructions for making a protein that helps maintain the structure of the cornea.
-
Inheritance Pattern: LCD2 follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. This means only one copy of the altered gene is needed to cause the disorder.
-
Symptoms Onset: Symptoms usually appear in the second or third decade of life. Early signs include blurred vision and eye discomfort.
-
Corneal Deposits: The hallmark of LCD2 is the presence of amyloid deposits in the cornea. These deposits form lattice-like patterns.
-
Progressive Condition: LCD2 is a progressive condition. Over time, the deposits can increase, leading to more severe vision problems.
How Does LCD2 Affect Vision?
LCD2 can significantly impact a person's vision. Understanding these effects can help in managing the condition better.
-
Blurry Vision: One of the first symptoms is blurry vision. This occurs due to the amyloid deposits scattering light as it enters the eye.
-
Light Sensitivity: Many individuals with LCD2 experience increased sensitivity to light. This can make it difficult to be in bright environments.
-
Eye Pain: As the condition progresses, eye pain can become more common. This pain is often due to the corneal surface becoming irregular.
-
Recurrent Corneal Erosions: LCD2 can cause recurrent corneal erosions. These are painful episodes where the outer layer of the cornea breaks down.
-
Vision Loss: In severe cases, LCD2 can lead to significant vision loss. This is usually due to extensive corneal scarring.
Diagnosis and Detection
Early diagnosis of LCD2 is crucial for managing symptoms and slowing progression. Here are some key points about how it is diagnosed.
-
Slit-Lamp Examination: An eye doctor uses a slit-lamp microscope to examine the cornea. This helps in identifying the characteristic lattice patterns.
-
Genetic Testing: Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis. It identifies mutations in the TGFBI gene.
-
Family History: A detailed family history can provide clues. Since LCD2 is inherited, other family members may also have the condition.
-
Corneal Topography: This imaging test maps the surface of the cornea. It helps in assessing the extent of the deposits.
-
Confocal Microscopy: This advanced imaging technique provides detailed images of the cornea. It can reveal the presence of amyloid deposits.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for LCD2, several treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Lubricating Eye Drops: These can help relieve dryness and discomfort. They are often the first line of treatment.
-
Bandage Contact Lenses: These lenses protect the cornea and reduce pain from erosions. They can also improve vision temporarily.
-
Corneal Transplant: In severe cases, a corneal transplant may be necessary. This involves replacing the damaged cornea with a healthy donor cornea.
-
Phototherapeutic Keratectomy (PTK): This laser procedure removes superficial corneal deposits. It can improve vision and reduce pain.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular eye exams are essential. They help in monitoring the progression of the condition and adjusting treatments as needed.
Living with LCD2
Living with LCD2 requires adjustments and support. Here are some tips to help manage daily life with this condition.
-
Protective Eyewear: Wearing sunglasses can help with light sensitivity. They also protect the eyes from UV rays.
-
Healthy Diet: A diet rich in vitamins A and C can support eye health. Leafy greens, carrots, and citrus fruits are good options.
-
Avoid Eye Rubbing: Rubbing the eyes can worsen symptoms. It can lead to more frequent corneal erosions.
-
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps keep the eyes moist. This can reduce dryness and discomfort.
-
Support Groups: Joining a support group can provide emotional support. It helps to connect with others who understand the challenges of living with LCD2.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is crucial for finding better treatments and possibly a cure for LCD2. Here are some exciting developments in this field.
-
Gene Therapy: Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment. This involves correcting the faulty gene responsible for LCD2.
-
Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cell therapy holds promise for regenerating damaged corneal tissue. It could offer a long-term solution for LCD2.
-
New Medications: Scientists are developing new medications to reduce amyloid deposits. These drugs aim to slow the progression of the condition.
-
Clinical Trials: Participating in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments. It also helps advance research in this field.
-
Patient Registries: Patient registries collect data on individuals with LCD2. This information is valuable for understanding the condition and developing new treatments.
Final Thoughts on Lattice Corneal Dystrophy Type 2
Lattice Corneal Dystrophy Type 2 (LCD2) is a rare genetic eye disorder that affects the cornea, leading to vision problems. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help manage this condition better. Symptoms often include blurred vision, eye pain, and sensitivity to light. LCD2 is caused by mutations in the TGFBI gene, which affects the corneal structure. Treatments range from medications to corneal transplants depending on severity.
Staying informed about the latest research and advancements in genetic testing can offer hope for those affected. Regular check-ups with an eye specialist are crucial for monitoring and managing symptoms. By raising awareness and supporting research, we can improve the quality of life for individuals with LCD2. Remember, early detection and proper care can make a significant difference.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
