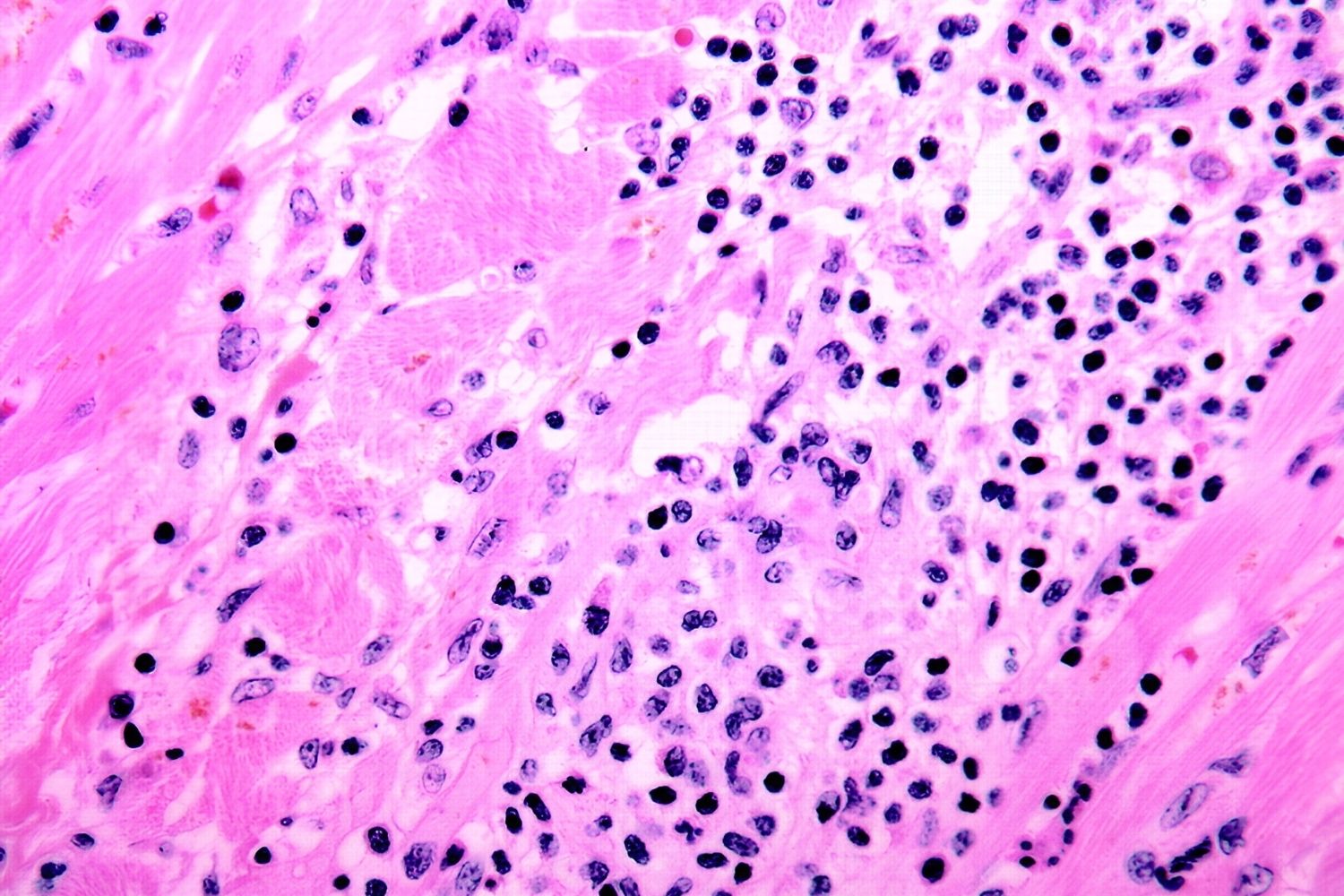
Infectious myocarditis is a condition where the heart muscle becomes inflamed due to an infection. This can be caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, or parasites. Symptoms often mimic those of other heart conditions, making it tricky to diagnose. Common signs include chest pain, fatigue, shortness of breath, and irregular heartbeats. Diagnosis typically involves blood tests, imaging, and sometimes a biopsy. Treatment varies based on the underlying infection but often includes medications to manage symptoms and fight the infection. Understanding infectious myocarditis is crucial because it can lead to severe complications like heart failure or sudden cardiac death if left untreated.
Key Takeaways:
- Infectious myocarditis can be caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites, affecting anyone regardless of age or gender. Symptoms vary widely, and early detection is crucial for effective treatment.
- Good hygiene, vaccinations, and prompt treatment of infections can help prevent infectious myocarditis. Ongoing research is exploring new therapies and genetic predispositions for better understanding and management.
What is Infectious Myocarditis?
Infectious myocarditis is a condition where the heart muscle becomes inflamed due to an infection. This inflammation can affect the heart's ability to pump blood and cause various symptoms. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Infectious myocarditis can be caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. Viruses are the most common culprits, with enteroviruses, adenoviruses, and the influenza virus being frequent offenders.
-
The condition can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. While it can strike anyone, young adults and athletes are often more susceptible.
-
Symptoms can vary widely. Some people may experience severe chest pain, while others might only have mild flu-like symptoms.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how infectious myocarditis is diagnosed can help in early detection and treatment.
-
Common symptoms include fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest pain. These symptoms can sometimes be mistaken for other conditions like a heart attack or flu.
-
In severe cases, it can lead to heart failure. This occurs when the heart muscle becomes too weak to pump blood effectively.
-
Electrocardiograms (ECGs) are often used to detect abnormalities in heart function. This test measures the electrical activity of the heart and can reveal signs of myocarditis.
-
Blood tests can detect markers of inflammation. Elevated levels of certain proteins can indicate the presence of an infection and inflammation in the heart.
Causes and Risk Factors
Knowing what causes infectious myocarditis and the risk factors involved can help in prevention and management.
-
Coxsackievirus B is a common cause of viral myocarditis. This virus is known for causing hand, foot, and mouth disease but can also infect the heart.
-
Bacterial infections like Lyme disease can lead to myocarditis. The bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi, transmitted by ticks, is responsible for this condition.
-
Fungal infections, though rare, can also cause myocarditis. People with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to fungal myocarditis.
Treatment and Management
Treatment options for infectious myocarditis vary depending on the severity and cause of the condition.
-
Antiviral medications can be used to treat viral myocarditis. These medications help reduce the viral load and inflammation in the heart.
-
Antibiotics are prescribed for bacterial myocarditis. These drugs target the specific bacteria causing the infection.
-
In severe cases, patients may require mechanical support. Devices like ventricular assist devices (VADs) can help the heart pump blood more effectively.
-
Corticosteroids can reduce inflammation. These drugs are often used in conjunction with other treatments to manage symptoms.
Complications and Prognosis
Understanding the potential complications and long-term outlook for infectious myocarditis is crucial for patients and caregivers.
-
Myocarditis can lead to arrhythmias. These irregular heartbeats can be life-threatening if not managed properly.
-
Some patients may develop dilated cardiomyopathy. This condition occurs when the heart becomes enlarged and weakened.
-
The prognosis varies widely. Some people recover completely, while others may have lasting heart damage.
Prevention and Awareness
Raising awareness and taking preventive measures can reduce the risk of developing infectious myocarditis.
-
Good hygiene practices can prevent viral infections. Regular handwashing and avoiding close contact with sick individuals are effective strategies.
-
Vaccinations can protect against certain viruses. Vaccines for influenza and other viruses can reduce the risk of myocarditis.
-
Early treatment of infections can prevent complications. Prompt medical attention for bacterial and viral infections can reduce the risk of myocarditis.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is crucial for improving the understanding and treatment of infectious myocarditis.
-
Researchers are exploring new antiviral therapies. These treatments aim to target specific viruses more effectively.
-
Stem cell therapy shows promise. Early studies suggest that stem cells could help repair damaged heart tissue.
-
Genetic research is uncovering new insights. Understanding genetic predispositions can help identify individuals at higher risk.
Real-Life Cases
Examining real-life cases can provide valuable insights into the impact of infectious myocarditis.
-
Athletes are often affected. High levels of physical activity can make athletes more susceptible to viral infections and myocarditis.
-
Children can also develop myocarditis. Pediatric cases often present differently and require specialized care.
-
Survivors often share their stories. These personal accounts can raise awareness and provide support for others.
Myths and Misconceptions
Dispelling myths and misconceptions about infectious myocarditis can help in better understanding and managing the condition.
-
Myocarditis is not always caused by a heart attack. While symptoms can be similar, the underlying causes are different.
-
It is not always a chronic condition. Many people recover fully with appropriate treatment.
-
Exercise is not always harmful. Moderate physical activity can be beneficial, but intense exercise should be avoided during recovery.
-
It is not a rare condition. While not extremely common, it is more prevalent than many people realize.
Final Thoughts on Infectious Myocarditis
Infectious myocarditis, a condition where the heart muscle becomes inflamed due to an infection, can be serious. Knowing the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial. Early detection and proper care can make a big difference in outcomes. Viruses, bacteria, and even fungi can cause this condition, making it important to maintain good hygiene and seek medical attention if you experience unusual symptoms like chest pain, fatigue, or shortness of breath.
Prevention includes regular hand washing, vaccinations, and avoiding close contact with sick individuals. If diagnosed, treatments range from medications to manage symptoms to more intensive therapies like intravenous antibiotics or even mechanical support for the heart.
Staying informed and proactive about heart health can help you or your loved ones manage or prevent infectious myocarditis effectively. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
