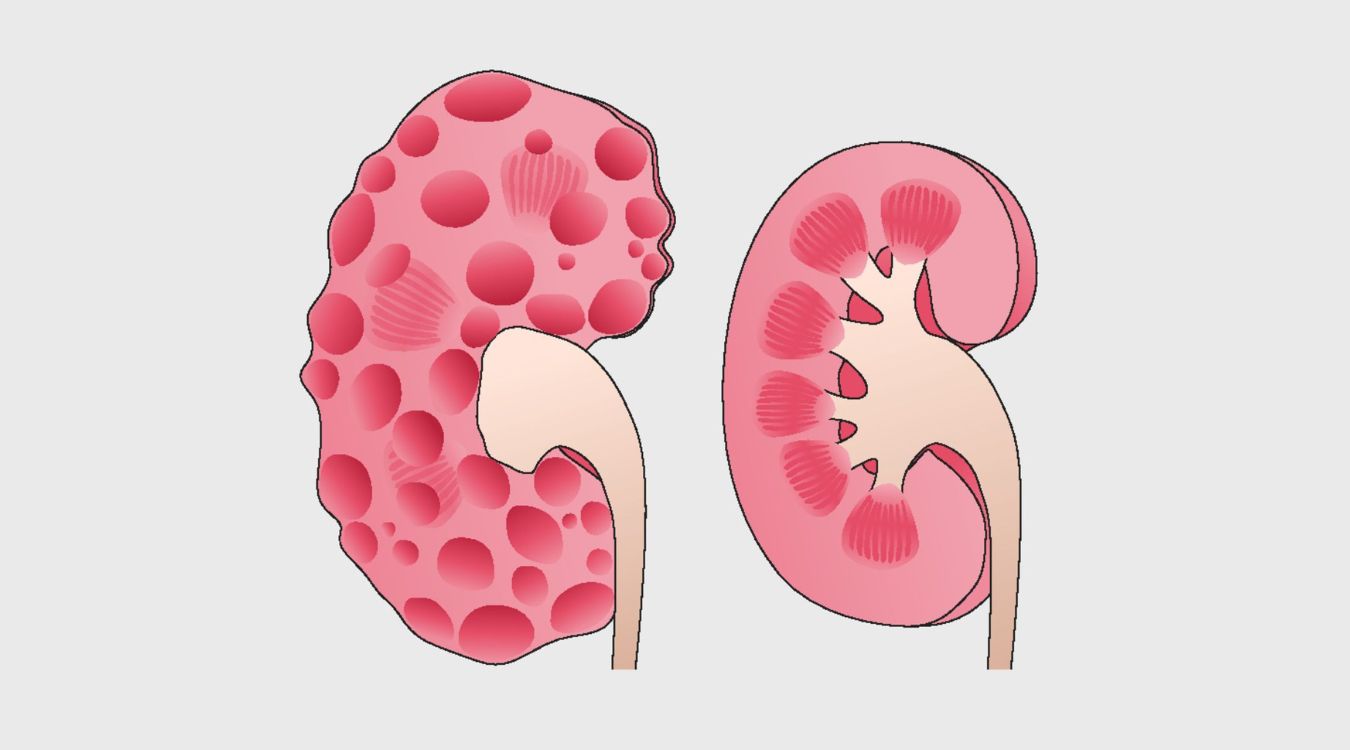
Infantile Polycystic Kidney Disease (IPKD) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the kidneys and liver. Characterized by the formation of numerous cysts, this condition can lead to kidney failure and other serious complications. IPKD is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning both parents must carry the gene for a child to be affected. Symptoms often appear early in life, sometimes even before birth, and can include high blood pressure, urinary tract infections, and growth problems. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing the disease and improving quality of life. Understanding IPKD can help families prepare and seek appropriate medical care.
Key Takeaways:
- Infantile Polycystic Kidney Disease (IPKD) is a rare genetic disorder causing cysts in the kidneys and other organs. Early diagnosis, symptom management, and family support are crucial for children affected by IPKD.
- Ongoing research on IPKD focuses on gene therapy, stem cell research, drug development, clinical trials, and patient registries to improve understanding and treatment options for this rare genetic disorder.
What is Infantile Polycystic Kidney Disease (IPKD)?
Infantile Polycystic Kidney Disease (IPKD) is a rare genetic disorder affecting the kidneys and other organs. It causes cysts to form in the kidneys, leading to various health complications. Here are some key facts about this condition:
-
Genetic Disorder: IPKD is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning both parents must carry the gene for a child to be affected.
-
Cyst Formation: The disease causes numerous fluid-filled cysts to develop in the kidneys, which can impair their function.
-
Early Onset: Symptoms often appear in infancy or even before birth, making early diagnosis crucial.
-
Kidney Enlargement: Affected kidneys can become significantly enlarged due to the cysts, sometimes up to three times their normal size.
-
Liver Involvement: Besides kidneys, the liver is often affected, leading to fibrosis and other complications.
Symptoms of IPKD
Recognizing the symptoms of IPKD early can help in managing the condition more effectively. Here are some common signs:
-
High Blood Pressure: Many infants with IPKD develop hypertension, which needs careful monitoring.
-
Urinary Tract Infections: Frequent UTIs are common due to the abnormal kidney structure.
-
Abdominal Swelling: Enlarged kidneys can cause noticeable swelling in the abdomen.
-
Breathing Difficulties: The enlarged kidneys can press against the diaphragm, leading to respiratory issues.
-
Growth Delays: Children with IPKD may experience slower growth and development compared to their peers.
Diagnosis of IPKD
Diagnosing IPKD involves several tests and procedures to confirm the presence of cysts and assess kidney function. Here are some methods used:
-
Ultrasound: This imaging technique is often the first step in diagnosing IPKD, revealing cysts in the kidneys.
-
Genetic Testing: Identifying mutations in the PKHD1 gene can confirm the diagnosis.
-
MRI and CT Scans: These provide detailed images of the kidneys and other affected organs.
-
Blood Tests: Checking kidney function through blood tests helps assess the severity of the disease.
-
Prenatal Diagnosis: In some cases, IPKD can be detected before birth through prenatal ultrasound or genetic testing.
Treatment Options for IPKD
While there is no cure for IPKD, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some common approaches:
-
Blood Pressure Management: Medications to control hypertension are often necessary.
-
Antibiotics: Frequent UTIs may require regular antibiotic treatment.
-
Dialysis: In severe cases, dialysis may be needed to perform the kidneys' filtering functions.
-
Kidney Transplant: A transplant may be considered if kidney function deteriorates significantly.
-
Supportive Care: Nutritional support, physical therapy, and other supportive measures can improve overall health.
Prognosis and Life Expectancy
The prognosis for children with IPKD varies widely, depending on the severity of the disease and the effectiveness of treatments. Here are some important points:
-
Variable Outcomes: Some children may have mild symptoms and live relatively normal lives, while others may face severe complications.
-
Early Intervention: Prompt diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes and extend life expectancy.
-
Chronic Kidney Disease: Many children with IPKD develop chronic kidney disease, requiring ongoing medical care.
-
Liver Complications: Liver fibrosis can lead to additional health issues, necessitating regular monitoring.
-
Family Support: Emotional and psychological support for families is crucial in managing the challenges of IPKD.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand IPKD and develop new treatments. Here are some areas of focus:
-
Gene Therapy: Scientists are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment to correct the genetic mutations causing IPKD.
-
Stem Cell Research: Stem cells may offer new ways to repair or replace damaged kidney tissue.
-
Drug Development: New medications are being tested to slow the progression of cyst formation and improve kidney function.
-
Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments and contribute to advancing medical knowledge.
-
Patient Registries: Collecting data from patients with IPKD helps researchers track the disease's progression and identify potential treatments.
Final Thoughts on IPKD
Infantile polycystic kidney disease (IPKD) is a rare but serious condition that affects newborns. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help families navigate this challenging diagnosis. Early detection is crucial for managing the disease and improving the quality of life for affected infants. While there's no cure, medical advancements offer hope for better management and potential future treatments. Support from healthcare professionals, along with emotional and educational resources, can make a significant difference for families dealing with IPKD. Staying informed and connected with support networks can provide much-needed strength and guidance. Remember, knowledge is power, and being proactive in seeking information and support can lead to better outcomes for your child.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
