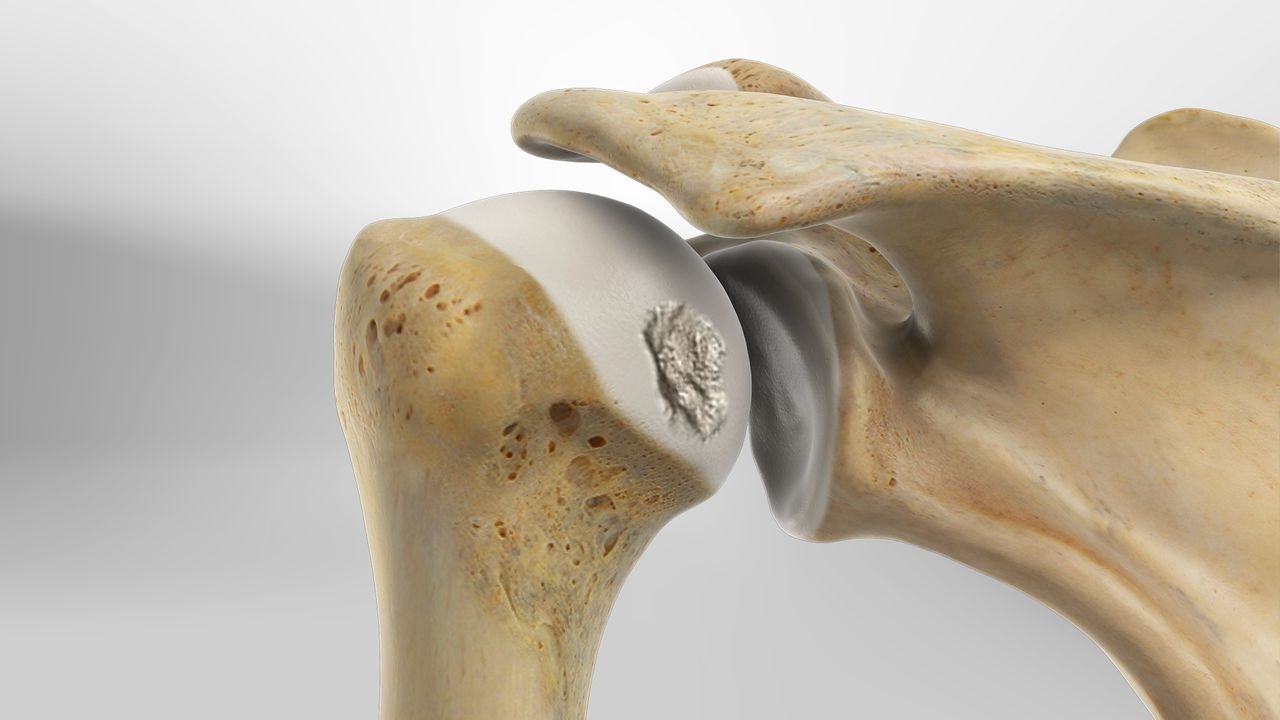
Hill-Sachs lesion is a term that might sound unfamiliar, but it's crucial for anyone dealing with shoulder injuries. This condition involves a dent or groove in the humerus bone, often resulting from a shoulder dislocation. But what exactly causes a Hill-Sachs lesion? When the shoulder pops out of its socket, the humerus can slam against the edge of the shoulder blade, creating this indentation. Athletes, especially those in contact sports, are more prone to this injury. Symptoms can include pain, limited range of motion, and a feeling of instability in the shoulder. Understanding Hill-Sachs lesions can help in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment. Whether you're an athlete, a coach, or just someone curious about shoulder health, these facts will shed light on this common yet often misunderstood injury.
Key Takeaways:
- Shoulder dislocations can lead to a Hill-Sachs lesion, causing pain, swelling, and limited motion. Treatment options include rest, physical therapy, and surgery for severe cases. Recovery takes time and patience.
- Athletes, especially young adults, are at higher risk for Hill-Sachs lesions. Prevention involves proper warm-up, strength training, and avoiding high-risk activities. Stay informed about shoulder injury risks and symptoms.
What is a Hill-Sachs Lesion?
A Hill-Sachs lesion is a specific type of injury to the shoulder. It involves a dent or fracture in the humeral head, which is the ball part of the ball-and-socket shoulder joint. This injury often occurs alongside shoulder dislocations.
-
Named After Doctors: The lesion is named after Harold Hill and Maurice Sachs, who first described it in 1940.
-
Common in Athletes: Athletes, especially those in contact sports, are more prone to this injury due to the high risk of shoulder dislocations.
-
Associated with Dislocations: Nearly 80% of shoulder dislocations result in a Hill-Sachs lesion.
-
Location of Injury: The lesion typically occurs on the posterolateral aspect of the humeral head.
-
Caused by Impact: It happens when the humeral head impacts the edge of the glenoid cavity during a dislocation.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and diagnosing a Hill-Sachs lesion is crucial for proper treatment. Here are some key points to consider.
-
Pain and Swelling: Immediate pain and swelling in the shoulder are common symptoms.
-
Limited Range of Motion: Patients often experience a reduced range of motion in the affected shoulder.
-
Popping Sensation: A popping or grinding sensation may be felt during shoulder movement.
-
X-rays for Diagnosis: X-rays are typically used to diagnose a Hill-Sachs lesion, revealing the dent or fracture in the humeral head.
-
MRI for Detailed View: An MRI can provide a more detailed view of the lesion and any associated soft tissue damage.
Treatment Options
Treatment for a Hill-Sachs lesion varies depending on the severity of the injury. Here are some common approaches.
-
Rest and Ice: Initial treatment often involves rest and ice to reduce pain and swelling.
-
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help restore strength and range of motion in the shoulder.
-
Sling for Immobilization: A sling may be used to immobilize the shoulder and allow it to heal.
-
Surgical Intervention: Severe cases may require surgery to repair the lesion and stabilize the shoulder.
-
Arthroscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive arthroscopic surgery is often used to treat Hill-Sachs lesions.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from a Hill-Sachs lesion can be a lengthy process. Here are some important aspects of rehabilitation.
-
Gradual Return to Activity: Patients should gradually return to physical activity to avoid re-injury.
-
Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises can help strengthen the shoulder muscles and improve stability.
-
Avoiding High-Risk Activities: Avoiding activities that put the shoulder at risk of dislocation is crucial during recovery.
-
Regular Follow-ups: Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor progress.
-
Patience is Key: Recovery can take several months, and patience is important for a full recovery.
Interesting Facts
Here are some intriguing facts about Hill-Sachs lesions that you might not know.
-
Common in Young Adults: This injury is most common in young adults aged 18-30.
-
Bilateral Lesions: In rare cases, Hill-Sachs lesions can occur in both shoulders.
-
First Described in 1940: The lesion was first described in medical literature in 1940.
-
Named After Doctors: The lesion is named after Harold Hill and Maurice Sachs, who first described it.
-
Associated with Bankart Lesion: A Hill-Sachs lesion is often associated with a Bankart lesion, another type of shoulder injury.
Prevention Tips
Preventing a Hill-Sachs lesion involves taking steps to protect the shoulder from dislocations. Here are some tips.
-
Proper Warm-Up: Always warm up properly before engaging in physical activity.
-
Strength Training: Strengthening the shoulder muscles can help stabilize the joint and prevent dislocations.
-
Avoid High-Risk Activities: Avoid activities that put the shoulder at risk of dislocation, especially if you have a history of shoulder injuries.
-
Use Protective Gear: Wearing protective gear, such as shoulder pads, can help reduce the risk of injury in contact sports.
-
Stay Informed: Educate yourself about the risks and symptoms of shoulder injuries to seek prompt treatment if needed.
Final Thoughts on Hill-Sachs Lesion
Understanding a Hill-Sachs lesion is crucial for anyone dealing with shoulder injuries. This condition often accompanies shoulder dislocations, making it a double whammy for patients. Knowing the symptoms, like pain and limited movement, can help in seeking timely medical advice. Treatment options range from physical therapy to surgery, depending on the severity. Early diagnosis and proper care can prevent further complications, ensuring a quicker recovery.
For athletes, especially those in contact sports, awareness and preventive measures are key. Regular check-ups and strengthening exercises can make a big difference. If you suspect a Hill-Sachs lesion, consult a healthcare professional immediately. Don’t ignore the signs; your shoulder’s health is vital for overall well-being. Stay informed, stay proactive, and take care of your shoulders.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
