Foix–Alajouanine syndrome might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it doesn't have to be complicated. This rare neurological disorder affects the spinal cord's blood vessels, leading to various symptoms. Ever wondered why some people experience sudden back pain, muscle weakness, or even paralysis? These could be signs of this condition. Named after French neurologists Charles Foix and Théophile Alajouanine, this syndrome primarily impacts adults, often going unnoticed until symptoms become severe. Curious about the causes, symptoms, and treatments? Keep reading to uncover 30 intriguing facts about Foix–Alajouanine syndrome that will help you grasp this rare but significant medical condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Foix–Alajouanine syndrome is a rare spinal cord disorder causing weakness and paralysis. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
- Living with Foix–Alajouanine syndrome presents unique challenges, but building a strong support network, managing mental health, and advocating for awareness can make a difference.
What is Foix–Alajouanine Syndrome?
Foix–Alajouanine syndrome is a rare neurological disorder that affects the spinal cord. Named after French neurologists Charles Foix and Théophile Alajouanine, this condition can lead to severe disability if not diagnosed and treated promptly. Here are some intriguing facts about this syndrome.
-
Rare Condition: Foix–Alajouanine syndrome is extremely rare, with only a few hundred cases reported worldwide.
-
Spinal Cord Impact: This syndrome primarily affects the lower part of the spinal cord, causing progressive weakness and paralysis.
-
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM): The condition is often associated with an arteriovenous malformation, a tangle of abnormal blood vessels.
-
Symptoms Onset: Symptoms usually begin in adulthood, often between the ages of 30 and 60.
-
Initial Symptoms: Early signs include back pain, leg weakness, and difficulty walking.
-
Progressive Nature: The syndrome is progressive, meaning symptoms worsen over time without treatment.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how doctors diagnose Foix–Alajouanine syndrome is crucial for early intervention. Here are some key points.
-
Sensory Loss: Patients may experience loss of sensation in the legs and lower body.
-
Bladder and Bowel Dysfunction: Incontinence or difficulty controlling bladder and bowel functions is common.
-
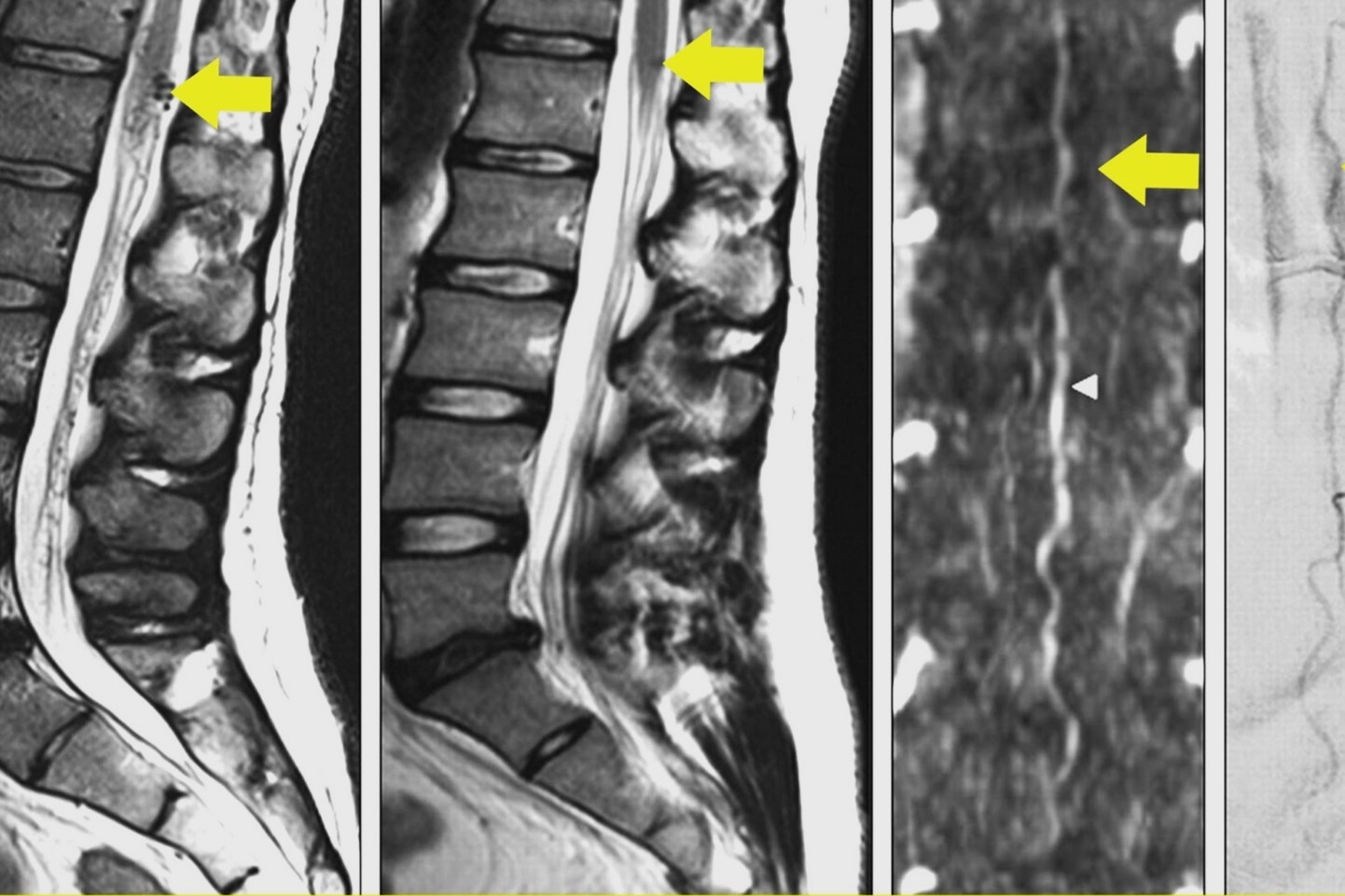
MRI Scans: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the primary tool for diagnosing this syndrome.
-
Spinal Angiography: This imaging technique helps visualize blood vessels in the spinal cord to identify AVMs.
-
Misdiagnosis Risk: Due to its rarity, Foix–Alajouanine syndrome is often misdiagnosed as multiple sclerosis or other spinal disorders.
-
Neurological Exams: Comprehensive neurological exams are essential for accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for Foix–Alajouanine syndrome, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Surgery: Surgical removal of the AVM can alleviate symptoms and prevent further damage.
-
Embolization: This minimally invasive procedure involves injecting materials to block abnormal blood vessels.
-
Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy can help maintain mobility and strength.
-
Pain Management: Medications and other therapies can help manage chronic pain associated with the syndrome.
-
Assistive Devices: Wheelchairs, walkers, and other devices can aid mobility.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can improve overall well-being.
Historical Context
The history behind Foix–Alajouanine syndrome provides insight into its discovery and the evolution of its understanding.
-
Discovery: Charles Foix and Théophile Alajouanine first described the syndrome in the early 20th century.
-
Initial Cases: The first documented cases involved patients with progressive paraplegia and spinal cord lesions.
-
Medical Advances: Advances in imaging technology have significantly improved the diagnosis and treatment of this syndrome.
-
Research: Ongoing research aims to better understand the underlying causes and develop more effective treatments.
-
Case Studies: Detailed case studies have provided valuable information about the syndrome's progression and response to treatment.
Living with Foix–Alajouanine Syndrome
Living with a rare condition like Foix–Alajouanine syndrome presents unique challenges. Here are some aspects of daily life for those affected.
-
Support Networks: Building a strong support network of family, friends, and healthcare professionals is vital.
-
Mental Health: Managing mental health is crucial, as chronic illness can lead to depression and anxiety.
-
Advocacy: Patients and families often become advocates for rare disease awareness and research funding.
-
Education: Educating oneself and others about the syndrome can help reduce stigma and improve understanding.
-
Financial Burden: The cost of medical care, assistive devices, and other expenses can be significant.
-
Community Resources: Many communities offer resources and support groups for individuals with rare diseases.
-
Hope for the Future: Advances in medical research and technology continue to offer hope for better treatments and improved quality of life.
Final Thoughts on Foix–Alajouanine Syndrome
Foix–Alajouanine Syndrome, a rare spinal cord disorder, often goes unnoticed due to its subtle symptoms. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can make a significant difference in managing the condition. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for improving quality of life. While there's no cure, treatments like physical therapy, medications, and sometimes surgery can help manage symptoms and slow progression. Awareness and education about this syndrome are essential for both patients and healthcare providers. If you or someone you know shows signs of this condition, seeking medical advice promptly is vital. Knowledge empowers us to take control of our health. Stay informed, stay proactive, and don't hesitate to reach out to medical professionals for guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
