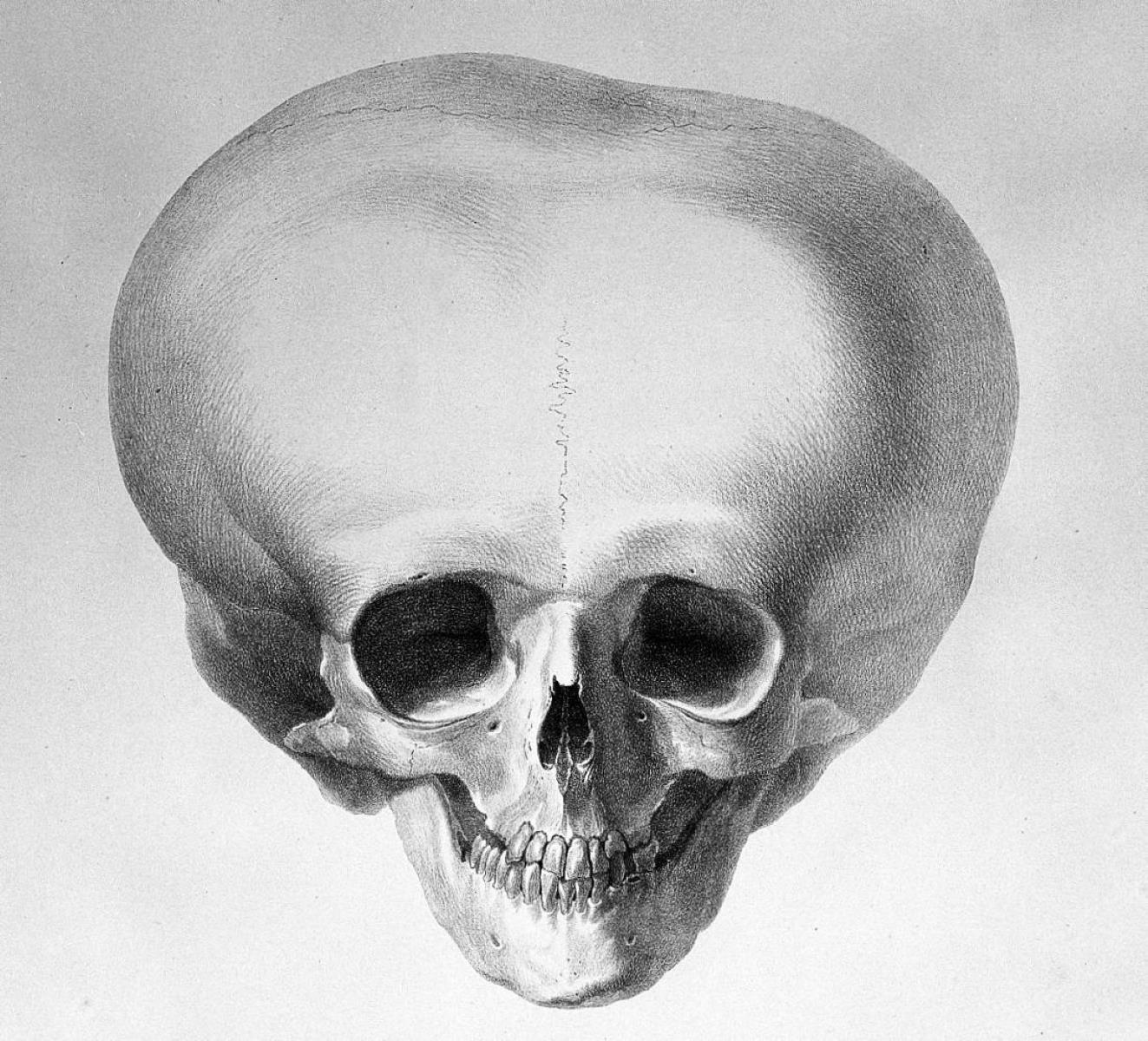
Facial clefting and corpus callosum agenesis are two distinct medical conditions that can significantly impact an individual's life. Facial clefting involves gaps or splits in the upper lip, roof of the mouth, or both, which occur when facial structures do not fuse properly during fetal development. Corpus callosum agenesis is a rare brain malformation where the corpus callosum, the structure connecting the two hemispheres of the brain, fails to develop. Both conditions present unique challenges and require specialized care. Understanding these conditions can help in recognizing symptoms, seeking appropriate treatments, and providing support for affected individuals and their families. Let's delve into 30 intriguing facts about these conditions to broaden our knowledge and awareness.
Key Takeaways:
- Facial clefting and corpus callosum agenesis are common birth defects with genetic and environmental factors. Early intervention and multidisciplinary care are crucial for improving outcomes in affected children.
- Children with facial clefting and corpus callosum agenesis may face challenges in speech, feeding, and cognitive development. Support groups, awareness, and tailored resources can make a significant difference in their quality of life.
What is Facial Clefting?
Facial clefting is a congenital condition where there is an opening or gap in the face. This can affect the lips, palate, or both. Here are some interesting facts about facial clefting:
- Common Birth Defect: Facial clefting is one of the most common birth defects worldwide.
- Types of Clefts: There are different types of clefts, including cleft lip, cleft palate, and both combined.
- Genetic Factors: Genetics play a significant role in the occurrence of facial clefts.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors like maternal smoking and alcohol use can increase the risk.
- Surgical Repair: Surgery is the primary treatment for facial clefts and is usually performed within the first year of life.
- Speech Therapy: Many children with cleft palate require speech therapy to improve their communication skills.
- Feeding Challenges: Babies with cleft palate often face feeding difficulties and may need special bottles or feeding techniques.
- Hearing Issues: Ear infections and hearing loss are common in children with cleft palate.
- Dental Problems: Dental issues, including missing or misaligned teeth, are frequent in children with facial clefts.
- Psychosocial Impact: Facial clefts can affect a child's self-esteem and social interactions.
Understanding Corpus Callosum Agenesis
Corpus callosum agenesis (CCA) is a rare brain condition where the corpus callosum, the structure connecting the two hemispheres of the brain, is partially or completely absent. Here are some key facts about CCA:
- Rare Condition: CCA affects approximately 1 in 4,000 individuals.
- Developmental Delays: Children with CCA often experience developmental delays.
- Seizures: Seizures are common in individuals with CCA.
- Motor Skills: Motor skill development can be significantly impacted.
- Cognitive Function: Cognitive abilities can range from normal to severely impaired.
- Behavioral Issues: Behavioral problems, including ADHD and autism spectrum disorders, are more prevalent.
- Prenatal Diagnosis: CCA can often be diagnosed before birth through ultrasound or MRI.
- Genetic Causes: Genetic mutations or chromosomal abnormalities can cause CCA.
- Associated Conditions: CCA is often associated with other brain abnormalities.
- Therapies: Physical, occupational, and speech therapies are crucial for managing symptoms.
The Link Between Facial Clefting and Corpus Callosum Agenesis
While facial clefting and corpus callosum agenesis are distinct conditions, they can sometimes occur together. Here are some facts about their connection:
- Syndromic Cases: Both conditions can be part of a syndrome, such as Aicardi syndrome.
- Genetic Overlap: Certain genetic mutations can lead to both facial clefting and CCA.
- Prenatal Indicators: Ultrasound can sometimes detect both conditions during pregnancy.
- Multidisciplinary Care: Children with both conditions often require care from multiple specialists.
- Early Intervention: Early intervention is critical for improving outcomes in children with both conditions.
- Research: Ongoing research aims to better understand the genetic and environmental factors linking these conditions.
- Support Groups: Families can benefit from support groups and resources tailored to these conditions.
- Awareness: Raising awareness about these conditions can lead to earlier diagnosis and better support.
- Educational Needs: Children with both conditions may have unique educational needs.
- Quality of Life: With proper care and support, many children with facial clefting and CCA can lead fulfilling lives.
Final Thoughts on Facial Clefting and Corpus Callosum Agenesis
Facial clefting and corpus callosum agenesis are complex conditions that impact many lives. Understanding these conditions can help foster empathy and support for those affected. Facial clefting, often visible at birth, can be addressed with surgery and therapy, improving quality of life. Corpus callosum agenesis, a brain anomaly, may present with various symptoms, from mild to severe, requiring tailored interventions.
Raising awareness about these conditions is crucial. It encourages early diagnosis and intervention, which can significantly improve outcomes. Support networks and resources play a vital role in helping families navigate challenges.
Knowledge empowers us to make informed decisions and advocate for better healthcare. By sharing facts and stories, we contribute to a more inclusive and understanding society. Let's continue to learn, support, and spread awareness about facial clefting and corpus callosum agenesis.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
