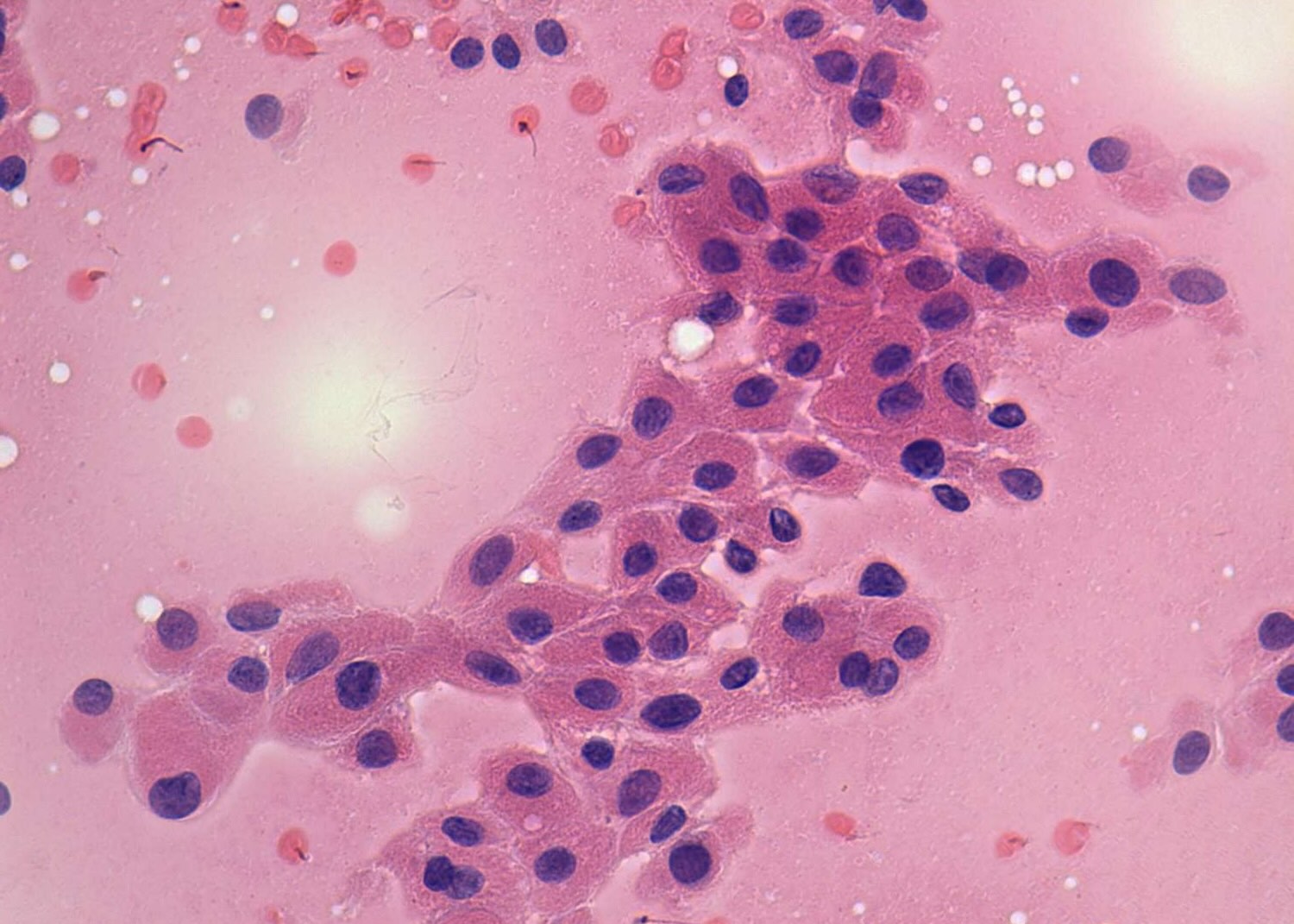
Cell oxyphilia might sound like a complex term, but it’s actually quite fascinating. Oxyphilic cells are cells that have a high affinity for oxygen, often appearing in various tissues and organs. These cells play crucial roles in our bodies, from energy production to maintaining healthy tissues. Understanding these cells can help us appreciate how our bodies function at a microscopic level. In this post, we’ll dive into 30 intriguing facts about cell oxyphilia, shedding light on their importance, where they’re found, and how they contribute to our overall health. Get ready to uncover the tiny yet mighty world of oxyphilic cells!
Key Takeaways:
- Oxyphilic cells, also known as acidophilic cells, have a strong affinity for oxygen and play vital roles in energy production, hormone secretion, and detoxification in various organs of the body.
- Research on oxyphilic cells is paving the way for potential cancer treatments, regenerative medicine, gene therapy, and drug development, offering hope for improved health and longevity.
What is Cell Oxyphilia?
Cell oxyphilia refers to the affinity of certain cells for oxygen. These cells play crucial roles in various biological processes. Here are some fascinating facts about cell oxyphilia.
-
Oxyphilic Cells: These cells are also known as acidophilic cells due to their affinity for acidic dyes.
-
Mitochondria: Oxyphilic cells contain a high number of mitochondria, which are the powerhouses of the cell.
-
Thyroid Gland: In the thyroid gland, oxyphilic cells are called Hurthle cells.
-
Parathyroid Gland: Oxyphilic cells are also found in the parathyroid gland, where they are involved in calcium regulation.
-
Kidney: In the kidney, these cells are part of the renal tubules and help in filtering blood.
Functions of Oxyphilic Cells
Oxyphilic cells have various functions depending on their location in the body. Let's explore some of these functions.
-
Energy Production: Due to their high mitochondrial content, oxyphilic cells are essential for energy production.
-
Hormone Secretion: In the thyroid and parathyroid glands, these cells are involved in hormone secretion.
-
Calcium Regulation: In the parathyroid gland, oxyphilic cells help regulate calcium levels in the blood.
-
Detoxification: In the liver, oxyphilic cells assist in detoxifying harmful substances.
-
Oxygen Sensing: Some oxyphilic cells can sense oxygen levels and help the body respond to changes in oxygen availability.
Oxyphilic Cells in Disease
Oxyphilic cells can be involved in various diseases. Here are some examples.
-
Thyroid Cancer: Hurthle cell carcinoma is a type of thyroid cancer that originates from oxyphilic cells.
-
Parathyroid Adenoma: This benign tumor of the parathyroid gland often contains oxyphilic cells.
-
Kidney Disease: Damage to oxyphilic cells in the kidney can lead to impaired kidney function.
-
Liver Disease: In liver diseases like cirrhosis, oxyphilic cells can become damaged and lose their function.
-
Oxidative Stress: Oxyphilic cells are susceptible to oxidative stress, which can lead to cell damage and disease.
Interesting Facts about Oxyphilic Cells
Here are some more intriguing facts about these unique cells.
-
Staining: Oxyphilic cells stain pink with eosin due to their high mitochondrial content.
-
Size: These cells are usually larger than other cell types due to their abundant mitochondria.
-
Metabolism: Oxyphilic cells have a high metabolic rate because of their role in energy production.
-
Aging: The number of oxyphilic cells tends to increase with age, particularly in the thyroid and parathyroid glands.
-
Research: Scientists study oxyphilic cells to understand their role in health and disease better.
Oxyphilic Cells in Different Organs
Oxyphilic cells are found in various organs, each with unique roles. Let's look at some examples.
-
Thyroid: In the thyroid gland, oxyphilic cells help produce thyroid hormones.
-
Parathyroid: These cells in the parathyroid gland are involved in calcium homeostasis.
-
Kidney: In the kidney, oxyphilic cells help filter blood and produce urine.
-
Liver: Oxyphilic cells in the liver assist in detoxification and metabolism.
-
Adrenal Gland: These cells in the adrenal gland help produce hormones like adrenaline.
Future Research on Oxyphilic Cells
Research on oxyphilic cells is ongoing, with many exciting discoveries on the horizon.
-
Cancer Treatment: Scientists are exploring ways to target oxyphilic cells in cancer therapy.
-
Regenerative Medicine: Research is being conducted on using oxyphilic cells in regenerative medicine to repair damaged tissues.
-
Gene Therapy: Gene therapy techniques are being developed to correct genetic defects in oxyphilic cells.
-
Drug Development: New drugs are being tested to protect oxyphilic cells from oxidative stress and damage.
-
Aging: Studies are investigating the role of oxyphilic cells in the aging process and how to maintain their function as we age.
Final Thoughts on Cell Oxyphilia
Cell oxyphilia, a fascinating aspect of cellular biology, reveals how cells thrive in oxygen-rich environments. Understanding this phenomenon helps scientists develop treatments for diseases like cancer and respiratory disorders. Oxyphilic cells, often found in tissues with high metabolic rates, play crucial roles in energy production and overall cellular function.
By studying these cells, researchers can uncover new ways to enhance human health. From improving athletic performance to developing innovative therapies, the potential applications are vast. As science advances, the knowledge gained from cell oxyphilia will continue to shape our understanding of biology and medicine.
Stay curious and keep exploring the wonders of cellular biology. The more we learn about these tiny powerhouses, the better equipped we'll be to tackle health challenges and improve lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
