Small Uncloven Cell Lymphoma is a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system, which is part of the body's immune system. This disease involves the abnormal growth of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell. Lymphoma can occur in various parts of the body, including lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, and other organs. Understanding this condition is crucial for early detection and treatment. In this article, we will explore 25 essential facts about Small Uncloven Cell Lymphoma, covering its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options. Stay informed to better recognize and manage this serious health issue.
Key Takeaways:
- Small Uncloven Cell Lymphoma (SUCL) is a rare type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that primarily affects adults in their 60s. Symptoms include swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, fever, and unexplained weight loss.
- Genetic mutations, chemical exposure, weakened immune system, family history of cancer, and chronic infections are potential risk factors for SUCL. Early diagnosis and accurate staging are crucial for effective treatment.
What is Small Uncloven Cell Lymphoma?
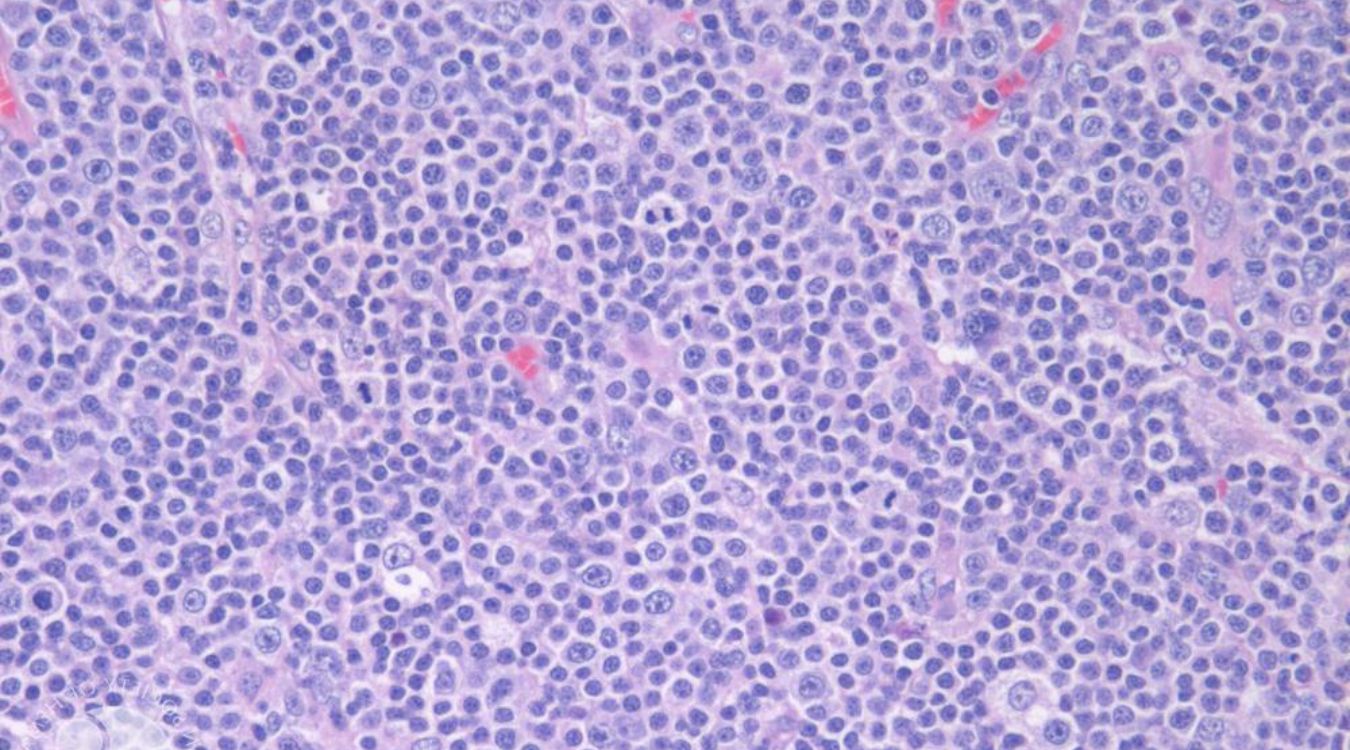
Small Uncloven Cell Lymphoma (SUCL) is a rare type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It affects the lymphatic system, which is part of the body's immune system. Understanding this disease can help patients and their families navigate the challenges it presents.
- SUCL is a subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which means it originates in the lymphatic system.
- This lymphoma is characterized by small, uncloven (not split) cells that appear under a microscope.
- SUCL is considered rare, accounting for a small percentage of all lymphoma cases.
- The disease primarily affects adults, with most patients being diagnosed in their 60s or older.
- Symptoms often include swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, fever, and unexplained weight loss.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of SUCL can help in early detection and prevention. While the exact cause remains unknown, several factors may increase the risk.
- Genetic mutations are believed to play a significant role in the development of SUCL.
- Exposure to certain chemicals, such as pesticides and herbicides, may increase the risk.
- A weakened immune system, whether due to HIV/AIDS or immunosuppressive drugs, can make one more susceptible.
- Family history of lymphoma or other cancers can be a contributing factor.
- Chronic infections, such as hepatitis C or Epstein-Barr virus, have been linked to higher SUCL risk.
Diagnosis and Staging
Accurate diagnosis and staging are crucial for effective treatment. Doctors use various methods to determine the presence and extent of SUCL.
- A biopsy, where a sample of lymph node tissue is examined, is the primary method for diagnosing SUCL.
- Imaging tests like CT scans, PET scans, and MRIs help determine the spread of the disease.
- Blood tests can reveal abnormalities that suggest lymphoma.
- Bone marrow biopsy may be performed to check if the lymphoma has spread to the bone marrow.
- SUCL is staged from I to IV, with Stage I being localized and Stage IV indicating widespread disease.
Treatment Options
Treatment for SUCL varies based on the stage and overall health of the patient. Multiple approaches can be used to manage the disease.
- Chemotherapy is a common treatment, using drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy targets specific areas to destroy lymphoma cells.
- Immunotherapy boosts the body's immune system to fight the cancer.
- Targeted therapy focuses on specific molecules involved in the growth of cancer cells.
- Stem cell transplant may be considered for patients who do not respond to other treatments.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for SUCL patients depends on various factors, including the stage at diagnosis and response to treatment.
- Early-stage SUCL has a better prognosis, with higher survival rates.
- Advanced stages may require more aggressive treatment and have lower survival rates.
- Regular follow-up care is essential to monitor for recurrence or complications.
- Clinical trials offer access to new treatments that may improve outcomes.
- Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support for patients and their families.
Final Thoughts on Small Uncloven Cell Lymphoma
Small uncloven cell lymphoma, though rare, holds significant importance in the medical field. Understanding its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options can make a huge difference in patient outcomes. Early detection often leads to better prognosis and more effective treatment plans.
Staying informed about the latest research and advancements in this area is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. Knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and treatment options.
Remember, if you or a loved one is facing a diagnosis of small uncloven cell lymphoma, seek out specialists and support groups. They can provide valuable resources and emotional support.
By spreading awareness and understanding, we can improve the lives of those affected by this condition. Stay proactive, stay informed, and never hesitate to ask questions or seek second opinions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
