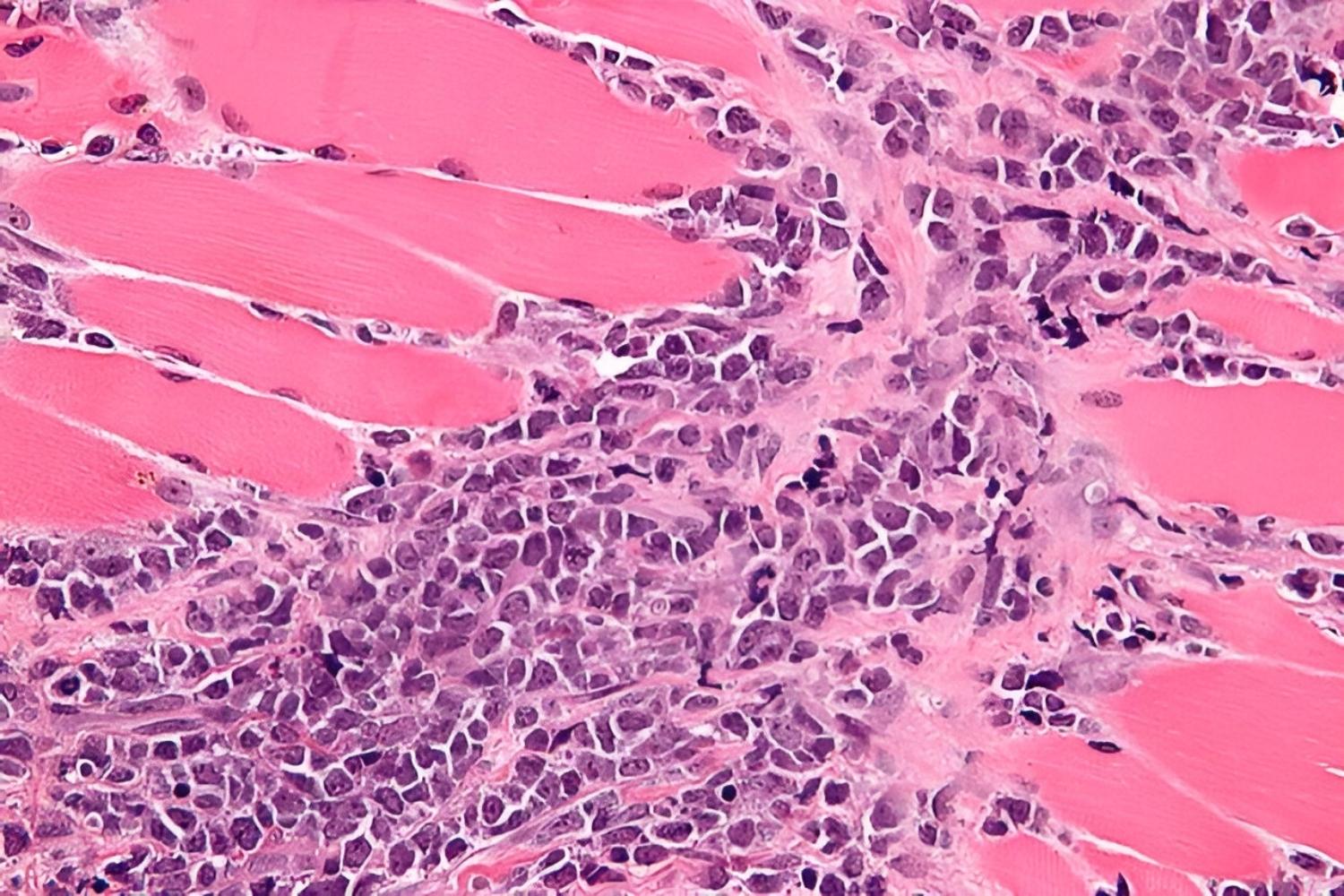
Primary Granulocytic Sarcoma might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it is crucial. This rare type of cancer, also known as chloroma, involves the formation of a tumor made up of immature white blood cells called myeloblasts. These tumors can appear in various parts of the body, including the skin, bones, and lymph nodes. Often associated with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), it can sometimes be the first sign of this blood cancer. Early detection and treatment are vital for better outcomes. Here, we’ll dive into 25 essential facts about this condition to help you grasp its complexities and significance.
Key Takeaways:
- Primary Granulocytic Sarcoma is a rare cancer linked to acute myeloid leukemia. Early diagnosis and chemotherapy are crucial for better survival rates.
- Ongoing research and new treatments offer hope for patients with Primary Granulocytic Sarcoma. Regular follow-ups and support groups are essential for managing the condition.
What is Primary Granulocytic Sarcoma?
Primary Granulocytic Sarcoma, also known as chloroma, is a rare type of cancer. It involves the formation of a solid tumor composed of immature white blood cells called myeloblasts. This condition can occur in various parts of the body, often preceding or coinciding with acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
-
Primary Granulocytic Sarcoma is rare. This type of cancer is uncommon, making up less than 1% of all AML cases.
-
It can appear anywhere in the body. Tumors can form in bones, skin, lymph nodes, or other tissues.
-
Often linked to AML. Many patients with this sarcoma either have or will develop acute myeloid leukemia.
Symptoms of Primary Granulocytic Sarcoma
Recognizing the symptoms can be challenging due to its rarity and varied presentation. Here are some common signs to watch for.
-
Localized pain or swelling. Tumors can cause discomfort or visible swelling in affected areas.
-
Skin lesions. Sometimes, the sarcoma manifests as skin nodules or rashes.
-
Bone pain. When tumors form in bones, they can cause significant pain and discomfort.
Diagnosis of Primary Granulocytic Sarcoma
Diagnosing this condition requires a combination of imaging studies and biopsies. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment.
-
Biopsy is essential. A tissue sample is needed to confirm the presence of myeloblasts.
-
Imaging studies help locate tumors. MRI, CT scans, and PET scans are commonly used.
-
Blood tests may show abnormalities. While not definitive, blood tests can indicate potential issues.
Treatment Options for Primary Granulocytic Sarcoma
Treatment typically involves chemotherapy, similar to that used for AML. Here are some common approaches.
-
Chemotherapy is the mainstay. Drugs used for AML are often effective against this sarcoma.
-
Radiation therapy can be used. In some cases, radiation helps shrink tumors.
-
Stem cell transplant is an option. For some patients, a stem cell transplant may be recommended.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for Primary Granulocytic Sarcoma varies based on several factors, including the patient’s overall health and response to treatment.
-
Early diagnosis improves outcomes. Catching the disease early can lead to better survival rates.
-
Prognosis is linked to AML. Patients with concurrent AML generally have a poorer prognosis.
-
Survival rates vary widely. Depending on treatment response, survival rates can range significantly.
Research and Advances
Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of this rare cancer. Here are some recent developments.
-
New drugs are being tested. Clinical trials are exploring novel chemotherapy agents.
-
Genetic studies offer insights. Research into genetic mutations helps tailor treatments.
-
Immunotherapy shows promise. Emerging therapies aim to harness the immune system against cancer cells.
Living with Primary Granulocytic Sarcoma
Managing life with this condition involves medical treatment and emotional support. Here are some tips for patients and caregivers.
-
Regular follow-ups are crucial. Continuous monitoring helps manage the disease.
-
Support groups can help. Connecting with others facing similar challenges provides emotional support.
-
Healthy lifestyle aids recovery. Proper nutrition and exercise can improve overall well-being.
Pediatric Cases of Primary Granulocytic Sarcoma
Though rare, children can also develop this type of sarcoma. Pediatric cases require specialized care.
-
Pediatric cases are rarer. This sarcoma is even less common in children than adults.
-
Treatment protocols differ. Children often receive different chemotherapy regimens.
-
Long-term monitoring is needed. Pediatric patients require extended follow-up to monitor for recurrence.
Importance of Awareness
Raising awareness about Primary Granulocytic Sarcoma can lead to earlier diagnosis and better outcomes. Here’s why it matters.
- Awareness leads to early detection. Educating healthcare providers and the public can help identify cases sooner.
Final Thoughts on Primary Granulocytic Sarcoma
Primary Granulocytic Sarcoma, also known as chloroma, is a rare and aggressive tumor. It often precedes or accompanies acute myeloid leukemia. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Symptoms can vary widely, making it tricky to identify. Common signs include lumps, pain, or neurological issues, depending on the tumor's location. Treatment usually involves chemotherapy, radiation, or a combination of both. Sometimes, surgery is necessary to remove the tumor. Despite its rarity, awareness is growing, leading to better outcomes for patients. Research continues to improve understanding and treatment options. If you or someone you know shows symptoms, consult a healthcare professional immediately. Early intervention can make a significant difference. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and support ongoing research efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
