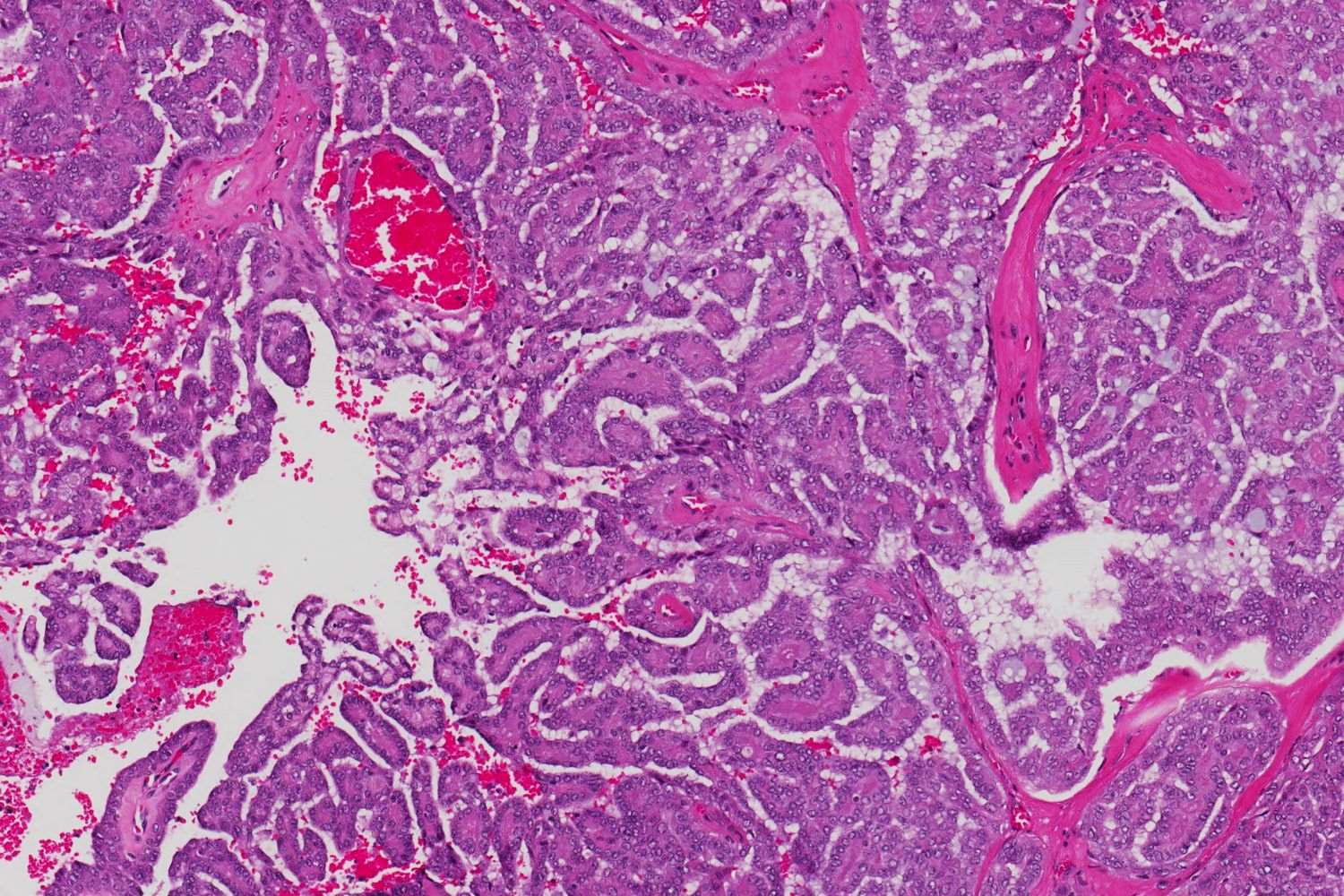
Polymorphous Low-Grade Adenocarcinoma (PLGA) is a rare type of cancer that primarily affects the salivary glands. What makes PLGA unique? This cancer grows slowly and has a low potential for spreading to other parts of the body. Who is at risk? PLGA often occurs in middle-aged adults, but it can affect people of any age. Where does it usually develop? Most cases are found in the minor salivary glands, particularly in the palate. How is it treated? Surgery is the most common treatment, sometimes followed by radiation therapy. Why is early detection important? Catching PLGA early can significantly improve the outcome. Want to know more? Keep reading to uncover 25 fascinating facts about this uncommon yet important condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Polymorphous Low-Grade Adenocarcinoma (PLGA) is a rare, slow-growing cancer that mostly affects the salivary glands. Early detection and surgical removal are crucial for a good prognosis.
- PLGA has a low recurrence rate and rare metastasis, with ongoing research focusing on genetic studies and new treatment options. Regular follow-up care is essential for long-term survival.
Understanding Polymorphous Low-Grade Adenocarcinoma
Polymorphous Low-Grade Adenocarcinoma (PLGA) is a rare type of cancer that primarily affects the salivary glands. Despite its rarity, understanding this condition is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Here are some essential facts about PLGA.
- PLGA is a rare cancer: It accounts for less than 2% of all salivary gland tumors.
- First identified in 1983: PLGA was first described in medical literature in 1983.
- Common in minor salivary glands: It most frequently occurs in the minor salivary glands, particularly in the palate.
- Slow-growing tumor: PLGA typically grows slowly, which can delay diagnosis.
- Low-grade malignancy: It is considered a low-grade malignancy, meaning it has a lower potential to spread compared to other cancers.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the diagnostic process can help in managing PLGA effectively. Here are some key points.
- Painless mass: The most common symptom is a painless mass in the mouth.
- Difficulty swallowing: Some patients may experience difficulty swallowing or a feeling of fullness in the throat.
- Biopsy for diagnosis: A biopsy is essential for diagnosing PLGA, as imaging alone cannot confirm it.
- Histopathological examination: The biopsy sample is examined under a microscope to identify characteristic features of PLGA.
- Immunohistochemistry: This technique helps differentiate PLGA from other types of salivary gland tumors.
Treatment Options
Treatment for PLGA usually involves surgery, but other methods may also be considered. Here are some treatment-related facts.
- Surgical excision: The primary treatment is surgical removal of the tumor.
- Wide local excision: Surgeons often perform a wide local excision to ensure complete removal.
- Radiation therapy: In some cases, radiation therapy may be used post-surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Chemotherapy is rare: Chemotherapy is rarely used for PLGA due to its low-grade nature.
- Follow-up care: Regular follow-up is crucial to monitor for any signs of recurrence.
Prognosis and Recurrence
Understanding the prognosis and potential for recurrence can help patients and caregivers manage expectations and plan for the future.
- Good prognosis: PLGA generally has a good prognosis with appropriate treatment.
- Low recurrence rate: The recurrence rate is relatively low compared to other salivary gland cancers.
- Long-term survival: Many patients achieve long-term survival following treatment.
- Metastasis is rare: Metastasis, or the spread of cancer to other parts of the body, is rare in PLGA.
- Importance of early detection: Early detection and treatment are key to improving outcomes.
Research and Developments
Ongoing research continues to improve our understanding of PLGA and develop better treatment options. Here are some recent developments.
- Genetic studies: Researchers are studying the genetic mutations associated with PLGA to develop targeted therapies.
- Molecular markers: Identifying molecular markers can help in the early diagnosis and differentiation of PLGA from other tumors.
- New surgical techniques: Advances in surgical techniques aim to reduce complications and improve recovery times.
- Immunotherapy potential: Although not yet standard, immunotherapy is being explored as a potential treatment for PLGA.
- Patient registries: Establishing patient registries helps collect data to improve understanding and management of PLGA.
Final Thoughts on Polymorphous Low-Grade Adenocarcinoma
Polymorphous Low-Grade Adenocarcinoma (PLGA) is a rare type of cancer that primarily affects the salivary glands. Understanding its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options can help in early detection and better management. Key symptoms include painless swelling, difficulty swallowing, and changes in speech. Diagnosis often involves imaging tests and biopsies. Treatment usually includes surgery, radiation therapy, or a combination of both. Early detection significantly improves the prognosis, making regular check-ups essential for those at risk. Awareness and education about PLGA can lead to timely medical intervention, potentially saving lives. Stay informed and consult healthcare professionals if you notice any unusual symptoms. Knowledge is power when it comes to managing health conditions like PLGA.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
