Poikiloderma Hereditary Acrokeratosis Weary Type might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it doesn't have to be complicated. This rare genetic disorder affects the skin, leading to changes in color, texture, and thickness. Symptoms often appear in early childhood, making early diagnosis crucial. Key features include reddish-brown skin patches, atrophy, and telangiectasia, primarily on the hands and feet. While it might seem daunting, knowing the facts can help manage the condition better. In this post, we'll break down 25 essential facts about Poikiloderma Hereditary Acrokeratosis Weary Type, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and management strategies.
Key Takeaways:
- Poikiloderma Hereditary Acrokeratosis Weary Type is a rare genetic skin disorder causing pigmentation changes, thin skin, and visible blood vessels. Early diagnosis and proper care can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Individuals with Poikiloderma Hereditary Acrokeratosis Weary Type can lead fulfilling lives with sun protection, regular monitoring, and support networks. Ongoing research aims to develop more effective treatments for this rare genetic condition.
What is Poikiloderma Hereditary Acrokeratosis Weary Type?
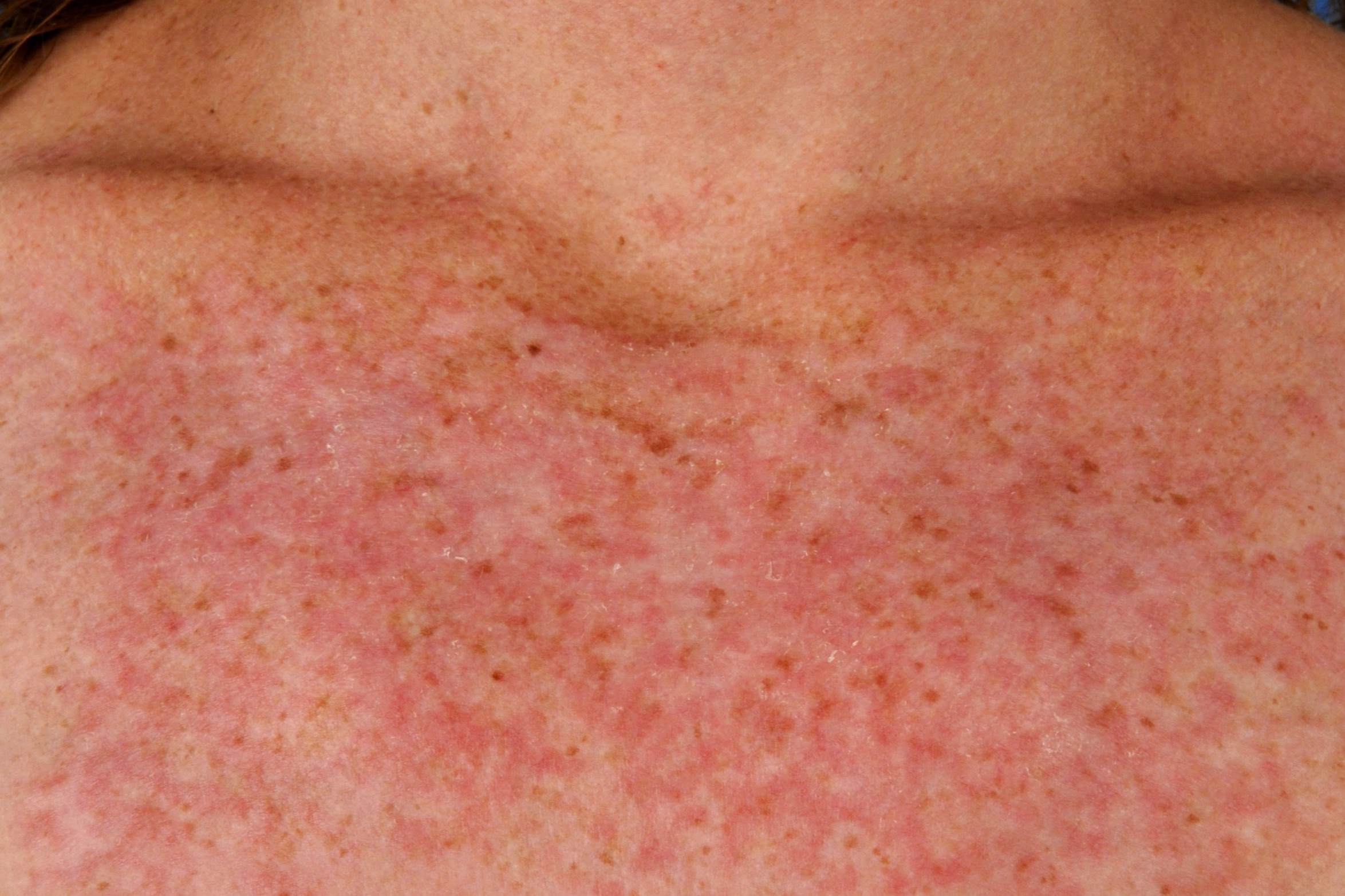
Poikiloderma Hereditary Acrokeratosis Weary Type is a rare genetic disorder. It affects the skin, causing a mix of pigmentation changes, atrophy, and telangiectasia. This condition is also known as Weary Syndrome.
-
Genetic Basis: This disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. A single copy of the altered gene in each cell is enough to cause the condition.
-
Skin Changes: Individuals with this condition often have skin that appears mottled or patchy. These changes usually start in childhood.
-
Atrophy: The skin may become thin and fragile, leading to easy bruising and tearing.
-
Telangiectasia: Small blood vessels become visible on the skin, giving it a reddish appearance.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can help in managing the condition better. Diagnosis usually involves a combination of clinical evaluation and genetic testing.
-
Early Onset: Symptoms typically appear in early childhood, often before the age of 5.
-
Photosensitivity: Affected individuals may have increased sensitivity to sunlight, leading to sunburns and further skin damage.
-
Nail Abnormalities: Nails may be thickened, ridged, or abnormally shaped.
-
Hair Changes: Some individuals may experience hair thinning or loss, particularly on the scalp.
-
Eye Involvement: In rare cases, the eyes may be affected, leading to vision problems.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for Poikiloderma Hereditary Acrokeratosis Weary Type, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Sun Protection: Using sunscreen and protective clothing can help prevent further skin damage.
-
Topical Treatments: Creams and ointments may be prescribed to manage skin symptoms and promote healing.
-
Laser Therapy: In some cases, laser treatments can reduce the appearance of telangiectasia.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups with a dermatologist are essential to monitor skin changes and manage symptoms.
-
Genetic Counseling: Families may benefit from genetic counseling to understand the inheritance pattern and risks for future generations.
Impact on Daily Life
Living with Poikiloderma Hereditary Acrokeratosis Weary Type can present challenges, but with proper care, individuals can lead fulfilling lives.
-
Psychological Support: Counseling or support groups can help individuals cope with the emotional impact of the condition.
-
Adaptive Clothing: Wearing soft, non-irritating fabrics can reduce skin irritation and discomfort.
-
Hydration: Keeping the skin well-moisturized can help manage dryness and atrophy.
-
Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall skin health.
-
Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding environmental triggers, such as harsh soaps or extreme temperatures, can prevent flare-ups.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand the genetic basis of the condition and develop more effective treatments.
-
Gene Therapy: Scientists are exploring the potential of gene therapy to correct the underlying genetic mutation.
-
New Medications: Research is underway to develop new medications that target specific symptoms of the condition.
-
Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments and contribute to scientific knowledge.
-
Patient Registries: Registries help researchers collect data on affected individuals, leading to better understanding and management of the condition.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Raising awareness about Poikiloderma Hereditary Acrokeratosis Weary Type can lead to earlier diagnosis and better support for affected individuals.
-
Support Networks: Building a strong support network of healthcare providers, family, and friends is crucial for managing the condition effectively.
Final Thoughts on Poikiloderma Hereditary Acrokeratosis Weary Type
Poikiloderma Hereditary Acrokeratosis Weary Type is a rare genetic disorder that affects the skin, causing a mix of hyperpigmentation, hypopigmentation, and telangiectasia. Understanding this condition helps in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Early diagnosis and treatment can make a significant difference. Genetic counseling is crucial for families affected by this disorder. Staying informed about the latest research and treatments can provide hope and better outcomes. Remember, while it’s a challenging condition, support from healthcare professionals and loved ones can make the journey easier. If you or someone you know is dealing with Poikiloderma Hereditary Acrokeratosis Weary Type, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice and support. Knowledge and awareness are powerful tools in managing any health condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
