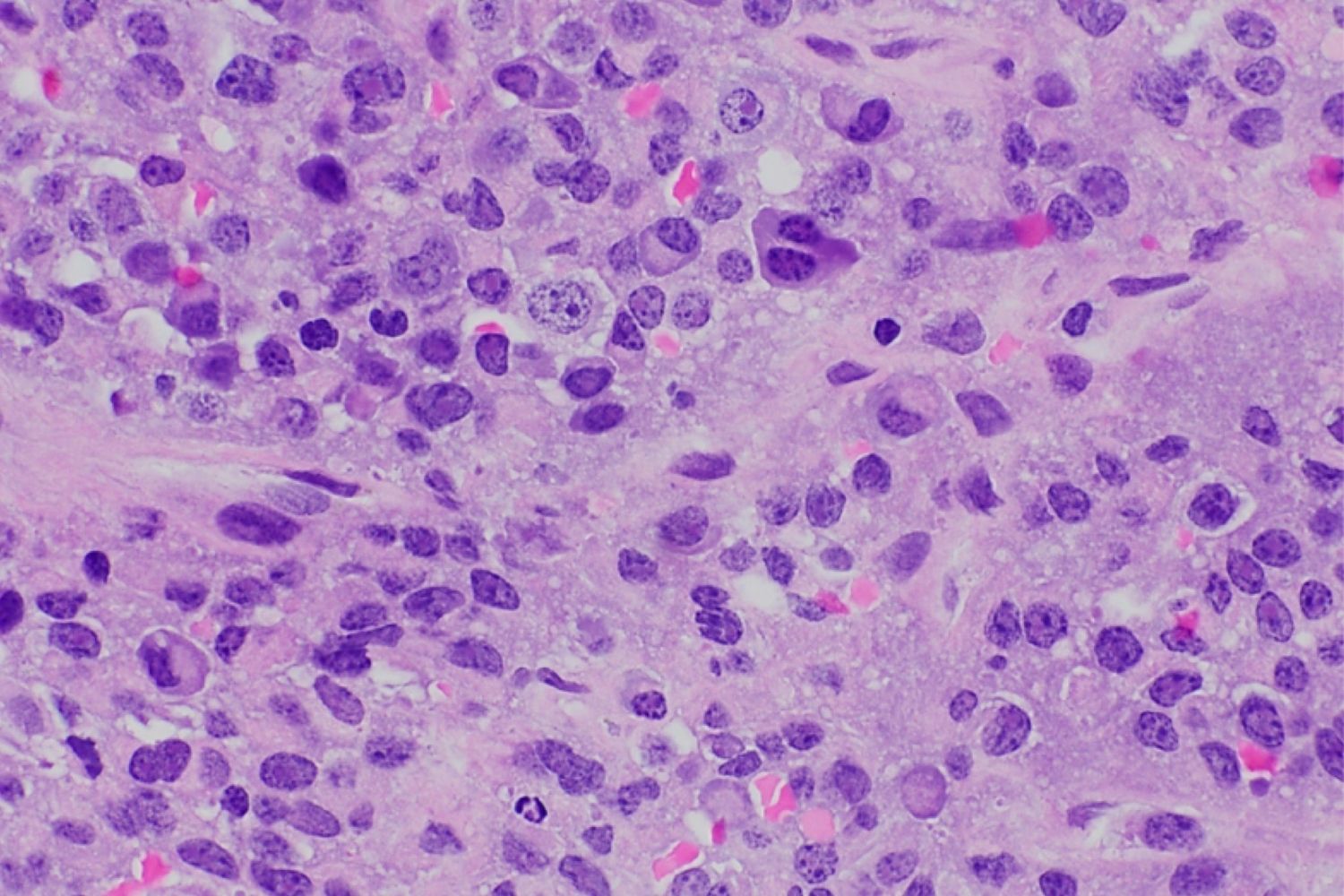
Plasmacytoma Anaplastic is a rare type of cancer that affects plasma cells, which are a type of white blood cell. These cells are crucial for producing antibodies to fight infections. When they become cancerous, they form tumors called plasmacytomas. Anaplastic means that the cancer cells look very different from normal cells and tend to grow and spread more aggressively. This condition can occur in bones or soft tissues and often requires a combination of treatments like radiation, chemotherapy, or surgery. Understanding the basics of this disease can help in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate medical care.
Key Takeaways:
- Plasmacytoma Anaplastic is a rare cancer that affects plasma cells. It can cause bone pain, fractures, and infections. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for better outcomes.
- Treatment options include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, stem cell transplants, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Awareness of risk factors can help in early detection and prevention.
What is Plasmacytoma Anaplastic?
Plasmacytoma anaplastic is a rare type of cancer that originates from plasma cells. These cells are a type of white blood cell responsible for producing antibodies. Understanding this disease can help in recognizing symptoms and seeking timely treatment.
-
Plasmacytoma anaplastic is a subtype of multiple myeloma. It is characterized by the presence of abnormal plasma cells in the bone marrow or other tissues.
-
This cancer is rare. It accounts for less than 5% of all plasma cell neoplasms.
-
Symptoms often include bone pain. Patients may also experience fractures, fatigue, and frequent infections.
-
Diagnosis typically involves blood tests. Imaging studies and bone marrow biopsies are also used to confirm the presence of abnormal plasma cells.
-
The exact cause is unknown. However, genetic mutations and environmental factors may play a role.
How is Plasmacytoma Anaplastic Treated?
Treatment options for plasmacytoma anaplastic vary depending on the stage and location of the cancer. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for better outcomes.
-
Radiation therapy is a common treatment. It targets and destroys cancerous cells in localized plasmacytoma.
-
Chemotherapy is often used. This treatment helps to kill or slow the growth of cancer cells.
-
Stem cell transplants may be considered. This procedure involves replacing damaged bone marrow with healthy cells.
-
Targeted therapy is an option. It uses drugs that specifically attack cancer cells without harming normal cells.
-
Immunotherapy is being explored. This treatment boosts the body's immune system to fight cancer.
What are the Risk Factors?
Certain factors may increase the likelihood of developing plasmacytoma anaplastic. Awareness of these can help in early detection and prevention.
-
Age is a significant risk factor. Most cases occur in individuals over 60 years old.
-
Gender plays a role. Men are more likely to develop this cancer than women.
-
Family history matters. Having a close relative with multiple myeloma or other plasma cell disorders increases risk.
-
Exposure to radiation. High levels of radiation exposure can increase the risk of developing plasmacytoma anaplastic.
-
Certain chemicals are linked. Exposure to chemicals like benzene may elevate the risk.
What are the Complications?
Plasmacytoma anaplastic can lead to various complications, affecting the patient's quality of life. Understanding these can help in managing the disease better.
-
Bone fractures are common. Weakened bones due to cancer can easily break.
-
Kidney damage may occur. Abnormal proteins produced by cancer cells can harm the kidneys.
-
Infections are frequent. The immune system is compromised, making patients more susceptible to infections.
-
Anemia is a concern. The disease can reduce red blood cell production, leading to fatigue and weakness.
-
Hypercalcemia can develop. High calcium levels in the blood can cause nausea, vomiting, and confusion.
How is Plasmacytoma Anaplastic Diagnosed?
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Various tests and procedures are used to identify plasmacytoma anaplastic.
-
Blood tests are crucial. They help detect abnormal proteins and calcium levels.
-
Imaging studies are used. X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans can reveal bone lesions and tumors.
-
Bone marrow biopsy is definitive. This procedure involves extracting a sample of bone marrow to examine for cancer cells.
-
Urine tests can help. They detect abnormal proteins produced by cancer cells.
-
Genetic testing is sometimes performed. It identifies specific mutations associated with the disease.
Final Thoughts on Plasmacytoma Anaplastic
Plasmacytoma anaplastic is a rare, aggressive form of cancer that originates in plasma cells. Understanding its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for managing the disease effectively. Early detection can significantly improve outcomes, so staying informed about potential warning signs is vital. Treatment often involves a combination of radiation, chemotherapy, and sometimes surgery, tailored to the individual's specific condition.
Research continues to evolve, offering hope for better therapies and improved survival rates. If you or someone you know is affected by plasmacytoma anaplastic, seeking support from healthcare professionals and connecting with patient communities can provide valuable resources and emotional support. Knowledge is power, and staying educated about this condition can make a significant difference in navigating the challenges it presents. Stay proactive, stay informed, and never hesitate to seek help when needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
