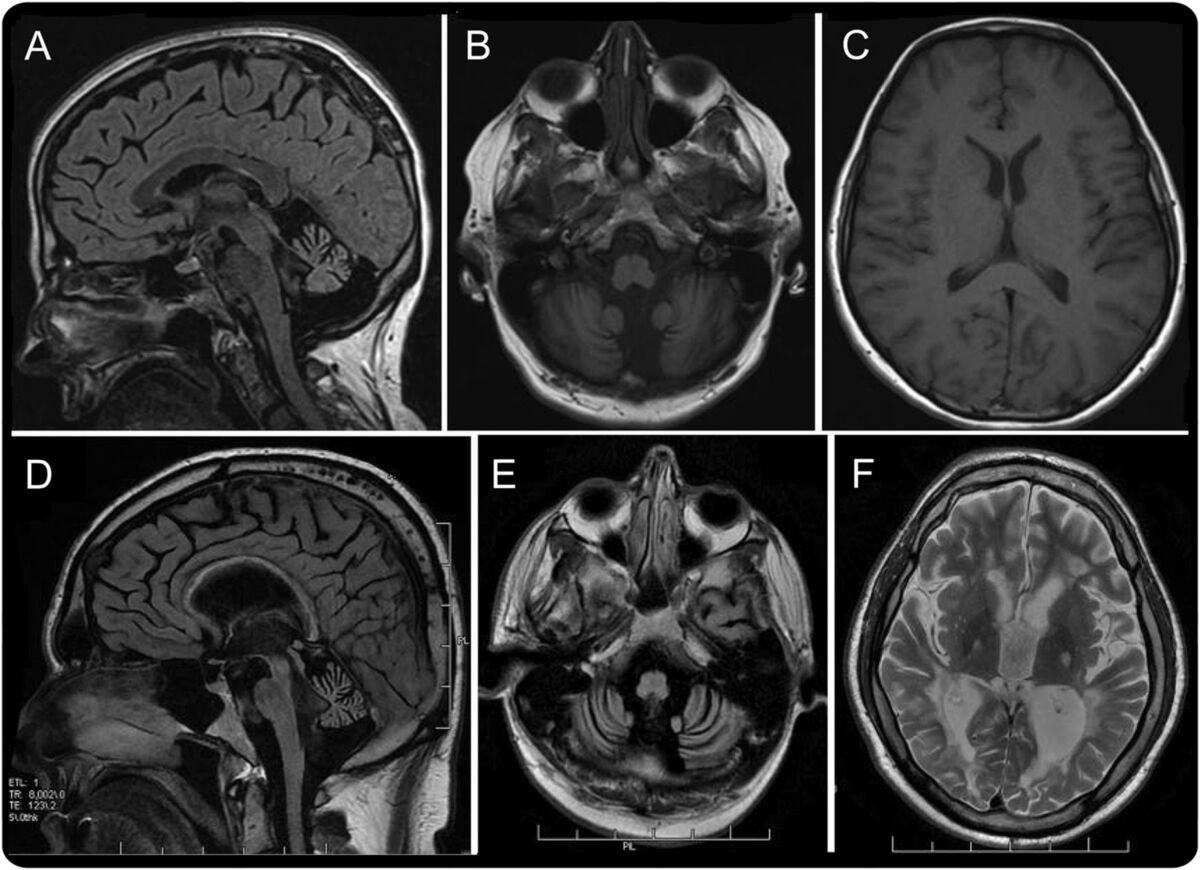
Peroxisomal Bifunctional Enzyme Deficiency is a rare genetic disorder that affects the body's ability to break down certain fatty acids. This condition can lead to severe health problems, including developmental delays, muscle weakness, and liver dysfunction. Caused by mutations in the HSD17B4 gene, this deficiency disrupts normal peroxisome function, which is crucial for cellular metabolism. Symptoms often appear in infancy and can vary widely in severity. Early diagnosis and intervention are essential for managing the symptoms and improving the quality of life for affected individuals. Understanding the complexities of this disorder can help families and healthcare providers better navigate the challenges it presents.
Key Takeaways:
- Peroxisomal Bifunctional Enzyme Deficiency (PBD) is a rare genetic disorder affecting the body's ability to break down certain fats, leading to severe health problems and developmental delays.
- While there is no cure for PBD, various treatments such as dietary management, medications, and physical therapy can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of this condition.
What is Peroxisomal Bifunctional Enzyme Deficiency?
Peroxisomal Bifunctional Enzyme Deficiency (PBD) is a rare genetic disorder affecting the body's ability to break down certain fats. This condition can lead to severe health problems, including developmental delays, neurological issues, and organ dysfunction. Here are some key facts about this condition.
-
PBD is a genetic disorder: It is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning both parents must carry the defective gene for a child to be affected.
-
Caused by mutations: Mutations in the HSD17B4 gene are responsible for PBD. This gene provides instructions for making an enzyme crucial for breaking down fatty acids.
-
Part of Zellweger spectrum disorders: PBD is one of several conditions within the Zellweger spectrum, which also includes Zellweger syndrome and neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy.
-
Affects peroxisomes: Peroxisomes are small structures within cells that help break down fatty acids and detoxify harmful substances. PBD impairs their function.
-
Symptoms appear early: Symptoms often manifest in infancy or early childhood, including poor muscle tone, feeding difficulties, and developmental delays.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how PBD is diagnosed can help in early detection and management. Here are some important points to consider.
-
Neurological symptoms: Children with PBD may experience seizures, hearing loss, and vision problems due to the buildup of toxic substances in the brain.
-
Liver dysfunction: The liver may become enlarged and function poorly, leading to jaundice and other complications.
-
Skeletal abnormalities: Some children may have distinctive facial features and skeletal abnormalities, such as a high forehead and broad nasal bridge.
-
Blood tests: Elevated levels of very long-chain fatty acids in the blood can indicate PBD.
-
Genetic testing: Confirming the diagnosis often involves genetic testing to identify mutations in the HSD17B4 gene.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for PBD, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some approaches used in managing this condition.
-
Dietary management: A special diet low in very long-chain fatty acids can help reduce the buildup of toxic substances.
-
Medications: Anti-seizure medications can help control seizures, while other drugs may be used to manage liver dysfunction and other symptoms.
-
Physical therapy: Physical and occupational therapy can help improve muscle tone and coordination.
-
Hearing aids: For children with hearing loss, hearing aids or cochlear implants can improve communication and quality of life.
-
Regular monitoring: Regular check-ups with a team of specialists, including neurologists, hepatologists, and geneticists, are essential for managing the condition.
Prognosis and Research
The prognosis for children with PBD varies widely, and ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of this condition. Here are some key points about prognosis and research efforts.
-
Variable prognosis: The severity of PBD can vary, with some children experiencing severe symptoms and others having milder forms of the disease.
-
Life expectancy: Life expectancy can be significantly reduced, particularly in severe cases, but some individuals with milder forms may live into adulthood.
-
Supportive care: Providing supportive care, including nutritional support and managing infections, can improve quality of life and outcomes.
-
Research efforts: Scientists are studying the underlying mechanisms of PBD and exploring potential treatments, including gene therapy and enzyme replacement therapy.
-
Clinical trials: Participation in clinical trials can provide access to new treatments and contribute to advancing knowledge about PBD.
Living with PBD
Living with PBD presents unique challenges for affected individuals and their families. Here are some important considerations for daily life.
-
Support networks: Connecting with support groups and other families affected by PBD can provide emotional support and practical advice.
-
Educational support: Children with PBD may require special education services and individualized education plans to support their learning and development.
-
Adaptive equipment: Using adaptive equipment, such as wheelchairs and communication devices, can enhance independence and quality of life.
-
Mental health: Addressing the mental health needs of both the affected individual and their family members is crucial for overall well-being.
-
Advocacy: Advocating for awareness, research funding, and access to care can help improve outcomes for individuals with PBD and their families.
Final Thoughts on Peroxisomal Bifunctional Enzyme Deficiency
Peroxisomal Bifunctional Enzyme Deficiency (PBD) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the body's ability to break down certain fatty acids. This condition can lead to severe developmental and neurological issues. Understanding PBD is crucial for early diagnosis and management. Genetic testing plays a key role in identifying this disorder, allowing for better care and support for affected individuals and their families. While there's no cure, treatments focus on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Research continues to explore potential therapies and interventions. Awareness and education about PBD can help in providing timely medical attention and support. By staying informed, we can contribute to better outcomes for those living with this challenging condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
