Otodental syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects both the ears and teeth. Ever wondered why some people have unusually large teeth or hearing issues? This condition might be the answer. Otodental syndrome often leads to macrodontia, where teeth grow larger than normal, and can cause hearing loss due to abnormalities in the inner ear. It's caused by mutations in the FGF3 gene, which plays a crucial role in the development of teeth and ears. Though rare, understanding this syndrome can help in early diagnosis and management. Let's dive into 25 intriguing facts about Otodental syndrome that will shed light on this unique condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Otodental Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder affecting teeth and ears, causing dental anomalies and hearing loss. It requires early intervention, regular check-ups, and emotional support for individuals and families.
- Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis of Otodental Syndrome, while dental X-rays and audiometric tests are crucial for identifying tooth anomalies and assessing hearing loss. Regular dental check-ups and orthodontic treatment are essential for managing the condition effectively.
What is Otodental Syndrome?
Otodental Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder affecting teeth and ears. It can cause significant dental anomalies and hearing loss. Let's explore some fascinating facts about this condition.
-
Otodental Syndrome is extremely rare, with only a few documented cases worldwide. This rarity makes it a subject of interest for genetic researchers.
-
The condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning only one copy of the altered gene is necessary for a person to be affected. This can lead to a 50% chance of passing it to offspring.
-
Mutations in the FGF3 gene are responsible for Otodental Syndrome. This gene plays a crucial role in the development of teeth and ears.
-
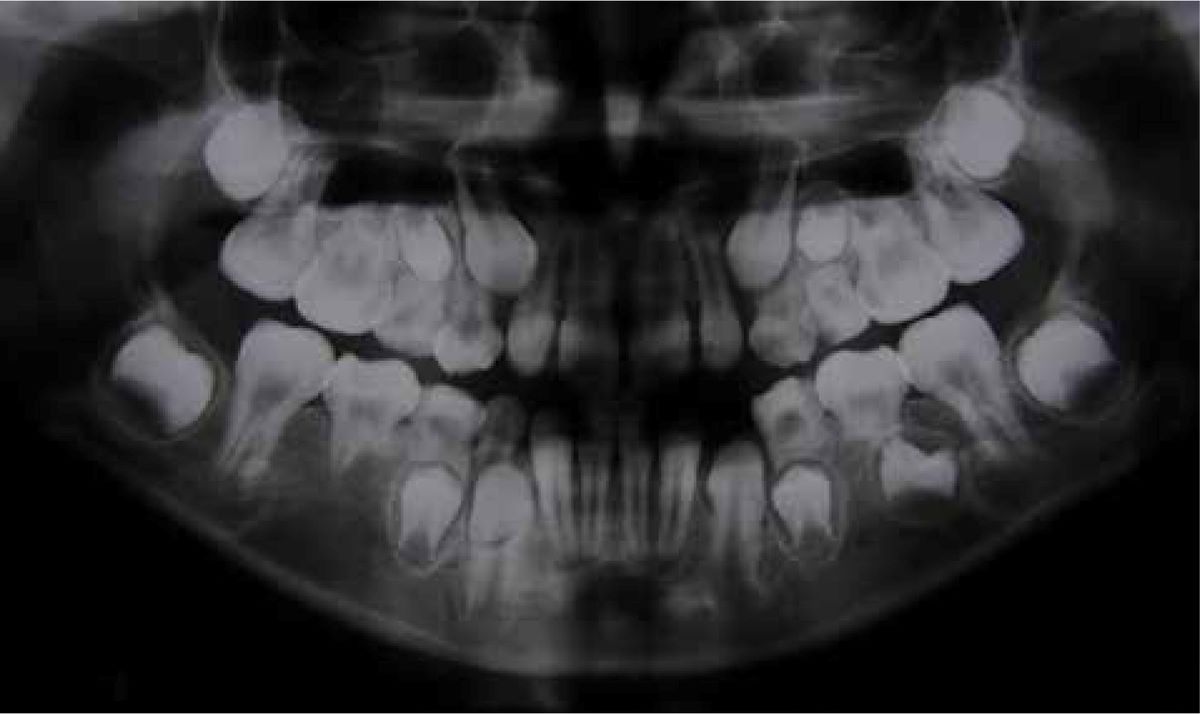
Individuals with Otodental Syndrome often have globodontia, a condition where teeth are abnormally large and bulbous. This can affect both primary and permanent teeth.
-
Hearing loss is a common symptom, often due to abnormalities in the inner ear structures. This can range from mild to severe.
Dental Anomalies in Otodental Syndrome
The dental issues associated with Otodental Syndrome are quite distinctive. Here are some key facts about these anomalies.
-
Globodontia affects the molars and canines most severely, making them appear globular or spherical. This unusual shape can cause difficulties in chewing and speaking.
-
Teeth may have multiple cusps, which are the pointed parts on the chewing surface. This can lead to an irregular bite and increased wear on the teeth.
-
Enamel hypoplasia is common, where the enamel is underdeveloped or thin. This can make teeth more susceptible to decay and damage.
-
Delayed eruption of teeth is often observed, meaning teeth come in later than usual. This can affect both primary and permanent teeth.
-
Dental crowding can occur, where there isn't enough space for all the teeth to fit properly. This may require orthodontic treatment.
Hearing Loss and Ear Anomalies
Hearing issues are another significant aspect of Otodental Syndrome. Let's delve into some facts about these auditory challenges.
-
Conductive hearing loss is prevalent, caused by problems in the middle ear. This can often be managed with hearing aids or surgery.
-
Sensorineural hearing loss can also occur, due to inner ear or nerve damage. This type of hearing loss is usually permanent.
-
Abnormalities in the cochlea, the spiral-shaped part of the inner ear, are common. This can affect the ability to hear high-frequency sounds.
-
Eustachian tube dysfunction may be present, leading to frequent ear infections and fluid buildup in the middle ear.
-
Some individuals may have malformed pinnae, the outer part of the ear. This can affect the overall appearance and function of the ear.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing and managing Otodental Syndrome involves a multidisciplinary approach. Here are some important facts about diagnosis and treatment.
-
Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis, identifying mutations in the FGF3 gene. This helps in understanding the inheritance pattern and planning for future pregnancies.
-
Dental X-rays are crucial for identifying the characteristic tooth anomalies. These images help in planning appropriate dental treatments.
-
Audiometric tests assess hearing loss, determining the type and severity. This information guides the choice of hearing aids or other interventions.
-
Regular dental check-ups are essential, as individuals with Otodental Syndrome are prone to cavities and other dental issues. Preventive care can help maintain oral health.
-
Orthodontic treatment may be necessary to address dental crowding and misalignment. Braces or other devices can improve the bite and appearance of teeth.
Living with Otodental Syndrome
Living with Otodental Syndrome can be challenging, but with proper care, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some facts about daily life with this condition.
-
Early intervention is key, especially for hearing loss. The sooner hearing aids or other treatments are provided, the better the outcomes for speech and language development.
-
Speech therapy can be beneficial, particularly for children. This helps in overcoming any speech delays or difficulties caused by hearing loss.
-
Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support, helping individuals and families cope with the challenges of the condition.
-
Educational accommodations may be necessary, such as seating arrangements in classrooms to optimize hearing or extra time for assignments.
-
Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure that any new issues are promptly addressed. This multidisciplinary care approach helps manage the condition effectively.
Final Thoughts on Otodental Syndrome
Otodental syndrome, a rare genetic disorder, affects both dental and ear development. Characterized by globodontia—unusually large, globe-shaped teeth—and hearing loss, this condition often requires specialized medical and dental care. Early diagnosis can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Genetic counseling is crucial for families affected by this syndrome, offering insights into inheritance patterns and future risks. While treatment focuses on symptom management, ongoing research aims to better understand the underlying genetic causes. Awareness and education about otodental syndrome can lead to earlier detection and better support for those affected. If you or someone you know shows signs of this condition, consulting healthcare professionals for a comprehensive evaluation is essential. Understanding otodental syndrome empowers individuals and families to navigate its challenges more effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
