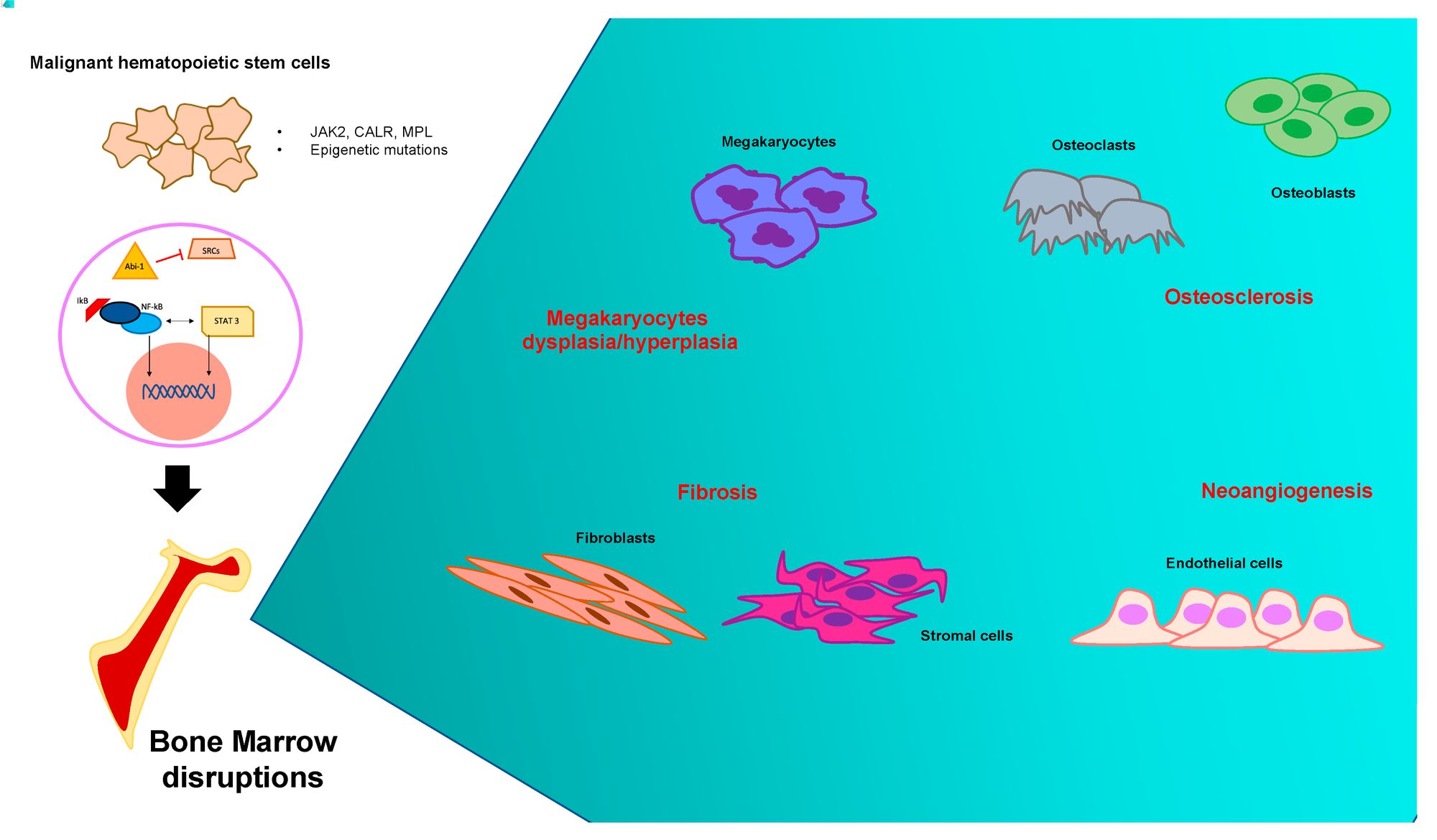
Myelofibrosis-Osteosclerosis is a rare bone marrow disorder that affects blood cell production and bone structure. Myelofibrosis causes scarring in the bone marrow, leading to severe anemia, fatigue, and an enlarged spleen. Osteosclerosis involves abnormal hardening of bone, often complicating the condition. Together, these disorders create a complex medical challenge. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatments can help manage this condition better. This post will provide 25 essential facts about Myelofibrosis-Osteosclerosis, offering insights into its impact on health, available treatments, and ongoing research. Whether you're a patient, caregiver, or curious reader, these facts aim to inform and support you.
Key Takeaways:
- Myelofibrosis-Osteosclerosis is a rare bone marrow disorder that causes fibrous tissue to replace bone marrow, leading to anemia, bone pain, and other symptoms. Genetic mutations and age are common risk factors.
- Diagnosis involves blood tests, bone marrow biopsy, genetic testing, and imaging. Treatment options include medications, blood transfusions, and supportive care to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
What is Myelofibrosis-Osteosclerosis?
Myelofibrosis-Osteosclerosis is a rare bone marrow disorder. It involves the replacement of bone marrow with fibrous tissue and the hardening of bones. This condition can lead to severe complications.
- Myelofibrosis-Osteosclerosis is a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm, a group of diseases that cause blood cells to grow abnormally in the bone marrow.
- The condition is characterized by the formation of scar tissue in the bone marrow, which disrupts normal blood cell production.
- Osteosclerosis refers to the abnormal hardening of bone, often seen in patients with myelofibrosis.
- This disorder can lead to anemia, a condition where the body doesn't have enough healthy red blood cells.
- Patients may also experience an enlarged spleen, known as splenomegaly, due to the body's attempt to produce blood cells outside the bone marrow.
Symptoms of Myelofibrosis-Osteosclerosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can help in managing the condition better. Here are some common signs to look out for.
- Fatigue is a common symptom, often due to anemia.
- Patients may experience bone pain or discomfort, particularly in the legs.
- Night sweats and fever are also reported symptoms.
- Weight loss without trying can be a sign of myelofibrosis-osteosclerosis.
- Easy bruising or bleeding can occur due to low platelet counts.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes this condition can help in its prevention and management. Here are some known causes and risk factors.
- The exact cause of myelofibrosis-osteosclerosis is unknown, but genetic mutations are believed to play a role.
- Mutations in the JAK2, CALR, and MPL genes are commonly associated with this disorder.
- Age is a significant risk factor; most patients are diagnosed after the age of 50.
- Exposure to certain chemicals, such as benzene, may increase the risk.
- Radiation exposure has also been linked to the development of myelofibrosis-osteosclerosis.
Diagnosis of Myelofibrosis-Osteosclerosis
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Here are some methods used to diagnose this condition.
- Blood tests are often the first step, checking for abnormal blood cell counts.
- A bone marrow biopsy can confirm the presence of fibrosis and osteosclerosis.
- Genetic testing may be conducted to identify mutations in specific genes.
- Imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans can help visualize bone changes.
- A physical exam, including checking for an enlarged spleen, is also essential.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some common treatments.
- Medications like ruxolitinib can help reduce spleen size and alleviate symptoms.
- Blood transfusions may be necessary for patients with severe anemia.
- Bone marrow or stem cell transplants offer a potential cure but come with significant risks.
- Radiation therapy can be used to shrink an enlarged spleen.
- Supportive care, including pain management and nutritional support, is crucial for patient well-being.
Final Thoughts on Myelofibrosis-Osteosclerosis
Myelofibrosis-Osteosclerosis is a complex condition that affects the bone marrow and bones. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help those affected manage their health better. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Regular check-ups and being aware of changes in your body can make a big difference.
While there's no cure yet, treatments like medications, blood transfusions, and sometimes bone marrow transplants can improve quality of life. Staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers ensures the best possible outcomes.
Remember, you're not alone. Support groups and resources are available to help you navigate this challenging journey. Stay proactive, seek support, and keep hope alive.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
