Microdamage in bone might sound like a tiny problem, but it plays a big role in our health. These small cracks can happen from everyday activities like walking or running. Bones are amazing because they can repair themselves, but too much damage can lead to issues like fractures. Understanding microdamage helps scientists and doctors figure out how to keep bones strong and healthy. This knowledge is especially important for athletes, older adults, and anyone who wants to maintain good bone health. Let's dive into 25 interesting facts about microdamage in bone and learn how it affects our bodies.
Key Takeaways:
- Microdamage in bones are tiny cracks that can weaken bones over time. It can result from repetitive stress and aging, but can be managed with proper nutrition and exercise.
- Detecting and treating microdamage is crucial for maintaining bone health. Advanced imaging and genetic testing can help personalize treatment plans for better bone care.
What is Microdamage in Bone?
Microdamage in bone refers to tiny cracks or fractures that occur within the bone structure. These small injuries can accumulate over time and affect bone strength and health. Understanding microdamage is crucial for maintaining bone integrity.
-
Microdamage is a natural part of bone remodeling. Bones constantly undergo cycles of damage and repair to maintain their strength and function.
-
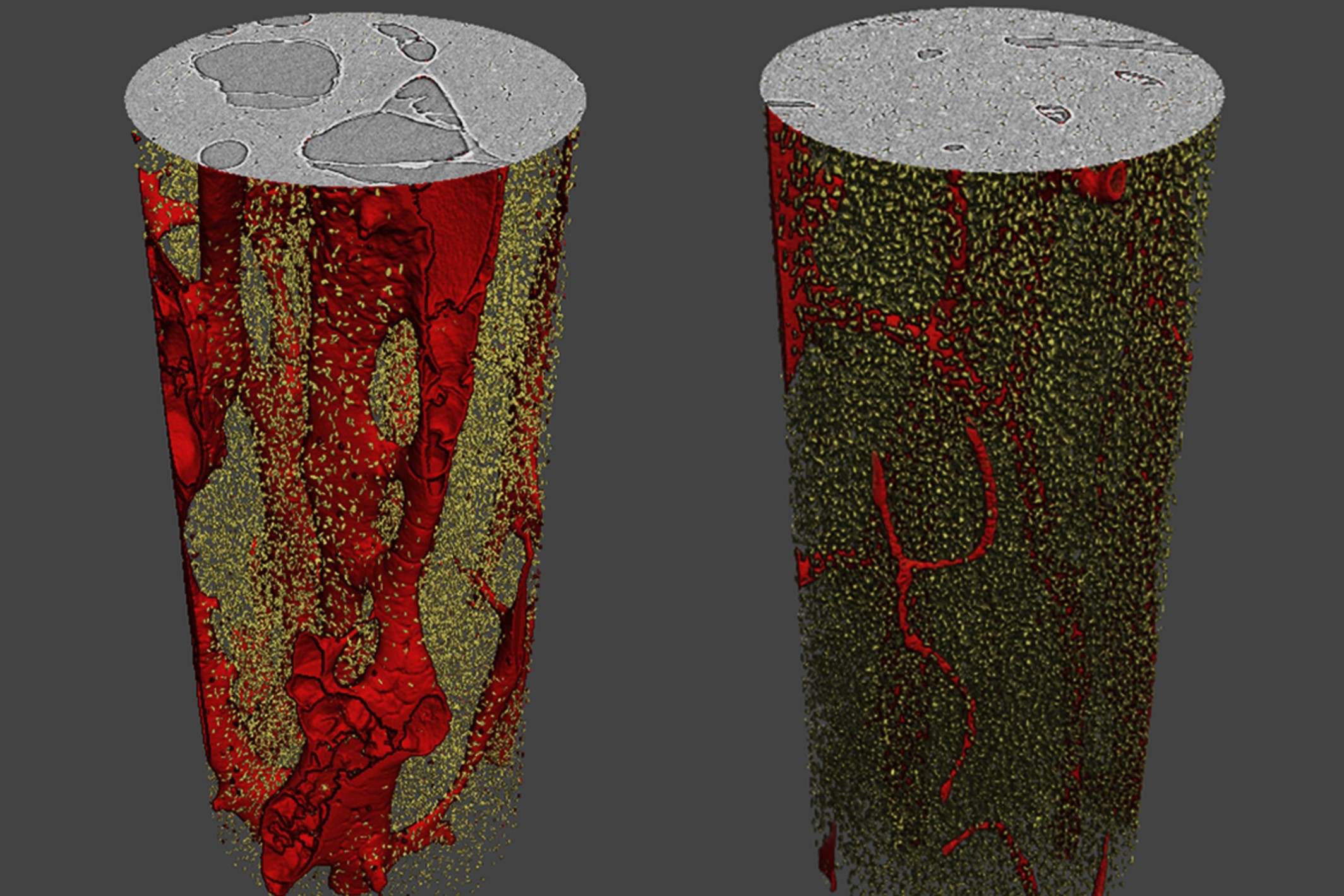
Tiny cracks in bones are often too small to be seen with the naked eye. Special imaging techniques, like micro-CT scans, are required to detect them.
-
Microdamage can result from repetitive stress. Activities like running or jumping can cause these small fractures due to repeated impact.
-
Aging increases the likelihood of microdamage. As bones become more brittle with age, they are more susceptible to tiny fractures.
-
Osteoporosis exacerbates microdamage. This condition weakens bones, making them more prone to developing microcracks.
How Does Microdamage Affect Bone Health?
Microdamage can have significant implications for overall bone health. It can weaken bones and increase the risk of fractures if not properly managed.
-
Accumulated microdamage can lead to larger fractures. If small cracks are not repaired, they can grow and cause more severe injuries.
-
Bone remodeling helps repair microdamage. The body has a natural process to replace old bone tissue with new, healthy tissue.
-
Excessive microdamage can outpace repair mechanisms. When damage occurs faster than the body can repair, bones become weaker.
-
Microdamage can affect bone density. Repeated microfractures can lead to a decrease in bone mass over time.
-
Athletes are at higher risk for microdamage. High-impact sports and intense training can increase the likelihood of developing these tiny fractures.
Detecting and Measuring Microdamage
Identifying microdamage is essential for preventing further bone injury. Various techniques and tools are used to detect and measure these small fractures.
-
Micro-CT scans provide detailed images of bone structure. This technology allows for the visualization of tiny cracks within the bone.
-
Histological analysis can reveal microdamage. Examining bone tissue under a microscope can show the presence of microcracks.
-
Bone biopsy is another method to detect microdamage. A small sample of bone tissue is taken and analyzed for signs of tiny fractures.
-
Mechanical testing assesses bone strength. By applying force to a bone sample, researchers can determine its ability to withstand stress and detect microdamage.
-
Advanced imaging techniques are continually improving. New technologies are being developed to better detect and measure microdamage in bones.
Preventing and Treating Microdamage
Preventing and treating microdamage is crucial for maintaining bone health. There are several strategies to minimize the risk and repair existing damage.
-
Adequate nutrition supports bone health. A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D can help strengthen bones and reduce the risk of microdamage.
-
Regular exercise promotes bone strength. Weight-bearing activities like walking and lifting weights can help maintain bone density.
-
Avoiding excessive stress on bones is important. Overtraining or repetitive high-impact activities can increase the risk of microdamage.
-
Medications can help manage bone health. Drugs like bisphosphonates can slow bone loss and reduce the risk of fractures.
-
Monitoring bone health is essential. Regular check-ups and bone density tests can help detect early signs of microdamage.
The Role of Genetics in Microdamage
Genetics can play a significant role in the susceptibility to microdamage. Understanding genetic factors can help in developing personalized strategies for bone health.
-
Genetic predisposition affects bone strength. Some individuals may be more prone to microdamage due to inherited traits.
-
Family history can indicate risk. If close relatives have experienced bone fractures or osteoporosis, there may be a higher risk of microdamage.
-
Genetic testing can provide insights. Tests can identify specific genes associated with bone health and susceptibility to microdamage.
-
Personalized treatment plans can be developed. Understanding genetic factors allows for tailored approaches to prevent and treat microdamage.
-
Research continues to explore genetic links. Ongoing studies aim to uncover more about how genetics influence bone health and microdamage.
The Final Word on Microdamage in Bone
Microdamage in bone is a fascinating subject. These tiny cracks, often invisible to the naked eye, play a crucial role in bone health. They help bones adapt to stress but can lead to bigger problems if not repaired. Factors like age, diet, and physical activity influence how bones handle microdamage. Understanding this helps in preventing fractures and maintaining strong bones.
Researchers continue to study microdamage to find better ways to treat and prevent bone-related issues. Advances in technology allow for more detailed analysis, leading to improved treatments. Staying informed about bone health and microdamage can make a big difference in overall well-being.
Remember, healthy bones are essential for a healthy life. Keep an eye on your diet, stay active, and consult healthcare professionals for advice on maintaining bone health. Knowledge about microdamage empowers you to take better care of your bones.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
