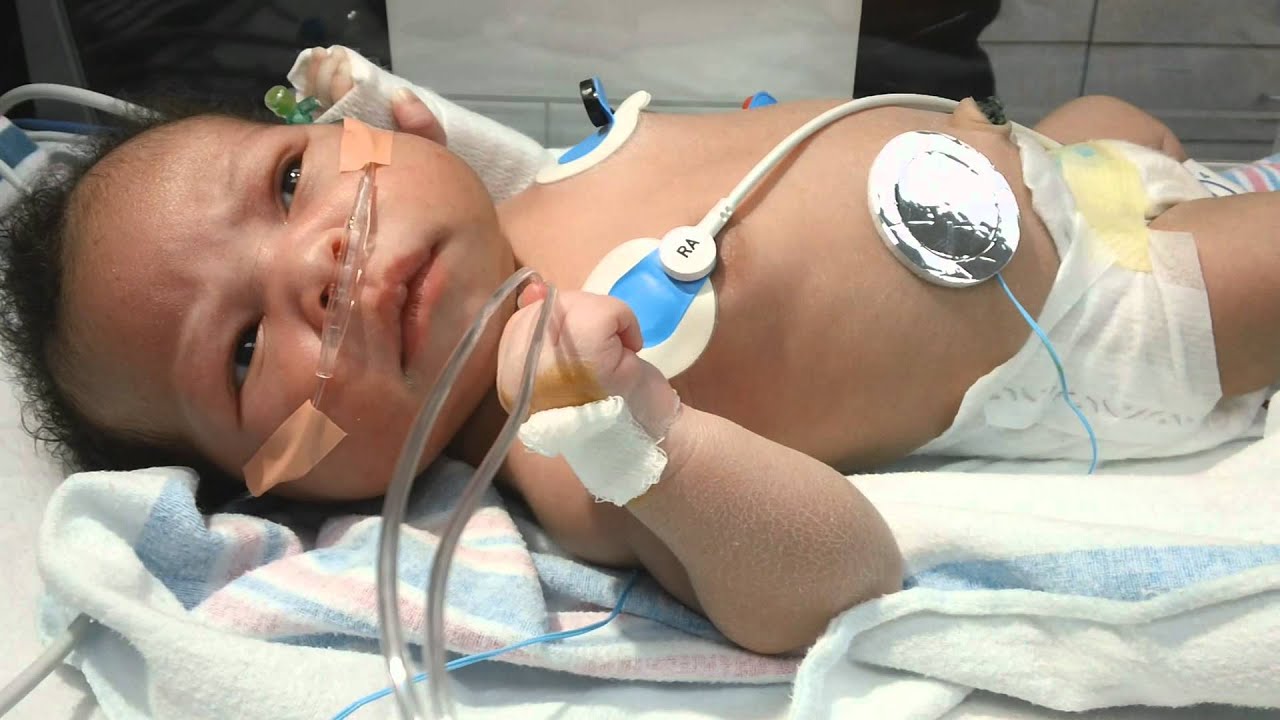
Infant epilepsy with migrant focal crisis is a rare and complex condition that affects young children. Understanding this condition can be challenging, but it's crucial for parents and caregivers to be informed. Epilepsy involves recurrent seizures, and in infants, these seizures can migrate from one part of the brain to another, making diagnosis and treatment more difficult. This condition often presents itself within the first few months of life, and recognizing the signs early can make a significant difference. Symptoms may include unusual movements, changes in behavior, or developmental delays. While the journey can be tough, knowing the facts can empower families to seek the right medical care and support. Let's dive into 25 essential facts about this condition to help you navigate this challenging path.
Key Takeaways:
- Infant epilepsy with migrant focal crisis is a rare condition that affects infants, causing seizures and developmental delays. Early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment are crucial for managing this complex condition.
- Families of infants with epilepsy face emotional stress and financial burden. Support networks and ongoing research offer hope for better treatments and outcomes in the future.
Understanding Infant Epilepsy With Migrant Focal Crisis
Infant epilepsy with migrant focal crisis is a rare and complex condition. It affects infants and can be challenging for parents and caregivers. Here are some important facts to help understand this condition better.
-
Rare Condition: Infant epilepsy with migrant focal crisis is extremely rare. It affects only a small number of infants worldwide.
-
Early Onset: Symptoms typically appear within the first few months of life. Early diagnosis is crucial for managing the condition.
-
Seizure Types: Infants experience focal seizures. These seizures start in one part of the brain and can spread to other areas.
-
Migrating Seizures: Seizures can migrate from one part of the brain to another. This makes the condition more complex.
-
Genetic Factors: Genetic mutations often play a role. Specific genes like KCNT1 and SCN2A are commonly involved.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and getting a proper diagnosis is vital. Here are some key points about symptoms and diagnosis.
-
Seizure Patterns: Seizures can vary in frequency and duration. They may occur multiple times a day.
-
Developmental Delays: Infants may show developmental delays. This can affect motor skills, speech, and cognitive abilities.
-
EEG Monitoring: An electroencephalogram (EEG) is used to monitor brain activity. It helps in diagnosing the type and location of seizures.
-
MRI Scans: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans can reveal brain abnormalities. These scans are often part of the diagnostic process.
-
Genetic Testing: Genetic testing can identify specific mutations. This helps in understanding the cause and planning treatment.
Treatment Options
Managing infant epilepsy with migrant focal crisis requires a comprehensive approach. Here are some treatment options.
-
Antiepileptic Drugs: Medications like phenobarbital and levetiracetam are commonly used. They help control seizures.
-
Ketogenic Diet: A high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet can reduce seizure frequency. This diet is often recommended for infants with epilepsy.
-
Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be an option. It involves removing the part of the brain where seizures originate.
-
Vagus Nerve Stimulation: This involves implanting a device that stimulates the vagus nerve. It can help reduce seizure frequency.
-
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can aid in developmental progress. It helps improve motor skills and overall development.
Impact on Families
Living with infant epilepsy with migrant focal crisis can be challenging for families. Here are some ways it impacts daily life.
-
Emotional Stress: Parents often experience high levels of stress. Managing seizures and developmental delays can be overwhelming.
-
Financial Burden: The cost of treatment and care can be significant. Families may face financial challenges.
-
Support Networks: Support groups and networks can provide emotional and practical help. Connecting with other families can be beneficial.
-
Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the condition is important. Educating others can lead to better support and understanding.
-
Caregiver Fatigue: Caregivers may experience fatigue and burnout. Taking breaks and seeking help is crucial.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is essential for improving treatment and outcomes. Here are some areas of focus.
-
Gene Therapy: Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment. This involves correcting genetic mutations.
-
New Medications: Development of new antiepileptic drugs is ongoing. These medications aim to be more effective with fewer side effects.
-
Brain Stimulation: Advanced brain stimulation techniques are being studied. These may offer new ways to control seizures.
-
Early Intervention: Emphasis on early intervention can improve outcomes. Early diagnosis and treatment are key.
-
Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials can provide access to new treatments. Families can contribute to research by joining trials.
Understanding Infant Epilepsy
Infant epilepsy with migrant focal crisis is a complex condition that requires attention and care. Knowing the facts about this condition can help parents, caregivers, and medical professionals provide better support for affected children. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Epilepsy in infants can manifest in various ways, and recognizing the signs early can make a significant difference. Treatments range from medications to specialized diets, and sometimes surgery. Each child's situation is unique, so personalized care plans are essential.
Staying informed and connected with healthcare providers ensures the best possible outcomes. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. Support groups and resources are available to help navigate the challenges of infant epilepsy. Knowledge empowers, and with the right information, you can make a positive impact on your child's health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
