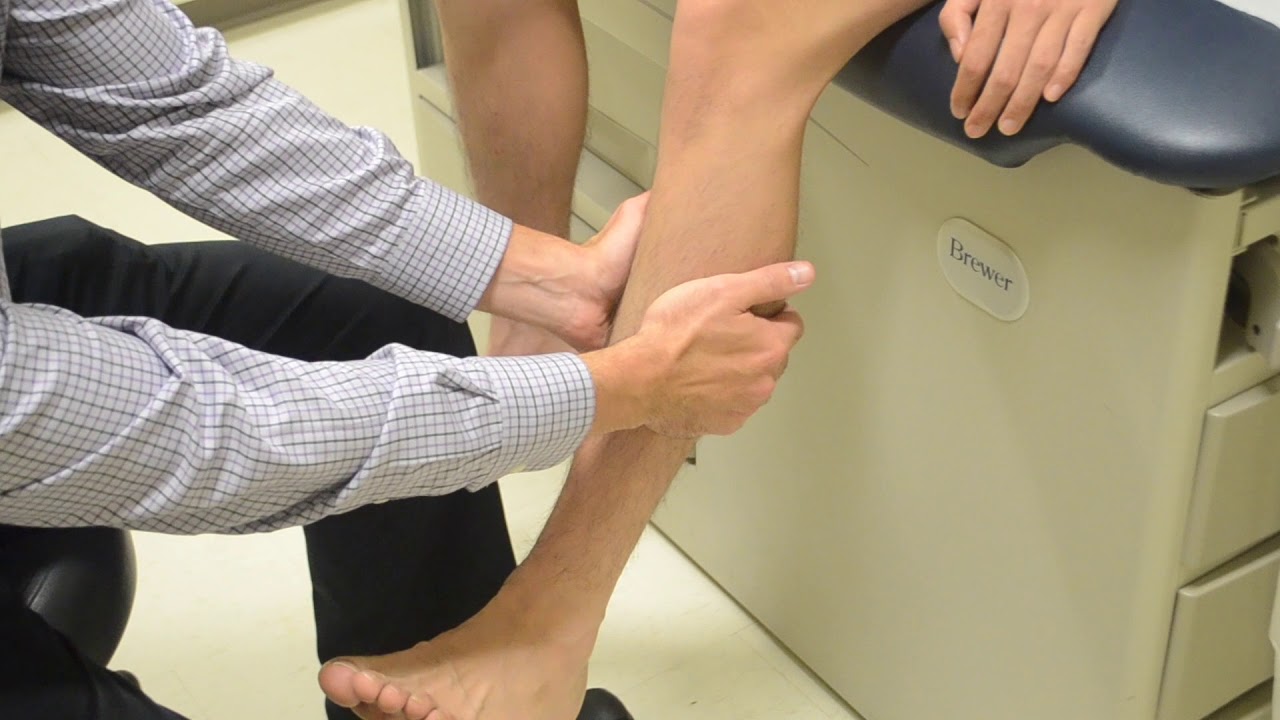
Homans' Sign is a medical term you might not hear every day, but it’s crucial for diagnosing deep vein thrombosis (DVT). What is Homans' Sign? It’s a physical exam finding where pain in the calf is triggered by dorsiflexion of the foot. This simple test can help doctors identify blood clots in the legs, which can be life-threatening if not treated. Knowing about Homans' Sign can be vital for anyone at risk of DVT, such as those who sit for long periods or have certain medical conditions. Let's dive into 25 facts about this important diagnostic tool.
Key Takeaways:
- Homans' sign is a test for leg blood clots, but it's not very reliable. Modern methods like ultrasound and blood tests are better for diagnosing this condition.
- Despite its historical significance, Homans' sign is outdated and not recommended by modern guidelines. It's still used in some places, but there are safer and more accurate ways to check for blood clots.
What is Homans' Sign?
Homans' sign is a clinical test used to check for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the leg. It involves dorsiflexing the foot to see if pain occurs in the calf. This test has been around for a while and is still used by some healthcare professionals.
-
Named after John Homans: The test is named after Dr. John Homans, an American surgeon who first described it in 1941.
-
DVT Indicator: Homans' sign is primarily used to detect DVT, a condition where blood clots form in deep veins, usually in the legs.
-
Simple Procedure: The test involves dorsiflexing the foot (pulling the toes towards the shin) while the leg is extended.
-
Pain in Calf: A positive Homans' sign is indicated by pain in the calf upon dorsiflexion.
How Reliable is Homans' Sign?
The reliability of Homans' sign has been a topic of debate among medical professionals. Some argue it is useful, while others believe it is outdated.
-
Low Sensitivity: Homans' sign has low sensitivity, meaning it often fails to detect DVT when it is present.
-
Low Specificity: It also has low specificity, meaning it can indicate DVT when other conditions are causing the pain.
-
Not Definitive: A positive Homans' sign is not definitive for DVT and should be followed up with more accurate tests like ultrasound.
-
False Positives: Conditions like muscle strain, cellulitis, or Baker's cyst can also cause a positive Homans' sign.
Alternatives to Homans' Sign
Given its limitations, there are other methods and tests that are more reliable for diagnosing DVT.
-
Ultrasound: Doppler ultrasound is the gold standard for diagnosing DVT, offering high sensitivity and specificity.
-
D-dimer Test: This blood test measures clot formation and breakdown in the body. Elevated levels can indicate DVT.
-
Venography: An imaging test where contrast dye is injected into a vein to visualize blood flow and detect clots.
-
MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging can also be used to detect DVT, especially in cases where ultrasound is inconclusive.
Historical Context of Homans' Sign
Understanding the historical context can provide insight into why Homans' sign was developed and how it has evolved.
-
World War II: During the 1940s, DVT was a significant concern for soldiers who were immobilized for long periods.
-
Early Detection: Homans' sign was one of the first clinical tests aimed at early detection of DVT, a life-threatening condition.
-
Medical Advancements: Over the years, advancements in medical technology have provided more accurate methods for diagnosing DVT.
Clinical Use Today
Despite its limitations, Homans' sign is still used in some clinical settings, often as a preliminary test.
-
Quick Assessment: It offers a quick, initial assessment for DVT, especially in settings where advanced imaging is not immediately available.
-
Combined Approach: Often used in combination with other clinical signs and symptoms to assess the likelihood of DVT.
-
Educational Tool: Medical students and trainees still learn about Homans' sign as part of their education on DVT.
Controversies and Criticisms
Homans' sign has faced its share of controversies and criticisms over the years.
-
Outdated: Many experts consider it outdated and prefer more reliable diagnostic methods.
-
Risk of Harm: Performing the test can potentially dislodge a clot, posing a risk to the patient.
-
Clinical Guidelines: Modern clinical guidelines often do not recommend relying solely on Homans' sign for DVT diagnosis.
Interesting Facts
There are some lesser-known, interesting facts about Homans' sign that add to its historical and clinical narrative.
-
Global Use: Despite its limitations, Homans' sign is still used in various parts of the world, especially in resource-limited settings.
-
Educational Value: It serves as a historical reference point in the evolution of medical diagnostics for DVT.
-
Patient Awareness: Some patients are aware of Homans' sign and may even ask for it during consultations.
-
Research Studies: Ongoing research continues to evaluate the effectiveness and relevance of Homans' sign in modern medicine.
Final Thoughts on Homans' Sign
Homans' Sign, a classic indicator of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), has been a valuable tool for healthcare professionals. While not foolproof, it provides a quick, non-invasive method to assess potential blood clots in the leg. Knowing about Homans' Sign can help you understand the importance of early detection and treatment of DVT, which can be life-saving.
Remember, though, that a positive Homans' Sign isn't a definitive diagnosis. Always consult a healthcare provider for comprehensive evaluation and treatment. Combining this sign with other diagnostic tools ensures a more accurate assessment.
Stay informed and proactive about your health. Awareness of signs like Homans' can make a significant difference. Keep learning, stay curious, and prioritize your well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
