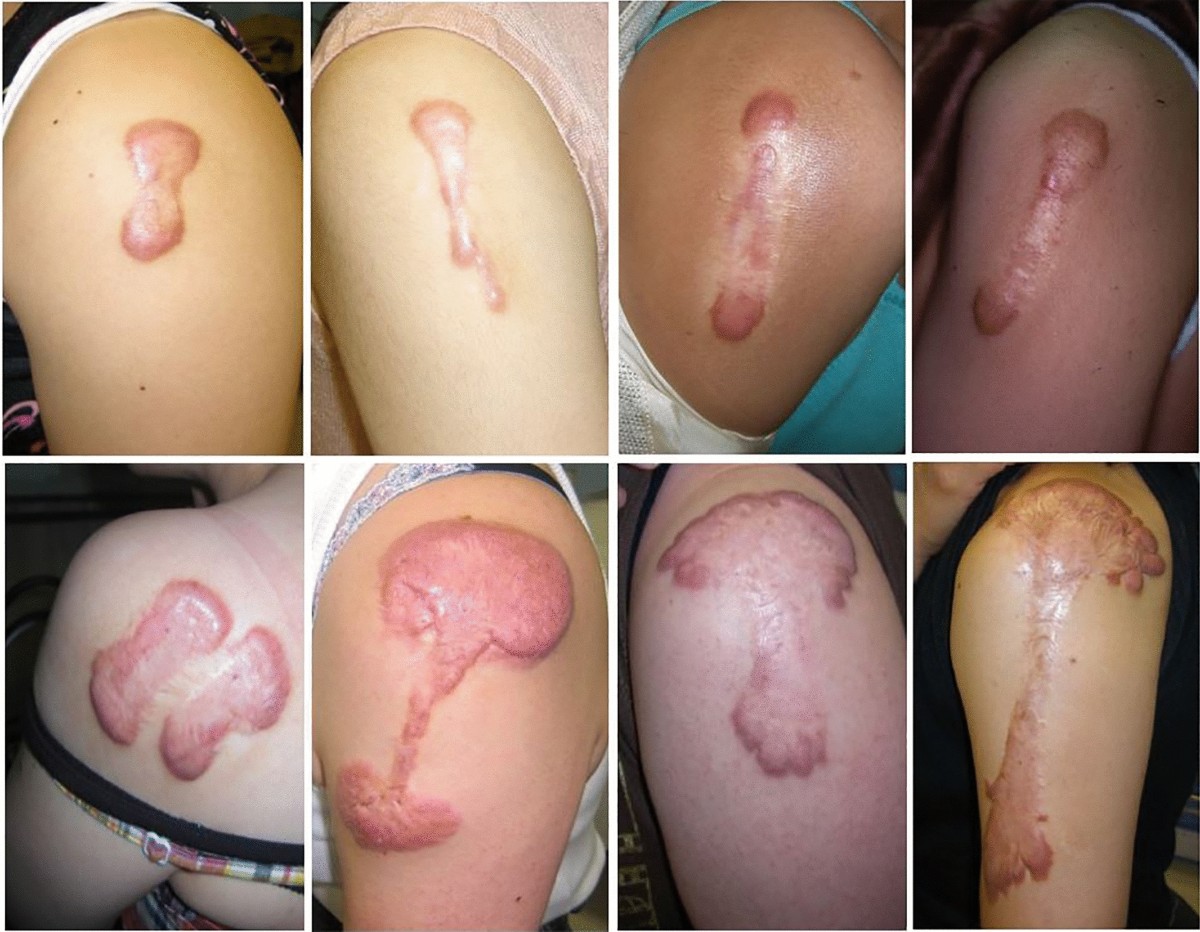
Why are some people more prone to infections even after receiving the BCG vaccine? This question has puzzled scientists for years. The BCG vaccine, primarily used against tuberculosis, doesn't work the same for everyone. Some folks get great protection, while others don't. This difference often boils down to genetic susceptibility. Our genes play a big role in how our bodies respond to vaccines and infections. Imagine genes as tiny instructions inside us. They tell our bodies how to fight germs. If these instructions aren't quite right, some people might not fight infections as well. Understanding these genetic differences is key to improving vaccines and treatments. Scientists are working hard to figure out which genes affect BCG's effectiveness. This knowledge could lead to better vaccines that work for everyone. Curious to learn more about these genetic mysteries? Let's dive into the fascinating world of genetics and vaccines!
Key Takeaways:
- Your genes can affect how well vaccines like BCG work. Factors like nutrition and stress also play a role in susceptibility to infections.
- Research on genetic susceptibility to BCG-related infections can lead to personalized medicine and better vaccines, benefiting global health.
Understanding Genetic Susceptibility to Infections
Genetic susceptibility to infections is a fascinating area of study. It explores how our genes can make us more or less vulnerable to certain diseases. One such infection is caused by the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine, primarily used against tuberculosis. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this topic.
-
Genes and Immunity
Our genes play a crucial role in shaping our immune system. They determine how our bodies respond to pathogens, including those introduced by vaccines like BCG. -
BCG Vaccine Basics
The BCG vaccine is derived from a strain of Mycobacterium bovis. It is mainly used to prevent tuberculosis, especially in countries where the disease is common. -
Genetic Variability
Not everyone responds to the BCG vaccine in the same way. Genetic differences can influence the effectiveness of the vaccine. -
HLA Genes
Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) genes are essential for immune function. Variations in these genes can affect how well the BCG vaccine works. -
Cytokine Production
Cytokines are proteins that help regulate the immune response. Genetic factors can influence cytokine production, impacting vaccine efficacy. -
Innate Immunity
Our innate immune system is the first line of defense against infections. Genetic variations can affect how this system responds to the BCG vaccine. -
Adaptive Immunity
Adaptive immunity involves the body's ability to recognize and remember pathogens. Genes play a role in how effectively this system responds to the BCG vaccine.
The Role of Specific Genes
Certain genes have been identified as key players in determining susceptibility to infections caused by the BCG vaccine. Here are some of them:
-
IL-12 Gene
The IL-12 gene is involved in the production of a cytokine crucial for fighting infections. Variations in this gene can affect susceptibility to BCG-related infections. -
IFN-γ Gene
Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) is another cytokine essential for immune response. Genetic differences in the IFN-γ gene can influence how the body reacts to the BCG vaccine. -
TNF Gene
Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) is a cytokine that helps regulate immune cells. Variations in the TNF gene can impact susceptibility to infections. -
NOD2 Gene
The NOD2 gene plays a role in recognizing bacterial components. Genetic variations in NOD2 can affect how the immune system responds to the BCG vaccine. -
TLR Genes
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are proteins that recognize pathogens. Variations in TLR genes can influence the body's response to the BCG vaccine.
Environmental and Genetic Interactions
Genetic susceptibility to infections is not solely determined by genes. Environmental factors also play a significant role.
-
Nutrition
A person's nutritional status can influence how their genes affect susceptibility to infections. Proper nutrition supports a healthy immune system. -
Exposure to Pathogens
Frequent exposure to pathogens can impact how genetic factors influence susceptibility to infections. This exposure can either strengthen or weaken the immune response. -
Stress Levels
Stress can affect immune function. High stress levels may alter how genetic factors influence susceptibility to infections. -
Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices, such as smoking and exercise, can impact immune function. These choices can interact with genetic factors to influence susceptibility to infections.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research continues to uncover new insights into genetic susceptibility to infections caused by the BCG vaccine.
-
Genomic Studies
Advances in genomic studies are helping researchers identify new genes involved in susceptibility to BCG-related infections. -
Personalized Medicine
Understanding genetic susceptibility can lead to personalized medicine approaches, tailoring vaccines and treatments to individual genetic profiles. -
Vaccine Development
Insights into genetic susceptibility can inform the development of more effective vaccines, potentially improving global health outcomes. -
Public Health Strategies
Knowledge of genetic susceptibility can help shape public health strategies, ensuring vaccines are used effectively in different populations. -
Ethical Considerations
As research progresses, ethical considerations around genetic testing and susceptibility must be addressed to protect individuals' rights.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite advances, challenges remain in understanding genetic susceptibility to infections caused by the BCG vaccine.
-
Complex Interactions
The interactions between genes and environmental factors are complex, making it challenging to pinpoint specific causes of susceptibility. -
Population Diversity
Genetic diversity across populations can complicate research, as findings in one group may not apply to others. -
Data Limitations
Limited data availability can hinder research efforts, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions. -
Resource Allocation
Allocating resources for research and public health initiatives requires careful consideration to ensure equitable access to vaccines and treatments.
Understanding Genetic Susceptibility to BCG Infections
Grasping genetic susceptibility to BCG infections is crucial for advancing medical research and improving public health strategies. This knowledge helps identify individuals at higher risk, allowing for targeted interventions and personalized treatments. Genetic factors play a significant role in how our bodies respond to BCG vaccines, which are primarily used against tuberculosis. By studying these genetic influences, scientists can develop more effective vaccines and therapies, potentially reducing the global burden of infectious diseases.
Moreover, understanding genetic susceptibility can lead to better diagnostic tools and preventive measures, ultimately saving lives. It also opens doors for further research into other infectious diseases, paving the way for broader medical advancements. As we continue to unravel the complexities of genetics and infections, the potential for improving health outcomes becomes increasingly promising. This knowledge empowers us to make informed decisions about vaccination and disease prevention.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
