Distichiasis heart congenital anomalies might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it is crucial for those affected. This condition involves an extra row of eyelashes, known as distichiasis, combined with heart defects present at birth. These heart issues can range from mild to severe, impacting how the heart functions.
Why does this happen? It's often linked to genetic mutations, which can be inherited or occur spontaneously. Some people with this condition might not even realize they have it until symptoms appear. These can include heart murmurs, fatigue, or even more serious complications.
Is there a treatment? Yes, treatments vary depending on the severity of the heart anomalies. Regular check-ups with a cardiologist are essential to monitor heart health. Understanding this condition can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Let's dive deeper into the facts surrounding this unique condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Distichiasis involves extra eyelashes causing irritation, while heart congenital anomalies are structural heart problems at birth. Both can be linked through genetic syndromes, requiring comprehensive care and lifestyle adjustments for management.
- Regular check-ups, protecting the eyes, maintaining heart health, and joining support networks are essential for managing distichiasis and heart congenital anomalies. Ongoing research offers hope for improved understanding and treatment.
Understanding Distichiasis
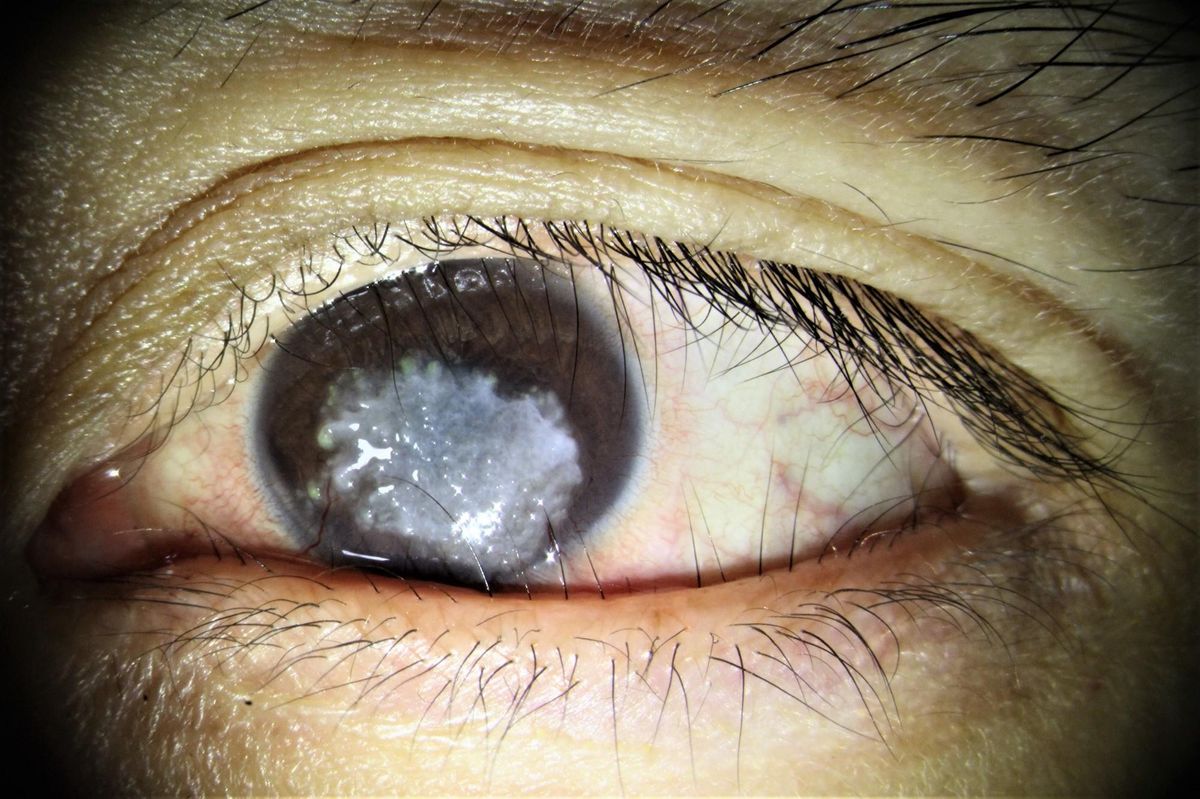
Distichiasis is a condition where extra eyelashes grow from the eyelid's oil glands. These additional lashes can cause irritation and discomfort. It's a rare condition but can be associated with other health issues.
-
Extra Lashes: Distichiasis involves the growth of an extra row of eyelashes. These lashes often grow from the meibomian glands, which are typically responsible for secreting oils that keep the eyes moist.
-
Irritation and Discomfort: The extra lashes can rub against the eye, leading to irritation, redness, and even corneal damage if not treated properly.
-
Genetic Link: This condition can be inherited. If a parent has distichiasis, there's a chance their children might have it too.
-
Treatment Options: Treatments include removing the extra lashes through electrolysis, cryotherapy, or surgery. These methods aim to prevent further irritation and protect the eye.
Heart Congenital Anomalies
Heart congenital anomalies are structural problems with the heart present at birth. These can range from minor issues to severe defects that require immediate medical attention.
-
Common Birth Defects: Heart anomalies are among the most common congenital defects. They affect the heart's structure, impacting its ability to pump blood effectively.
-
Variety of Defects: There are many types of heart defects, including septal defects (holes in the heart), valve defects, and issues with the heart's walls or blood vessels.
-
Causes: While some heart defects are genetic, others can result from environmental factors during pregnancy, such as maternal illness or medication use.
-
Symptoms: Symptoms can include rapid breathing, fatigue, poor blood circulation, and cyanosis (bluish skin due to lack of oxygen).
-
Diagnosis: Heart anomalies are often diagnosed through prenatal ultrasounds or after birth using echocardiograms and other imaging techniques.
-
Treatment: Treatment varies based on the defect's severity and can include medication, surgery, or heart transplants in extreme cases.
Connection Between Distichiasis and Heart Anomalies
Though seemingly unrelated, distichiasis and heart congenital anomalies can sometimes be linked through genetic syndromes.
-
Lymphedema-Distichiasis Syndrome: This rare genetic disorder involves both distichiasis and lymphedema (swelling due to lymph fluid). It can also include heart defects.
-
FOXC2 Gene: Mutations in the FOXC2 gene are known to cause Lymphedema-Distichiasis Syndrome. This gene plays a role in the development of the heart and lymphatic system.
-
Family History: A family history of distichiasis or heart anomalies can increase the likelihood of these conditions appearing together.
-
Comprehensive Care: Managing both conditions requires a team of specialists, including ophthalmologists and cardiologists, to address the unique challenges they present.
Living with Distichiasis and Heart Anomalies
Managing these conditions involves regular medical care and lifestyle adjustments to maintain health and quality of life.
-
Regular Check-ups: Frequent visits to healthcare providers help monitor and manage symptoms effectively, preventing complications.
-
Protecting the Eyes: For those with distichiasis, using lubricating eye drops and wearing protective eyewear can help reduce irritation.
-
Heart Health: Maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, is crucial for those with heart anomalies.
-
Support Networks: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice from others facing similar challenges.
-
Education and Awareness: Understanding these conditions and educating others can help reduce stigma and improve access to resources.
Advances in Treatment and Research
Ongoing research continues to improve the understanding and treatment of both distichiasis and heart congenital anomalies.
-
Genetic Research: Studies on the FOXC2 gene and other genetic factors are helping to uncover the underlying causes of these conditions.
-
Innovative Treatments: New surgical techniques and therapies are being developed to improve outcomes for those affected.
-
Early Detection: Advances in prenatal screening and imaging technology are allowing for earlier diagnosis and intervention.
-
Patient Advocacy: Organizations and advocacy groups are working to raise awareness and funding for research into these rare conditions.
-
Collaboration: Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and patients is key to advancing treatment and care.
-
Hope for the Future: With continued research and medical advancements, there is hope for better management and outcomes for those living with distichiasis and heart congenital anomalies.
Understanding Distichiasis and Heart Congenital Anomalies
Distichiasis, a condition where extra eyelashes grow from the meibomian glands, can sometimes be linked to heart congenital anomalies. These anomalies are structural issues present at birth affecting the heart's function. Recognizing the connection between these two conditions is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment.
While distichiasis might seem like a minor inconvenience, its association with heart issues highlights the importance of comprehensive medical evaluations. Early detection can lead to better management and improved outcomes for those affected.
Awareness and education about these conditions can empower individuals and families to seek appropriate medical advice. By understanding the potential link between distichiasis and heart congenital anomalies, healthcare providers can offer more targeted care. This knowledge not only aids in treatment but also in improving the quality of life for those impacted by these conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
