Osteoporosis is a common but often overlooked health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a bone disease characterized by a decrease in bone mass and density, making the bones fragile and more prone to fractures. Despite its prevalence, there are still many misconceptions and misunderstandings surrounding osteoporosis. In this article, we will explore 20 fascinating facts about osteoporosis, shedding light on its causes, risk factors, prevention, and treatment. By gaining a deeper understanding of this condition, we can take proactive steps to protect our bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis-related complications. So, let’s dive into these intriguing facts and uncover the truth about osteoporosis.
Key Takeaways:
- Osteoporosis is a “silent disease” that weakens bones without symptoms, affecting over 200 million people worldwide. Prevention through exercise and a balanced diet is crucial for maintaining bone health.
- Family history, medications, and lifestyle choices can influence the risk of developing osteoporosis. Early prevention and screening are essential for managing and treating this widespread bone disease.
Osteoporosis affects over 200 million people worldwide.
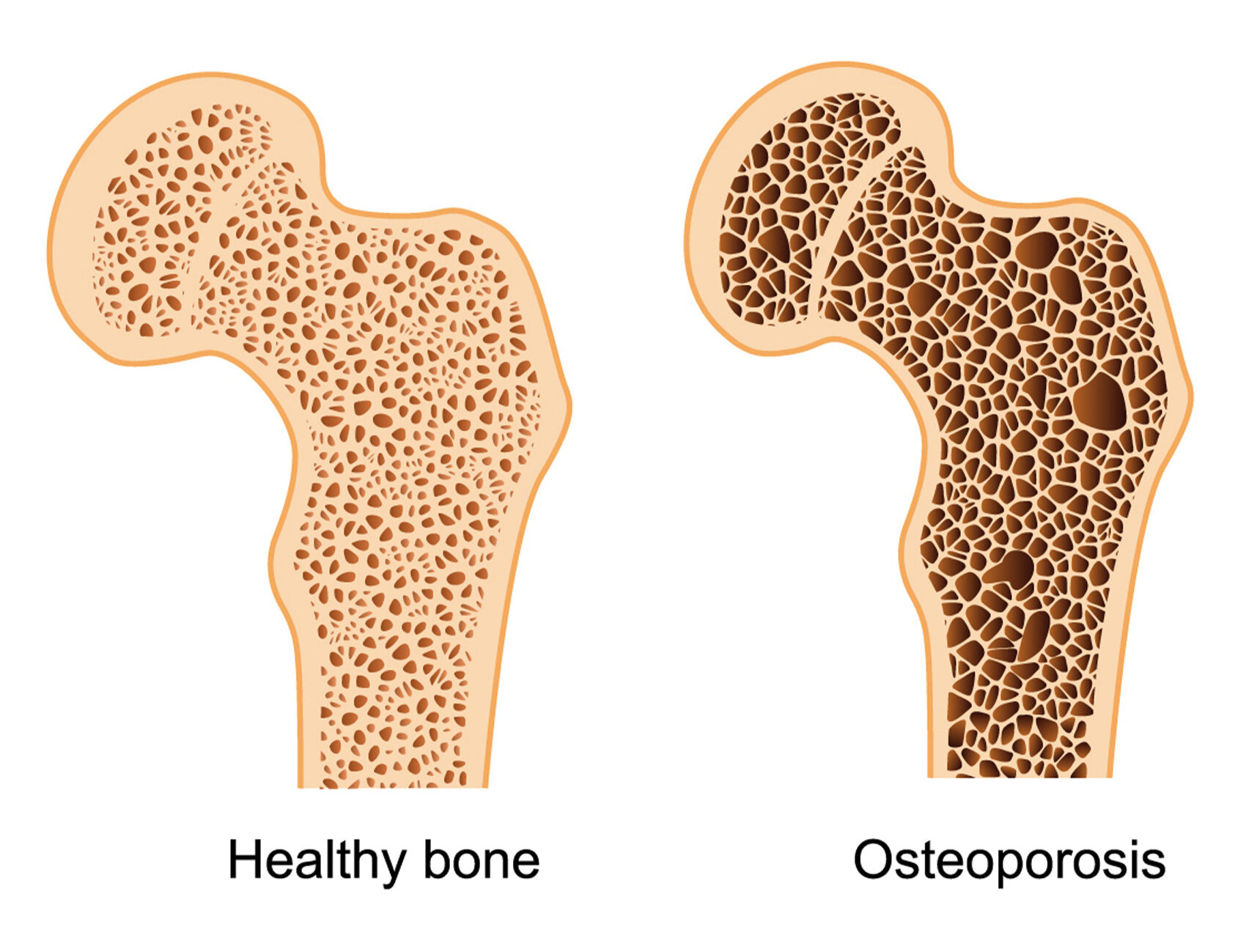
Osteoporosis is a widespread bone disease that weakens bones, making them fragile and more likely to break. It is a major public health concern, especially among the elderly.
Osteoporosis is often referred to as the “silent disease.”
It is called the “silent disease” because bone loss occurs without symptoms. Many individuals may not realize they have osteoporosis until they experience a fracture or break a bone.
Women are more likely to develop osteoporosis than men.
Postmenopausal women are particularly at risk due to the rapid decline in estrogen levels, which plays a protective role in bone health.
Osteoporosis can affect any bone in the body.
While fractures commonly occur in the hip, spine, and wrist, osteoporosis can impact any bone, including those in the arms, pelvis, and ribs.
Regular weight-bearing exercise can help prevent osteoporosis.
Engaging in activities such as walking, dancing, and weight training can help build and maintain bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
Calcium and vitamin D are essential for bone health.
These nutrients play a crucial role in maintaining strong bones and preventing osteoporosis. A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is vital for bone health.
Osteoporosis is often called a “pediatric disease with geriatric consequences.”
Building strong bones during childhood and adolescence can help prevent osteoporosis later in life. Peak bone mass is typically reached by the late 20s, making early bone health crucial.
Osteoporosis can lead to a stooped posture and loss of height.
Compression fractures in the spine due to osteoporosis can result in a curved or stooped posture, along with a noticeable decrease in height.
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
Both smoking and heavy alcohol use can negatively impact bone health, leading to an increased likelihood of developing osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis is often diagnosed through a bone density test.
A dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan is commonly used to measure bone density and assess the risk of fractures due to osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis-related fractures can significantly impact quality of life.
Fractures resulting from osteoporosis can lead to chronic pain, disability, and a reduced ability to perform daily activities, affecting overall well-being.
Individuals with osteoporosis are at a higher risk of experiencing a subsequent fracture.
Once a person experiences a fracture due to osteoporosis, they are at a significantly increased risk of suffering another fracture in the future.
Osteoporosis is not a normal part of aging.
While bone density naturally decreases with age, osteoporosis is not an inevitable consequence of getting older. There are proactive steps individuals can take to maintain bone health.
Some medications can contribute to bone loss.
Certain drugs, such as corticosteroids and some anticonvulsants, can increase the risk of osteoporosis by negatively affecting bone density.
Family history can influence the risk of developing osteoporosis.
Individuals with a family history of osteoporosis or fragility fractures may have a higher predisposition to the condition, emphasizing the importance of early prevention and screening.
Osteoporosis can be managed and treated with medications and lifestyle changes.
Various medications, including bisphosphonates and hormone therapy, can help slow bone loss and reduce the risk of fractures. Additionally, lifestyle modifications such as a balanced diet and regular exercise are key components of osteoporosis management.
Osteoporosis is a significant economic burden.
The costs associated with osteoporosis-related fractures and treatment place a substantial financial strain on healthcare systems and individuals, highlighting the need for preventive measures and effective management strategies.
Weight loss and low body weight can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
Being underweight or experiencing rapid weight loss can negatively impact bone density, raising the likelihood of developing osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis is a global health issue.
With an aging population and increasing life expectancy, osteoporosis presents a significant health challenge worldwide, underscoring the importance of awareness, prevention, and early intervention.
Osteoporosis can be asymptomatic until a fracture occurs.
Many individuals may be unaware of their osteoporosis status until they experience a fracture, highlighting the need for proactive screening and preventive measures.
Conclusion
Osteoporosis is a serious condition that affects millions of people worldwide. By understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and prevention methods, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain healthy bones and reduce the likelihood of developing osteoporosis. With a balanced diet, regular exercise, and medical guidance, it is possible to minimize the impact of this disease and protect bone health throughout life.
FAQs
What are the common risk factors for osteoporosis?
Common risk factors for osteoporosis include aging, family history, hormonal changes, certain medications, and lifestyle choices such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
What are the symptoms of osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is often referred to as a “silent disease” because it progresses without noticeable symptoms until a fracture occurs. However, individuals may experience back pain, loss of height, and a stooped posture as the condition advances.
How can osteoporosis be prevented?
Prevention strategies for osteoporosis include consuming a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, engaging in weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening exercises, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol intake, and discussing bone health with a healthcare provider.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
