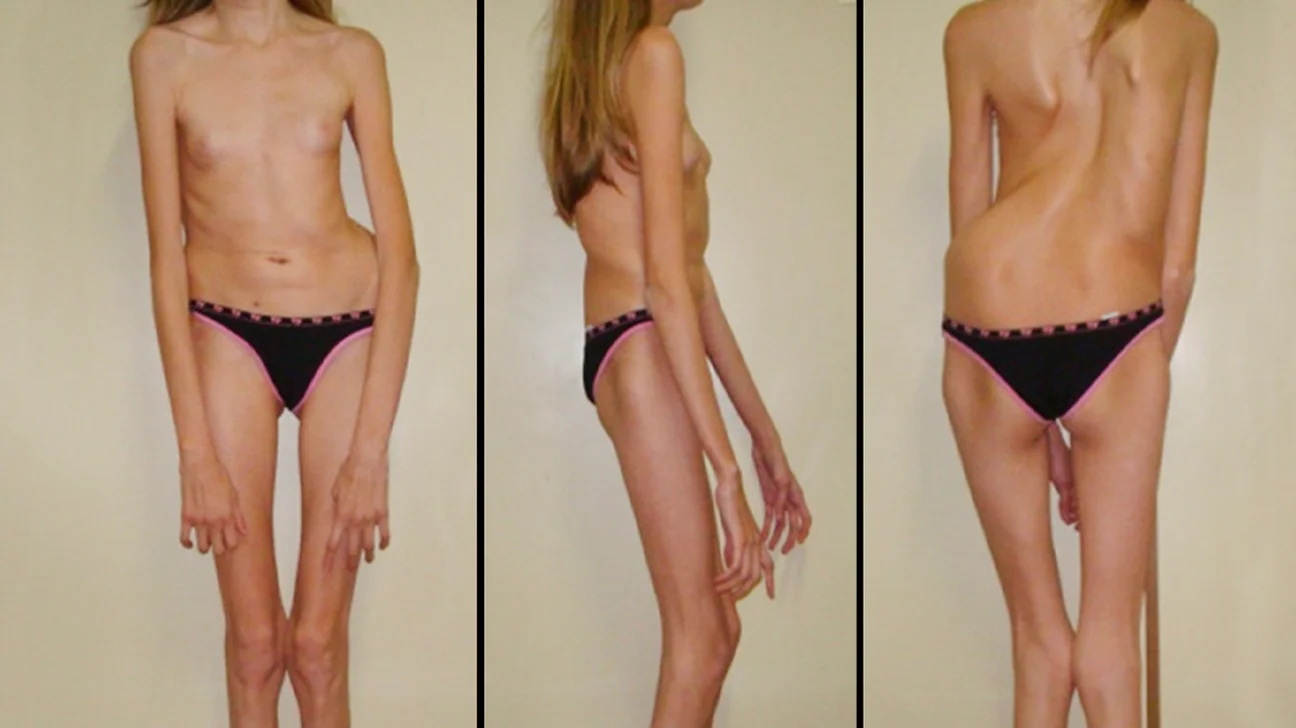
Marfan syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects the body’s connective tissue, causing a range of distinctive physical characteristics and potential health complications. While it’s a serious and potentially life-altering condition, there are many fascinating aspects to Marfan syndrome that are worth exploring. In this article, we’ll delve into 20 intriguing and entertaining facts about Marfan syndrome that shed light on this complex disorder. From its historical origins to its impact on the lives of those affected, we’ll uncover a diverse range of information that will enhance understanding and awareness of Marfan syndrome. So, let’s embark on a journey to discover the lesser-known, yet captivating, facets of this genetic condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Marfan Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder affecting 1 in 5,000 people worldwide, causing various health issues and distinctive physical traits. It requires regular monitoring and can impact people of all races and ethnicities.
- The syndrome was first described by a French doctor named Antoine Marfan in 1896. It can affect the eyes, heart, skeletal system, and dura, requiring careful consideration for physical activity and regular eye examinations.
Marfan Syndrome affects 1 in 5,000 people worldwide.
This genetic disorder, which impacts the body’s connective tissue, is relatively rare, with approximately 200,000 cases reported in the United States each year. Despite its low prevalence, Marfan Syndrome has garnered significant attention due to its distinctive features and potential health complications.
Abraham Lincoln is believed to have had Marfan Syndrome.
Many historians and medical experts have speculated that the 16th President of the United States exhibited physical characteristics consistent with Marfan Syndrome, including his tall stature, long limbs, and distinct facial features. While this theory remains unconfirmed, it has sparked widespread interest in the potential historical figures who may have been affected by the condition.
Marfan Syndrome can impact the eyes, heart, and skeletal system.
Individuals with Marfan Syndrome are susceptible to various health issues, including lens dislocation, retinal detachment, aortic aneurysms, and skeletal abnormalities. These diverse manifestations underscore the complex nature of the condition and the need for comprehensive medical management.
People with Marfan Syndrome tend to have long, slender fingers.
One of the characteristic physical traits associated with Marfan Syndrome is arachnodactyly, which causes elongated fingers and toes. This distinctive feature often serves as a visual indicator for healthcare professionals when evaluating potential cases of the syndrome.
Marfan Syndrome is caused by mutations in the FBN1 gene.
The FBN1 gene provides instructions for producing a protein called fibrillin-1, which plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of connective tissues. Mutations in this gene can disrupt the normal structure and function of connective tissue, leading to the various signs and symptoms associated with Marfan Syndrome.
Professional basketball player Isaiah Austin was diagnosed with Marfan Syndrome.
In 2014, Isaiah Austin, a promising basketball talent projected to enter the NBA draft, received the devastating news that he had Marfan Syndrome, effectively ending his basketball career. Despite this setback, Austin has become an advocate for Marfan awareness and continues to inspire others with his resilience.
Marfan Syndrome can be diagnosed through genetic testing and clinical evaluation.
Healthcare providers utilize a combination of genetic testing, physical examinations, and imaging studies to diagnose Marfan Syndrome. By assessing a patient’s medical history and conducting thorough evaluations, medical professionals can accurately identify and manage the condition.
Aortic dissection is a life-threatening complication of Marfan Syndrome.
Individuals with Marfan Syndrome face an increased risk of aortic dissection, a serious condition in which a tear develops in the inner layer of the aorta. Prompt medical intervention is crucial in addressing this potentially fatal complication, highlighting the importance of proactive monitoring and management.
The Marfan Foundation provides support and resources for individuals with the condition.
This nonprofit organization offers valuable assistance to individuals and families affected by Marfan Syndrome, providing educational materials, support networks, and research initiatives aimed at advancing treatment options and enhancing quality of life for those living with the condition.
Marfan Syndrome can affect people of all races and ethnicities.
While certain genetic conditions may be more prevalent in specific populations, Marfan Syndrome is observed across diverse racial and ethnic groups worldwide. This underscores the importance of raising awareness and promoting early detection and intervention to improve outcomes for individuals with the syndrome.
Michael Phelps, the Olympic swimmer, has been rumored to have Marfan Syndrome.
Speculation about Michael Phelps possibly having Marfan Syndrome has circulated due to his unique physical attributes, including his tall stature, long arms, and flexible joints. Despite these rumors, Phelps has not confirmed any diagnosis and continues to excel in his athletic pursuits.
Marfan Syndrome can impact the dura, the membrane surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
In some cases, individuals with Marfan Syndrome may experience dural ectasia, a condition characterized by the abnormal expansion of the dura. This can lead to symptoms such as lower back pain and neurological issues, highlighting the diverse effects of the syndrome on the body.
Regular monitoring is essential for individuals with Marfan Syndrome.
Given the potential for cardiovascular complications and other health issues associated with Marfan Syndrome, regular medical evaluations and monitoring are crucial for early detection and intervention. This proactive approach can help mitigate the risks and optimize the overall well-being of individuals with the condition.
Marfan Syndrome can affect both men and women.
Unlike certain genetic conditions that predominantly impact one gender, Marfan Syndrome affects both males and females. This underscores the importance of inclusive healthcare practices and tailored management strategies to address the unique needs of individuals with the syndrome.
Marfan Syndrome was first described by a French doctor named Antoine Marfan.
In 1896, Dr. Antoine Marfan documented a case series of individuals presenting with similar physical characteristics, leading to the recognition of the syndrome that would later bear his name. His pioneering work laid the foundation for subsequent research and advancements in understanding this complex genetic disorder.
Physical activity and sports participation may require careful consideration for individuals with Marfan Syndrome.
Due to the potential cardiovascular implications and musculoskeletal vulnerabilities associated with Marfan Syndrome, healthcare providers often provide guidance on safe and appropriate levels of physical activity to minimize risks while promoting overall fitness and well-being.
Marfan Syndrome can lead to the development of scoliosis, a curvature of the spine.
Individuals with Marfan Syndrome may be predisposed to developing scoliosis, a condition characterized by an abnormal sideways curvature of the spine. Management of scoliosis in the context of Marfan Syndrome requires a multidisciplinary approach to address the specific needs of affected individuals.
Eye examinations are an essential component of Marfan Syndrome management.
Regular eye screenings are crucial for individuals with Marfan Syndrome due to the increased risk of ocular complications, such as lens dislocation and retinal issues. Early detection and intervention can help preserve vision and prevent potential vision-related complications associated with the syndrome.
Marfan Syndrome can manifest with variable expressivity.
The presentation of Marfan Syndrome can vary widely among affected individuals, leading to differences in the severity and combination of symptoms. This variability underscores the importance of personalized medical care and tailored interventions to address the unique needs of each individual with the condition.
Advancements in medical research have led to improved understanding and management of Marfan Syndrome.
Ongoing research initiatives have contributed to enhanced insights into the underlying mechanisms of Marfan Syndrome, paving the way for innovative treatment approaches and improved patient outcomes. These advancements offer hope for individuals living with the condition and drive progress in the field of genetic disorders.
Conclusion
Marfan syndrome is a complex and fascinating genetic disorder that can have a significant impact on an individual’s health and well-being. By understanding the various aspects of this condition, we can better appreciate the challenges faced by those living with Marfan syndrome and work towards improving their quality of life. From the unique genetic mutation to the potential complications affecting the heart, eyes, and skeletal system, Marfan syndrome presents a range of medical considerations that require ongoing attention and care. Through ongoing research and medical advancements, there is hope for improved treatment options and outcomes for individuals with Marfan syndrome. It’s essential to continue raising awareness and promoting understanding of this condition to support those affected and their families.
FAQs
What causes Marfan syndrome?
Marfan syndrome is caused by a mutation in the FBN1 gene, which provides instructions for producing a protein called fibrillin-1. This protein plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s connective tissues.
Is Marfan syndrome a common condition?
Marfan syndrome is considered a rare genetic disorder, with an estimated prevalence of 1 in 5,000 individuals. However, due to its variable presentation and potential for undiagnosed cases, the actual prevalence may be higher.
Can Marfan syndrome be diagnosed at any age?
Marfan syndrome can be diagnosed at any stage of life, from infancy to adulthood. Genetic testing and a thorough clinical evaluation by a healthcare professional are essential for an accurate diagnosis.
What are the potential complications of Marfan syndrome?
Individuals with Marfan syndrome are at risk for various complications, including aortic aneurysms, dislocated lenses in the eyes, skeletal abnormalities, and cardiovascular issues. Regular monitoring and medical management are crucial for addressing these potential complications.
Is there a cure for Marfan syndrome?
Currently, there is no cure for Marfan syndrome. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, preventing complications, and improving quality of life through a multidisciplinary approach involving medical, surgical, and supportive interventions.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
