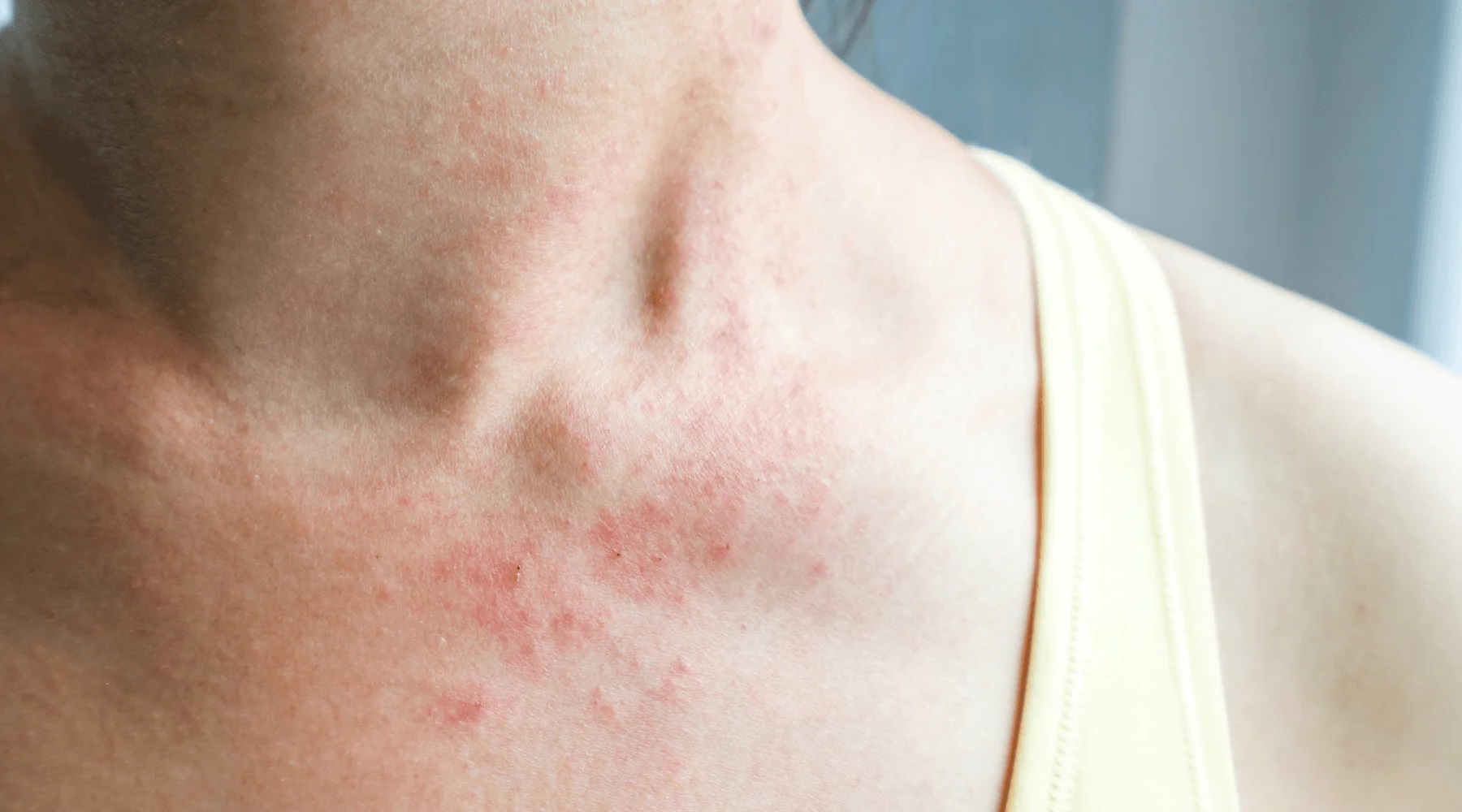
Histamine plays a crucial role in your body's immune response, but what exactly is it? Histamine is a chemical produced by your immune system that helps protect you from allergens and infections. When your body detects a threat, histamine is released, causing symptoms like sneezing, itching, and swelling. These reactions are part of your body's defense mechanism. However, too much histamine can lead to uncomfortable symptoms, often seen in allergic reactions. Understanding histamine can help you manage allergies better and improve your overall health. Let's dive into 20 fascinating facts about this essential chemical and how it impacts your daily life.
What is Histamine?
Histamine is a chemical found in the body that plays a crucial role in the immune system, digestion, and the central nervous system. It acts as a neurotransmitter and is involved in local immune responses. Here are some fascinating facts about histamine:
-
Histamine is a Biogenic Amine: This means it is derived from an amino acid, specifically histidine, through a process called decarboxylation.
-
Stored in Mast Cells: In the body, histamine is primarily stored in mast cells and basophils, which are types of white blood cells.
-
Involved in Allergic Reactions: When the immune system detects an allergen, histamine is released, causing symptoms like itching, swelling, and redness.
Histamine's Role in the Body
Histamine isn't just about allergies. It has several roles that are vital for normal bodily functions. Let's explore these roles:
-
Regulates Stomach Acid: Histamine stimulates the production of gastric acid in the stomach, aiding in digestion.
-
Acts as a Neurotransmitter: In the brain, histamine helps regulate sleep, appetite, and mood.
-
Involved in Inflammation: Histamine increases the permeability of blood vessels, allowing white blood cells to access infected tissues more easily.
Histamine Intolerance
Some people experience adverse reactions to histamine due to an inability to break it down properly. This condition is known as histamine intolerance. Here are some key points:
-
Caused by Enzyme Deficiency: Histamine intolerance often results from a deficiency in diamine oxidase (DAO), the enzyme responsible for breaking down histamine.
-
Symptoms Mimic Allergies: Symptoms include headaches, hives, digestive issues, and nasal congestion, similar to allergic reactions.
-
Diet Plays a Role: Foods high in histamine, like aged cheeses, fermented foods, and alcohol, can exacerbate symptoms.
Histamine in Food
Histamine is present in various foods, and its levels can vary significantly. Understanding which foods contain high levels of histamine can help manage intake:
-
Fermented Foods: Sauerkraut, kimchi, and yogurt are high in histamine due to the fermentation process.
-
Aged Cheeses: Cheeses like cheddar, gouda, and parmesan contain high levels of histamine.
-
Processed Meats: Salami, pepperoni, and other cured meats are rich in histamine.
Histamine and Medication
Certain medications can influence histamine levels in the body. Knowing how these medications interact with histamine can be crucial for managing health:
-
Antihistamines: These drugs block histamine receptors, reducing allergic symptoms.
-
Histamine Blockers: H2 blockers, like ranitidine, reduce stomach acid by blocking histamine receptors in the stomach.
-
Certain Drugs Increase Histamine: Some medications, like morphine and certain antibiotics, can trigger histamine release.
Histamine and the Immune System
Histamine plays a pivotal role in the immune response, particularly in fighting off pathogens and healing injuries. Here are some insights:
-
Promotes Healing: By increasing blood flow to affected areas, histamine helps deliver essential nutrients and immune cells to promote healing.
-
Defends Against Pathogens: Histamine release helps the body respond quickly to infections by making blood vessels more permeable.
-
Triggers Sneezing and Coughing: These reflexes help expel pathogens from the respiratory system.
Histamine Receptors
Histamine exerts its effects through different receptors in the body. Each receptor has a unique role:
-
H1 Receptors: Found in smooth muscles, endothelium, and the brain, these receptors are involved in allergic reactions and sleep regulation.
-
H2 Receptors: Located in the stomach lining, these receptors regulate gastric acid secretion.
Final Thoughts on Histamine
Histamine plays a crucial role in our bodies, affecting everything from allergies to digestion. Understanding its functions can help manage symptoms and improve overall health. Knowing that histamine is involved in immune responses and acts as a neurotransmitter highlights its importance. Foods high in histamine, like aged cheese and fermented products, can trigger reactions in sensitive individuals. Medications like antihistamines can provide relief but come with side effects. Natural remedies, such as quercetin and vitamin C, offer alternative options. Awareness of histamine intolerance can lead to better dietary choices and symptom management. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice. Histamine's impact on our well-being is significant, making it essential to stay informed. By recognizing its effects and taking appropriate measures, we can lead healthier, more comfortable lives. Stay curious and proactive about your health.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


