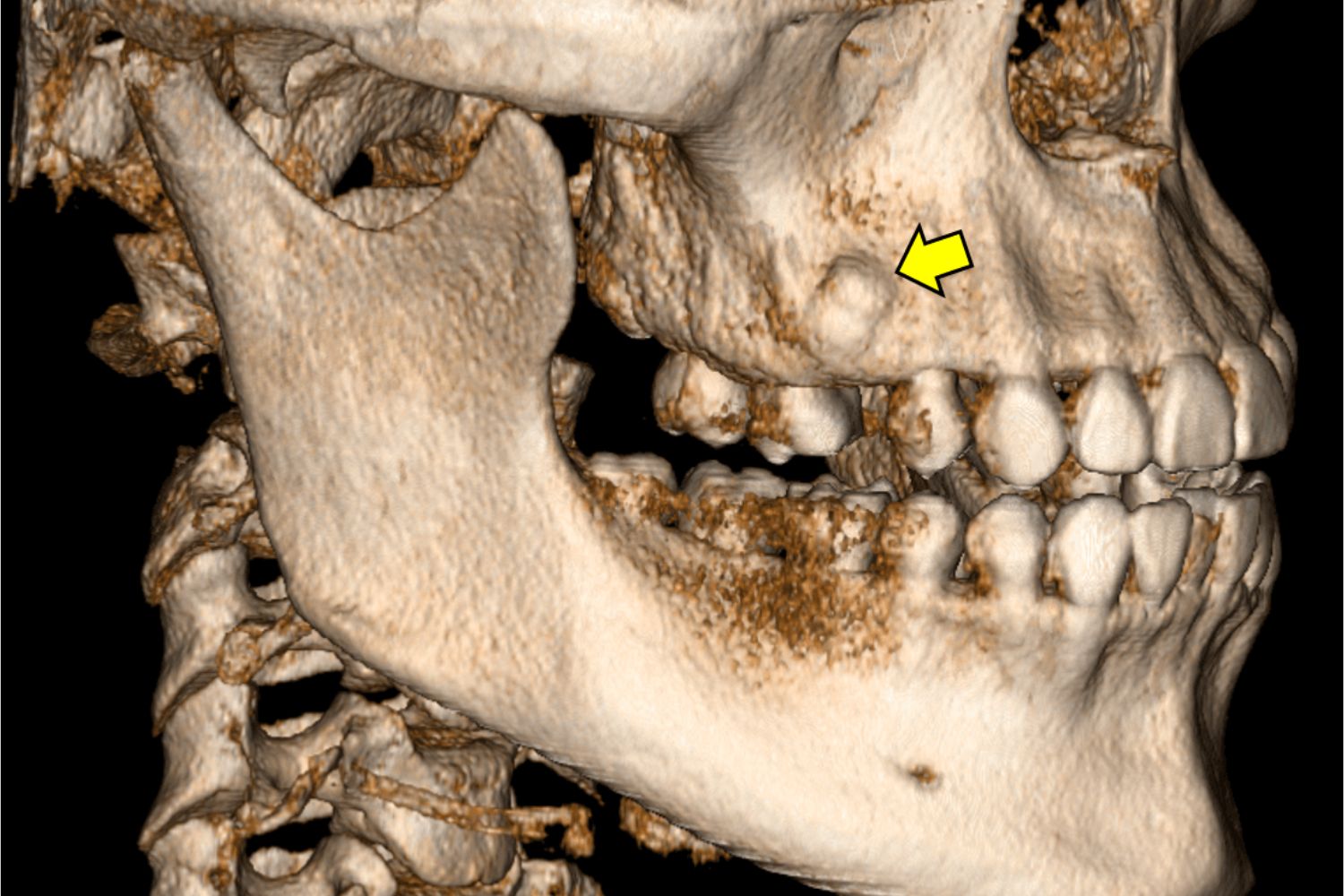
Odontoma might sound like a mysterious term, but it's actually a type of benign tumor related to teeth. These growths are made up of dental tissue like enamel, dentin, and cementum. Odontomas are usually discovered during routine dental X-rays since they often don't cause any symptoms. They can be classified into two main types: compound and complex. Compound odontomas resemble small, tooth-like structures, while complex odontomas appear as a mass of dental tissue. Although they are non-cancerous, odontomas can sometimes interfere with the normal eruption of teeth, making early detection and treatment important. Curious about more details? Keep reading to uncover 50 fascinating facts about odontomas!
Key Takeaways:
- Odontomas are benign tumors related to tooth development, often found in children and young adults. They can cause delays in permanent tooth eruption and are usually treated with surgical removal.
- Understanding the causes and risk factors of odontomas, such as genetic factors and trauma to the mouth, can help in early detection and prevention. Good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups are important for maintaining oral health.
What is an Odontoma?
An odontoma is a type of benign tumor linked to tooth development. These growths are made up of dental tissue, including enamel, dentin, and pulp. They are often discovered during routine dental X-rays.
- Odontomas are the most common type of odontogenic tumor.
- They are usually asymptomatic, meaning they don't cause pain or discomfort.
- These tumors are often found in children and young adults.
- Odontomas can be classified into two types: compound and complex.
- Compound odontomas resemble small, tooth-like structures.
- Complex odontomas appear as a mass of dental tissue without any resemblance to a tooth.
- They are typically discovered during routine dental X-rays.
- Odontomas can cause delays in the eruption of permanent teeth.
- They are usually located in the upper jaw, especially around the front teeth.
- Surgical removal is the standard treatment for odontomas.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of odontomas can help in early detection and prevention. While the exact cause is not always clear, several factors may contribute to their development.
- Genetic factors can play a role in the development of odontomas.
- Trauma to the mouth or jaw can increase the risk of developing an odontoma.
- Infections in the mouth may also contribute to the formation of these tumors.
- Certain syndromes, like Gardner's syndrome, are associated with a higher risk of odontomas.
- Hormonal changes during childhood and adolescence can influence their development.
- Odontomas are more common in males than females.
- They are often associated with impacted teeth.
- Poor oral hygiene is not a direct cause but can contribute to other risk factors.
- Some studies suggest a link between odontomas and developmental disturbances in teeth.
- Early diagnosis can prevent complications related to delayed tooth eruption.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Although odontomas are usually asymptomatic, they can sometimes cause noticeable symptoms. Diagnosis often involves a combination of clinical examination and imaging techniques.
- Odontomas are often discovered incidentally during routine dental X-rays.
- They can cause swelling in the affected area.
- Delayed eruption of permanent teeth is a common symptom.
- In rare cases, they can cause pain or discomfort.
- A dentist may notice a missing tooth or an abnormal growth during an examination.
- Panoramic X-rays are commonly used to diagnose odontomas.
- Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) can provide detailed images of the tumor.
- A biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
- Odontomas can sometimes be mistaken for other types of dental cysts or tumors.
- Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications.
Treatment and Management
Treating odontomas typically involves surgical removal. Post-surgery care is crucial for ensuring proper healing and preventing recurrence.
- Surgical removal is the most common treatment for odontomas.
- The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia.
- In some cases, general anesthesia may be required, especially for young children.
- Post-surgery, patients may experience swelling and discomfort.
- Pain management often involves over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent infection.
- Regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor healing.
- In rare cases, additional surgery may be needed if the odontoma recurs.
- Orthodontic treatment may be required to address any issues with tooth alignment.
- Maintaining good oral hygiene can aid in the healing process.
Prevention and Prognosis
While it may not always be possible to prevent odontomas, understanding the risk factors and maintaining good oral health can help. The prognosis for individuals with odontomas is generally excellent.
- Regular dental check-ups can help in early detection.
- Good oral hygiene practices can reduce the risk of infections that may contribute to odontomas.
- Wearing a mouthguard during sports can prevent trauma to the mouth.
- Genetic counseling may be beneficial for individuals with a family history of odontomas.
- Early treatment can prevent complications related to delayed tooth eruption.
- The prognosis for individuals with odontomas is generally excellent.
- Most people recover fully after surgical removal.
- Recurrence of odontomas is rare but possible.
- Long-term follow-up may be necessary for individuals with a history of odontomas.
- Awareness and education about odontomas can help in early detection and treatment.
Final Thoughts on Odontomas
Odontomas, those mysterious dental tumors, are more common than you might think. They often go unnoticed until a routine dental check-up reveals their presence. While they sound scary, odontomas are usually benign and treatable. Early detection is key, so regular dental visits are crucial. If left untreated, they can cause issues like delayed tooth eruption or misalignment. Treatment typically involves surgical removal, which is straightforward and has a high success rate. Understanding odontomas helps in reducing anxiety and ensuring timely intervention. So, next time you're at the dentist, remember the importance of those X-rays. They might just catch something you didn't even know was there. Stay informed, keep up with your dental health, and you'll be well-prepared to handle any surprises that come your way.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
