Zirconia is a fascinating material with a wide range of applications, from jewelry to industrial uses. But what exactly makes zirconia so special? Zirconia is a crystalline form of zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), known for its impressive hardness and durability. It's often used as a diamond substitute in jewelry due to its brilliant sparkle and affordability. Beyond its aesthetic appeal, zirconia is also highly valued in engineering and medical fields. Its resistance to heat and wear makes it ideal for cutting tools, dental implants, and even fuel cells. Curious about more intriguing facts? Let's dive into 25 amazing things you might not know about zirconia!
What is Zirconia?
Zirconia, also known as zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium. It's a material with a wide range of applications due to its unique properties. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this versatile substance.
-
Natural Occurrence: Zirconia is found naturally in the mineral baddeleyite. However, most zirconia used in industries is synthetically produced.
-
High Melting Point: It has an incredibly high melting point of about 2,715°C (4,919°F), making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
-
Hardness: Zirconia is extremely hard, ranking about 8.5 on the Mohs scale, just below diamond and sapphire.
-
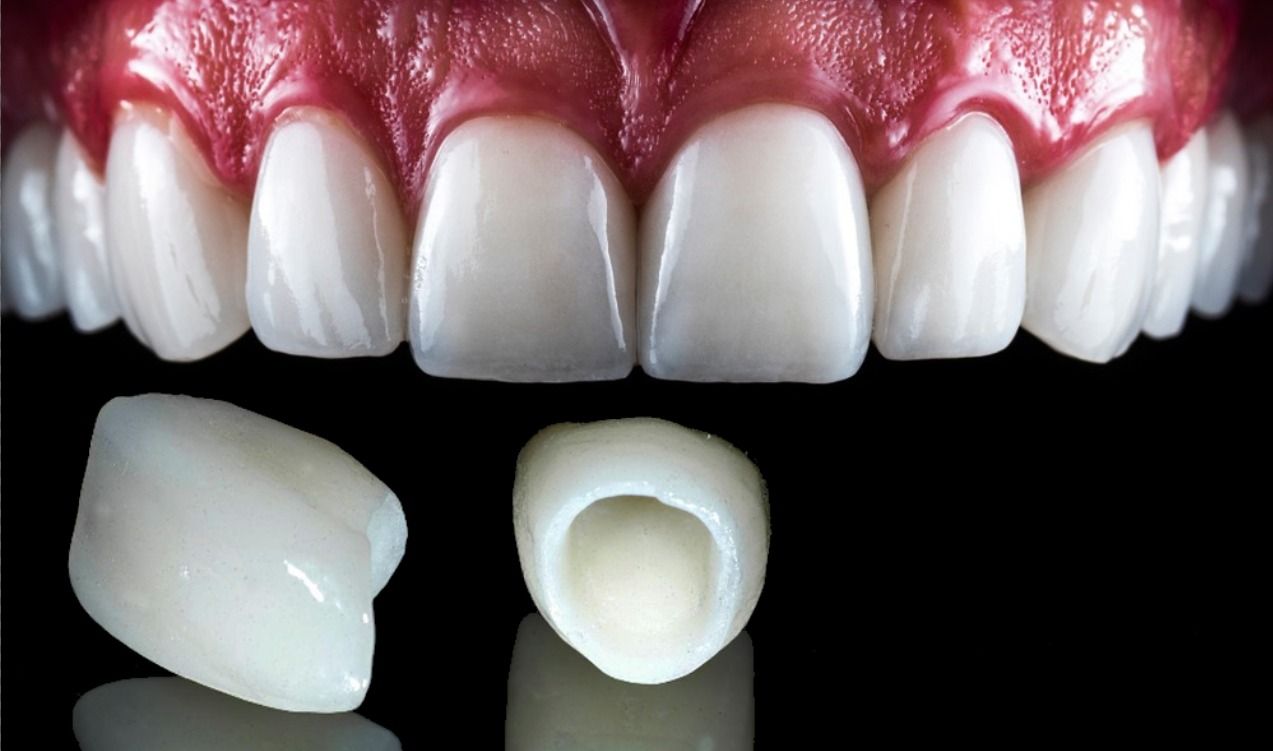
Dental Uses: It's widely used in dentistry for making crowns, bridges, and implants due to its biocompatibility and strength.
-
Ceramic Knives: Zirconia is used to make ceramic knives, which are known for their sharpness and durability.
Zirconia in Technology
Zirconia's unique properties make it invaluable in various technological applications. Here are some ways it contributes to modern tech.
-
Thermal Barrier Coatings: Used in jet engines and gas turbines, zirconia coatings protect components from extreme heat.
-
Fuel Cells: Zirconia is a key material in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), which convert chemical energy into electrical energy efficiently.
-
Oxygen Sensors: In automotive applications, zirconia-based oxygen sensors help control emissions by monitoring the oxygen levels in exhaust gases.
-
Electronics: Zirconia is used in the production of capacitors and resistors due to its excellent dielectric properties.
-
Optical Properties: It’s used in optical fibers and lenses because of its high refractive index and transparency.
Zirconia in Jewelry
Zirconia is also a popular material in the jewelry industry, often used as a diamond substitute. Here’s why it shines in this field.
-
Cubic Zirconia: This synthetic gemstone mimics the appearance of diamonds but is much more affordable.
-
Brilliance: Cubic zirconia has a higher dispersion rate than diamonds, giving it more fire and brilliance.
-
Color Variety: It can be manufactured in various colors, making it versatile for different jewelry designs.
-
Durability: While not as hard as diamonds, cubic zirconia is still quite durable and resistant to scratches.
-
Ethical Choice: Unlike diamonds, cubic zirconia is free from the ethical concerns associated with diamond mining.
Medical Applications of Zirconia
Zirconia's biocompatibility and strength make it ideal for various medical applications. Here are some ways it’s used in healthcare.
-
Prosthetics: Used in hip and knee replacements, zirconia provides a durable and biocompatible option for prosthetic joints.
-
Dental Implants: Its use in dental implants ensures long-lasting and natural-looking results.
-
Surgical Instruments: Zirconia is used to make surgical instruments that are both strong and resistant to corrosion.
-
Bone Scaffolds: Research is ongoing into using zirconia for bone scaffolds to aid in bone regeneration.
-
Orthodontic Brackets: Zirconia brackets are used in orthodontics for their strength and aesthetic appeal.
Environmental and Industrial Uses
Zirconia's properties also make it useful in various environmental and industrial applications. Here are some examples.
-
Catalysts: Zirconia is used as a catalyst in chemical reactions, particularly in the petrochemical industry.
-
Water Filtration: It’s used in water filtration systems to remove impurities and improve water quality.
-
Abrasives: Zirconia is used in abrasive materials for grinding and polishing due to its hardness.
-
Refractories: Its high melting point makes zirconia ideal for use in refractory materials that line furnaces and kilns.
-
Pigments: Zirconia is used as a white pigment in ceramics and paints, providing a bright and durable finish.
Zirconia's Fascinating World
Zirconia isn't just a pretty face in the gem world. This mineral, known for its brilliance and durability, has a rich history and a wide range of uses. From ancient times, where it was mistaken for diamonds, to modern applications in dentistry and industrial tools, zirconia proves its worth. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and resist wear makes it invaluable in many fields.
Whether you're fascinated by its geological origins or its role in cutting-edge technology, zirconia offers something for everyone. Next time you see a sparkling piece of jewelry, remember the incredible journey of zirconia from the depths of the Earth to your hand. This gem truly shines in more ways than one. So, keep an eye out for zirconia—it’s more than just a diamond look-alike.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
