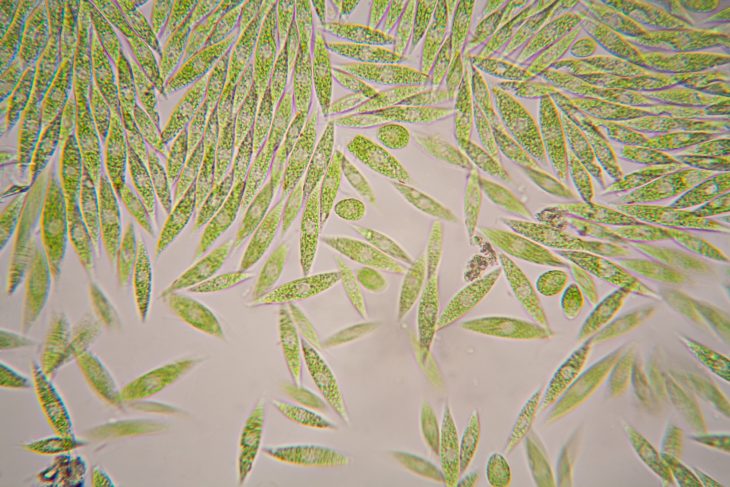
Nature’s diversity never ceases to amaze us, and Euglena is a perfect example of the wonders that lie within our world. Euglena is a single-celled microorganism that captivates scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. This versatile creature possesses characteristics of both plants and animals, making it a subject of fascination for researchers.
In this article, we delve into the captivating world of Euglena and unveil 19 intriguing facts that shed light on its peculiarities. From its structure and behavior to its ecological significance, prepare to be astounded by the remarkable attributes of this enigmatic microorganism.
Ancient Origins
Euglena has been thriving on Earth for millions of years, with fossil records dating back to the Late Precambrian period. This resilient microorganism has managed to adapt and survive through various environmental changes over time.
Diverse Habitat
Euglena can be found in various aquatic environments, including freshwater, saltwater, and even brackish water. Its adaptability allows it to thrive in diverse ecosystems such as ponds, lakes, and oceans across the globe.
Unique Cell Structure
At first glance, Euglena appears like an elongated cell with a whip-like tail called a flagellum. This structure allows Euglena to move through the water and find favorable conditions for growth.
Photosynthetic Abilities
Euglena possesses chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis. These specialized organelles enable Euglena to produce energy by converting sunlight into chemical energy, just like plants.
Mixotrophic Nature
While Euglena can photosynthesize and produce its own food, it can also switch to a heterotrophic mode of nutrition when sunlight is scarce. In such instances, Euglena feeds on organic matter in its environment.
Eye Spot or Stigma
Euglena features a unique sensory organelle called an eye spot or stigma. The eye spot is sensitive to light and helps Euglena detect the intensity and direction of light, allowing it to move towards or away from light sources.
Vibrant Coloration
Some species of Euglena exhibit striking colors, ranging from green and red to yellow and brown. These pigments provide protection against harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation and aid in the absorption of sunlight for photosynthesis.
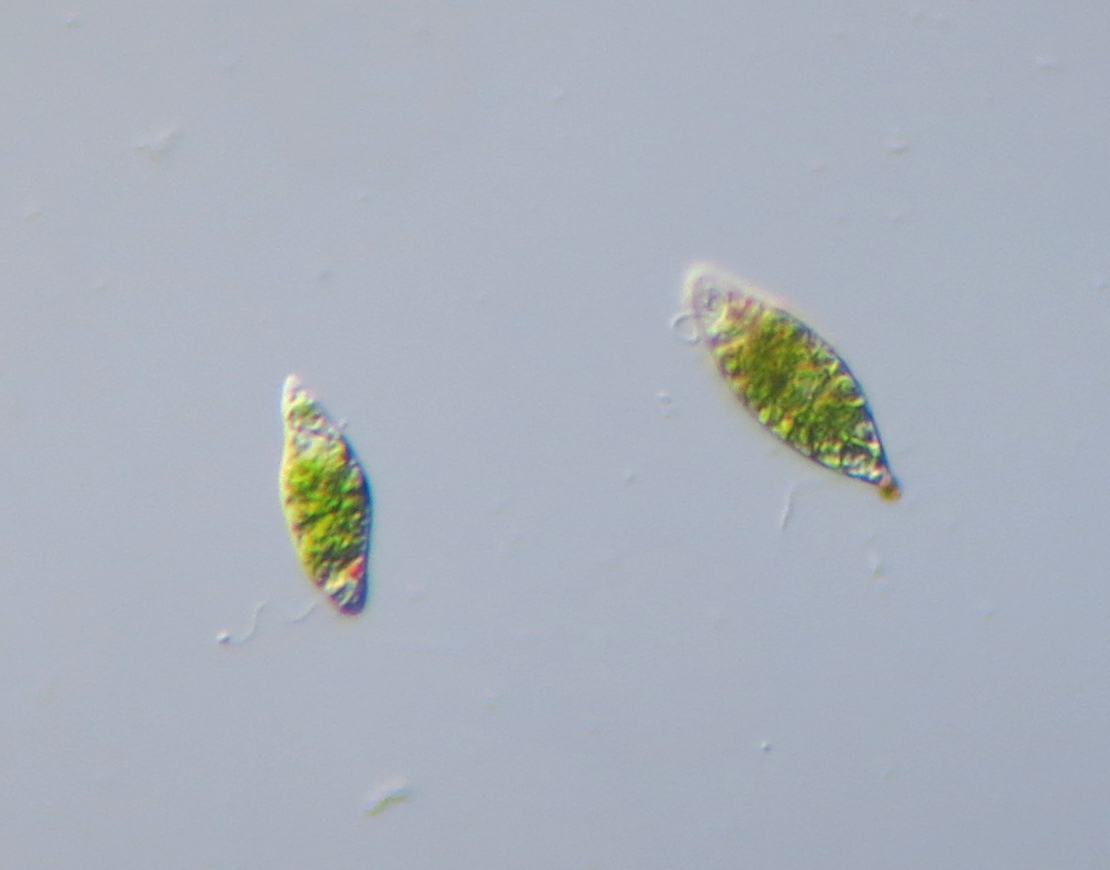
Asexual Reproduction
Euglena primarily reproduces asexually through a process called binary fission. During binary fission, the cell divides into two identical daughter cells, ensuring a rapid population growth rate.
Sexual Reproduction
Under unfavorable conditions, Euglena can engage in a form of sexual reproduction known as conjugation. During conjugation, two individuals exchange genetic material, promoting genetic diversity within the population.
Oxygen Production
As Euglena performs photosynthesis, it releases oxygen as a byproduct. This oxygen production contributes to the overall oxygenation of aquatic environments, benefiting other organisms in the ecosystem.
Bioremediation Potential
Euglena demonstrates the remarkable potential for bioremediation. This means it can help remove pollutants from water bodies by absorbing heavy metals, organic compounds, and other harmful substances.
Source of Biomass
Due to its rapid growth and high protein content, Euglena shows promise as a potential source of biomass for various applications, including animal feed, biofuels, and nutritional supplements.
Extremophile Adaptations
Certain species of Euglena have evolved to survive in extreme environments. Some can tolerate high salinity levels, while others thrive in acidic or alkaline conditions, expanding the frontiers of life as we know it.
Sensitivity to Environmental Factors
Euglena serves as a bioindicator, reflecting changes in its environment. It responds sensitively to factors like light intensity, nutrient availability, temperature, and pollution levels, making it useful in environmental monitoring.
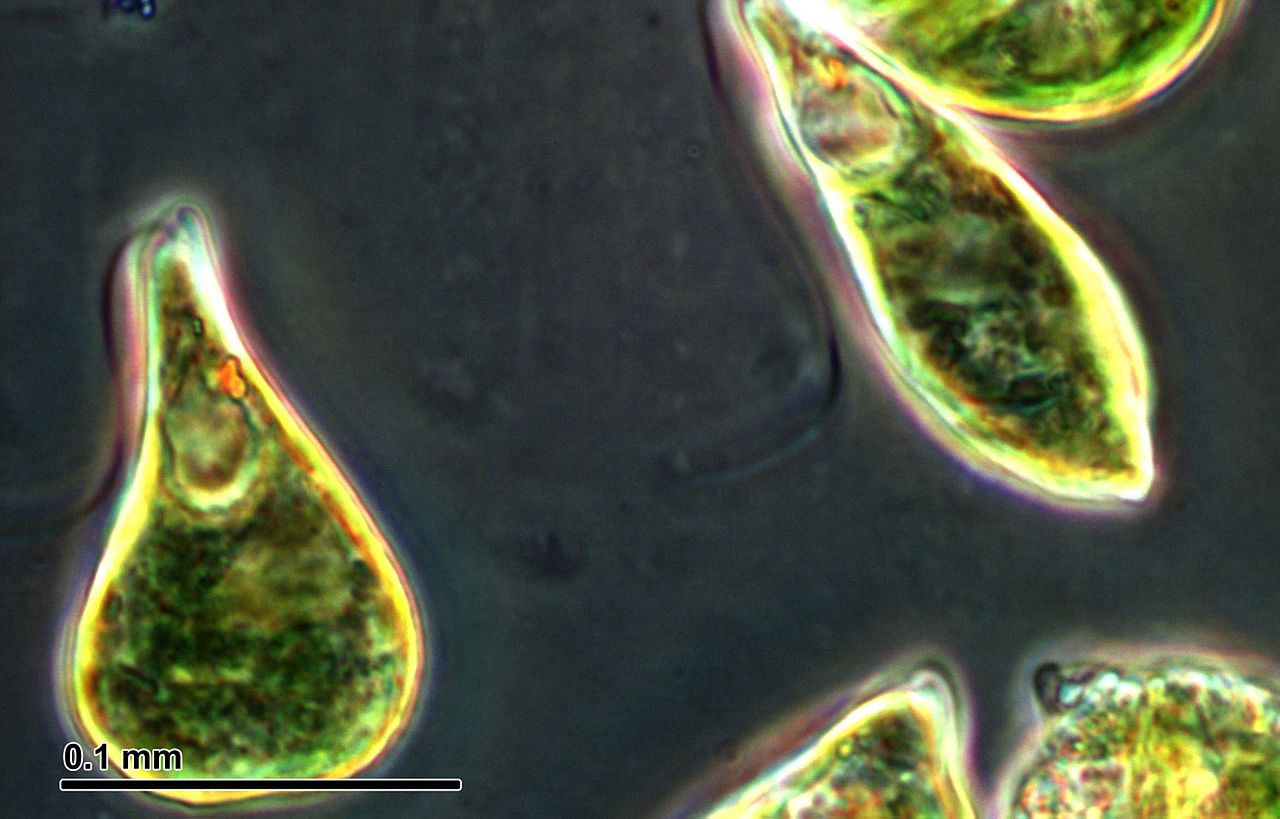
Research in Space
Euglena’s ability to adapt and survive in various conditions has attracted the attention of scientists studying the potential for life beyond Earth. Experiments involving Euglena have been conducted on space missions to investigate its response to microgravity and other extraterrestrial factors.
Potential for Medical Applications
Studies have shown that certain compounds derived from Euglena, such as paramylon, possess antimicrobial properties. Researchers are exploring the potential use of Euglena-based substances in the development of novel antibiotics and antifungal drugs.
Inspiration for Solar Technology
The unique light-harvesting capabilities of Euglena’s chloroplasts have inspired researchers in the field of solar technology. By studying the structure and function of Euglena’s photosynthetic apparatus, scientists seek to improve the efficiency of solar cells.
Educational Significance
Euglena serves as an excellent model organism for educational purposes, providing students and researchers with an accessible subject for studying cell biology, photosynthesis, and the interplay between organisms and their environment.
Biodiversity Treasure
Euglena’s incredible diversity and adaptability make it a treasure trove for biodiversity exploration. Scientists continue to discover new species and uncover the hidden intricacies of Euglena’s genetic makeup, enriching our understanding of life on Earth.
Conclusion
Euglena, the enigmatic microorganism that bridges the plant and animal kingdoms, offers a captivating glimpse into the marvels of nature. With its unique features, ecological significance, and potential applications, Euglena continues to be a subject of fascination and exploration for scientists worldwide. From its ability to produce oxygen and remove pollutants to its adaptability in extreme environments, Euglena truly exemplifies the resilience and diversity of life on our planet.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can Euglena be harmful to humans?
While most species of Euglena are harmless to humans, some can produce toxins under specific conditions. It is essential to exercise caution when encountering unknown Euglena species.
How do Euglena cells move?
Euglena cells move using their whip-like tail called a flagellum. The flagellum propels the cell through the water, allowing it to navigate its environment.
Is Euglena visible to the naked eye?
Euglena cells are generally microscopic and cannot be seen with the naked eye. They require a microscope for proper observation.
Can Euglena survive in extreme temperatures?
Different species of Euglena have varying tolerances for temperature extremes. Some can survive in freezing temperatures, while others thrive in hot springs with high temperatures.
Are Euglena cells found on land?
Euglena cells are primarily found in aquatic environments. While they can occasionally be present in moist soil or damp surfaces, they are predominantly aquatic organisms.
How do scientists classify Euglena?
Euglena belongs to the genus Euglena, which is classified under the phylum Euglenozoa. It is further categorized into various species based on their unique characteristics.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
