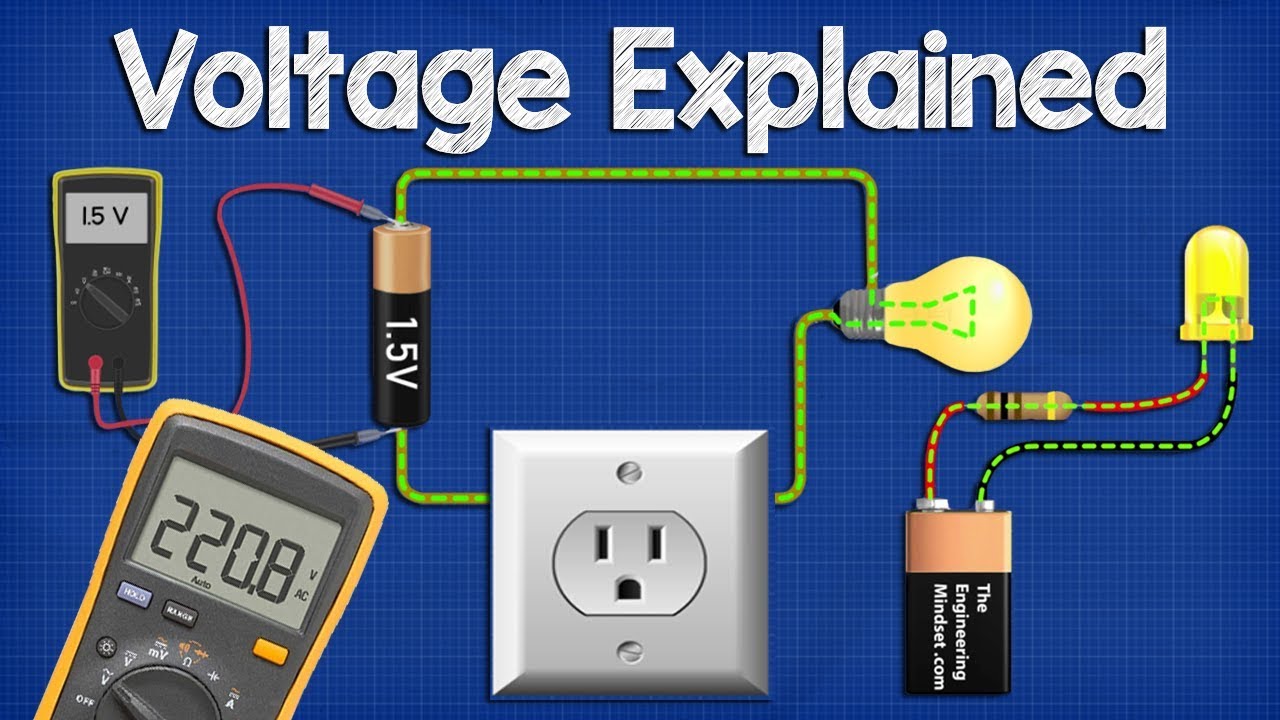
Voltage is a fundamental concept in electricity and electronics, but what exactly is it? Voltage is the difference in electric potential between two points. Think of it like the pressure that pushes electric charges through a conductor. Without voltage, electric current wouldn't flow, and our gadgets wouldn't work. From powering your smartphone to lighting up cities, voltage plays a crucial role in our daily lives. But there's more to it than just powering devices. Did you know that voltage can be found in nature, like in lightning or even within our own bodies? Let's dive into some intriguing facts about voltage that might just spark your curiosity!
What is Voltage?
Voltage, also known as electric potential difference, is a fundamental concept in the world of electricity. It measures the potential energy difference between two points in an electric field. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about voltage.
-
Voltage is measured in volts, named after Alessandro Volta, an Italian physicist who invented the electric battery.
-
Voltage can be thought of as the "pressure" that pushes electric charges through a conductor.
-
The symbol for voltage is "V," and it's often represented in equations by the letter "E" or "U."
-
A common household outlet in the United States typically provides 120 volts of alternating current (AC).
-
In Europe, standard household voltage is usually 230 volts AC.
-
Batteries provide direct current (DC) voltage, which flows in one direction, unlike AC which alternates direction.
How Voltage Works
Understanding how voltage works can help demystify many electrical concepts. Voltage is essential for the functioning of any electrical device.
-
Voltage is created by the separation of positive and negative charges.
-
In a simple circuit, voltage is supplied by a power source, like a battery, and drives the current through the circuit.
-
Ohm's Law states that voltage (V) equals current (I) times resistance (R): V = I * R.
-
Voltage drop occurs when electrical energy is lost as heat or light in a circuit component.
-
High voltage is used in power transmission to reduce energy loss over long distances.
-
Transformers are used to step up (increase) or step down (decrease) voltage levels in power systems.
Types of Voltage
Voltage comes in various forms, each with unique characteristics and applications. Knowing these types can help in understanding different electrical systems.
-
Direct Voltage (DC) remains constant and flows in one direction.
-
Alternating Voltage (AC) changes direction periodically, typically in a sine wave pattern.
-
Peak voltage is the maximum voltage level in an AC cycle.
-
Root Mean Square (RMS) voltage is the effective voltage value of AC, equivalent to a DC voltage that delivers the same power.
-
Static voltage is generated by static electricity, often seen when you get a shock after walking on a carpet.
-
Dynamic voltage changes over time and is used in various electronic devices.
Voltage in Everyday Life
Voltage plays a crucial role in our daily lives, powering everything from small gadgets to large appliances.
-
Most smartphones operate on a voltage of around 3.7 volts DC.
-
Car batteries typically provide 12 volts DC to start the engine and power electrical systems.
-
USB ports usually supply 5 volts DC to charge devices and transfer data.
-
High-voltage power lines can carry voltages as high as 765,000 volts to transport electricity over long distances.
-
Voltage stabilizers are used to maintain a constant voltage level to protect sensitive electronic equipment.
-
Lightning can produce voltages of up to 1 billion volts, causing massive electrical discharges.
Fun Facts about Voltage
Voltage isn't just a dry scientific concept; it has some intriguing and fun aspects too.
-
Electric eels can generate a voltage of up to 600 volts to stun prey and defend against predators.
-
The human body can generate a small voltage, typically around 0.1 volts, due to the movement of ions in cells.
Voltage is a fascinating and essential part of our world, influencing everything from the smallest electronic devices to the largest power grids. Understanding these facts can give you a deeper appreciation for the invisible force that powers our modern lives.
Voltage Facts: The Final Spark
Voltage, often called electric potential difference, is a fundamental concept in electricity. It powers our homes, gadgets, and even our cars. Understanding voltage helps us grasp how electrical circuits work and why safety measures are crucial.
From the basics of measuring voltage in volts to the fascinating fact that lightning can reach up to a billion volts, these tidbits highlight its importance. Voltage isn't just about numbers; it's about the energy that drives our modern world.
Whether you're a student, a hobbyist, or just curious, knowing these facts can spark a deeper interest in electricity. Voltage plays a vital role in our daily lives, often unnoticed but always essential. So next time you flip a switch or charge your phone, remember the incredible power of voltage at work.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
