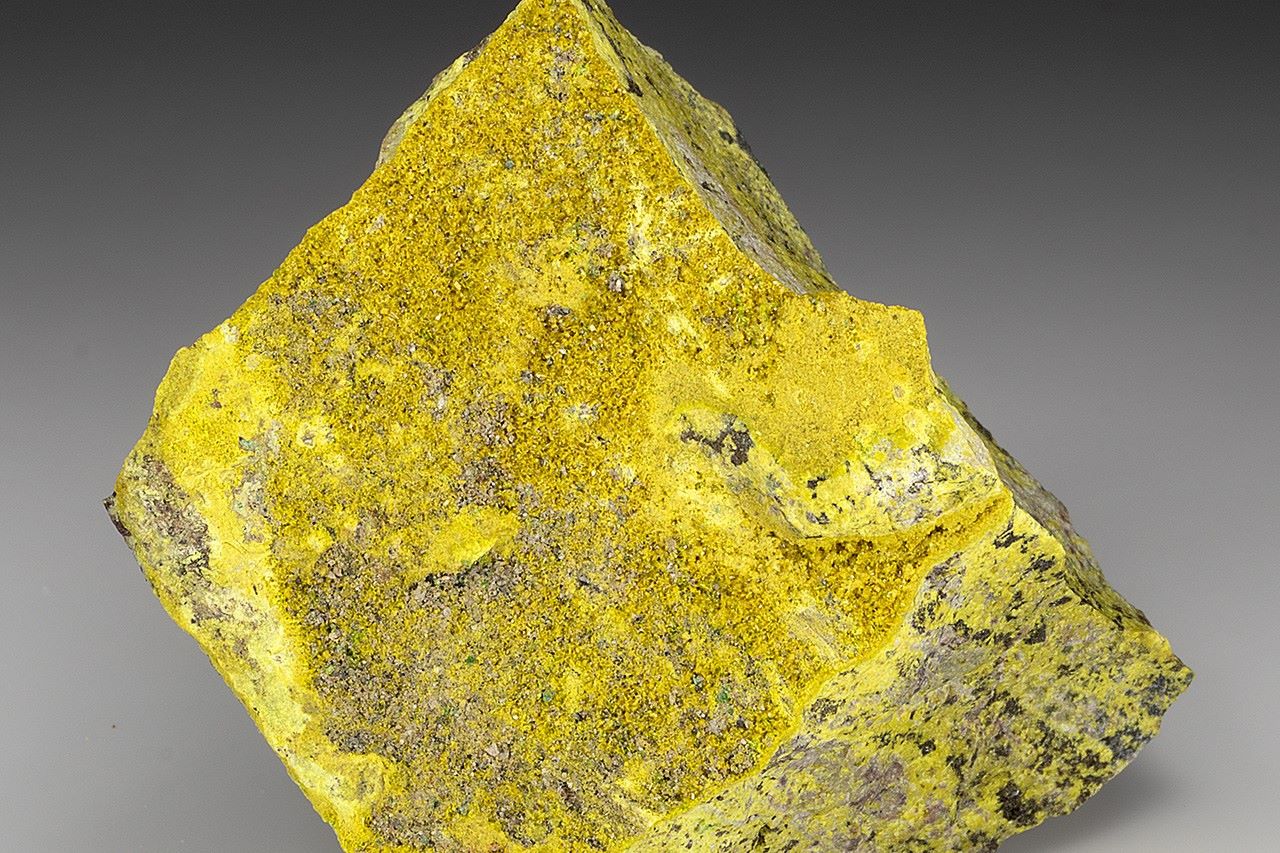
Schoepite is a fascinating mineral with a rich history and unique properties. Named after Belgian mineralogist Alfred Schoep, this mineral is primarily composed of uranium, making it highly radioactive. Found in the oxidized zones of uranium deposits, schoepite often appears as bright yellow crystals. Its striking color and rarity make it a sought-after specimen for collectors. Beyond its visual appeal, schoepite plays a crucial role in understanding uranium's behavior in the environment. Scientists study it to gain insights into radioactive decay and contamination. Schoepite also has industrial significance, particularly in the nuclear energy sector. Understanding its properties can help improve safety measures and waste management practices. Whether you're a geology enthusiast or just curious about minerals, learning about schoepite offers a glimpse into the intricate world of natural elements.
Key Takeaways:
- Schoepite is a bright yellow, radioactive mineral found in uranium-rich areas worldwide. It's used in nuclear energy, research, and as a teaching tool, but requires careful handling due to its radioactivity.
- Schoepite's unique properties, like its fluorescent nature and softness, make it a fascinating subject for scientists and mineral collectors. However, its radioactive nature demands cautious handling and storage to ensure safety.
What is Schoepite?
Schoepite is a fascinating mineral with a rich history and unique properties. Named after Belgian mineralogist Alfred Schoep, this mineral is known for its vibrant yellow color and association with uranium deposits. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about Schoepite.
-
Schoepite is a uranium mineral: It primarily consists of uranium oxide hydroxide, making it a significant source of uranium.
-
Discovered in 1923: Alfred Schoep first identified this mineral in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
-
Bright yellow color: Its striking yellow hue makes it easily recognizable among other minerals.
-
Radioactive: Due to its uranium content, Schoepite is naturally radioactive.
-
Hydrated mineral: Schoepite contains water molecules within its crystal structure.
Where is Schoepite Found?
Schoepite is not just limited to one location. It can be found in various parts of the world, often in regions rich in uranium deposits.
-
Democratic Republic of Congo: The first discovery site and one of the primary sources.
-
United States: Found in several states, including Colorado and Utah.
-
Canada: Notably present in the uranium-rich regions of Saskatchewan.
-
Australia: Known to occur in the Northern Territory's uranium mines.
-
Kazakhstan: Another significant source of Schoepite, contributing to its global distribution.
How is Schoepite Formed?
The formation of Schoepite involves specific geological processes, often linked to the oxidation of uranium minerals.
-
Oxidation of uraninite: Schoepite forms when uraninite, another uranium mineral, oxidizes.
-
Secondary mineral: It typically forms as a secondary mineral in the oxidation zones of uranium deposits.
-
Weathering process: The weathering of uranium-rich rocks can lead to the formation of Schoepite.
-
Hydrothermal activity: Sometimes, hydrothermal processes contribute to its formation.
-
Association with other minerals: Often found alongside minerals like becquerelite and curite.
Uses of Schoepite
While Schoepite itself is not widely used, its association with uranium makes it significant in various industries.
-
Uranium extraction: It serves as an important source of uranium for nuclear energy.
-
Scientific research: Used in studies related to mineralogy and geology.
-
Radiation shielding: Its radioactive properties make it useful in radiation shielding materials.
-
Educational purposes: Often used in academic settings to teach about radioactive minerals.
-
Collection: Mineral collectors value Schoepite for its unique properties and vibrant color.
Interesting Properties of Schoepite
Schoepite possesses several unique properties that make it a subject of interest for scientists and collectors alike.
-
Monoclinic crystal system: It crystallizes in the monoclinic system, giving it a distinct structure.
-
Soft mineral: With a Mohs hardness of 2-3, Schoepite is relatively soft.
-
Fluorescent: Under UV light, Schoepite exhibits fluorescence, adding to its visual appeal.
-
Solubility: It is soluble in acids, which can affect its stability in certain environments.
-
Density: Schoepite has a relatively high density due to its uranium content.
Safety and Handling of Schoepite
Given its radioactive nature, handling Schoepite requires caution and adherence to safety protocols.
-
Radiation precautions: Proper protective gear is essential when handling Schoepite to avoid radiation exposure.
-
Storage: It should be stored in lead-lined containers to contain its radioactivity.
-
Handling guidelines: Always use gloves and avoid inhaling dust particles when working with Schoepite.
-
Disposal: Follow local regulations for the disposal of radioactive materials to ensure environmental safety.
-
Health risks: Prolonged exposure to Schoepite can pose health risks, emphasizing the need for careful handling.
Schoepite: A Fascinating Mineral
Schoepite, a uranium mineral, holds a unique place in geology. Found primarily in uranium deposits, it’s known for its bright yellow color and complex structure. This mineral forms through the oxidation of uraninite and other uranium-bearing minerals. Its chemical composition, primarily uranium oxide, makes it a subject of interest for both scientists and collectors.
Understanding schoepite’s properties helps in studying uranium deposits and their environmental impact. This mineral’s radioactivity requires careful handling, but its study provides valuable insights into uranium’s behavior in nature. Collectors prize schoepite for its vibrant color and crystal formations.
In summary, schoepite is more than just a mineral. It’s a window into the world of uranium, offering clues about geological processes and environmental considerations. Whether you’re a scientist, collector, or just curious, schoepite’s story is a captivating chapter in the book of Earth’s minerals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
