Bilirubin is a fascinating compound that plays a crucial role in our bodies. Ever wondered why bruises change color or why newborns sometimes look a bit yellow? That's bilirubin at work! This yellowish pigment forms when red blood cells break down. The liver processes it, and then it's excreted from the body. If the liver doesn't handle bilirubin properly, it can lead to jaundice, a condition where the skin and eyes turn yellow. Understanding bilirubin helps us grasp how our bodies manage waste and maintain balance. Ready to dive into 50 intriguing facts about bilirubin? Let's get started!
What is Bilirubin?
Bilirubin is a yellow compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in vertebrates. It is responsible for the yellow color of bruises and the brown color of feces. Here are some fascinating facts about bilirubin.
- Bilirubin is produced when red blood cells break down.
- The liver processes bilirubin, making it water-soluble.
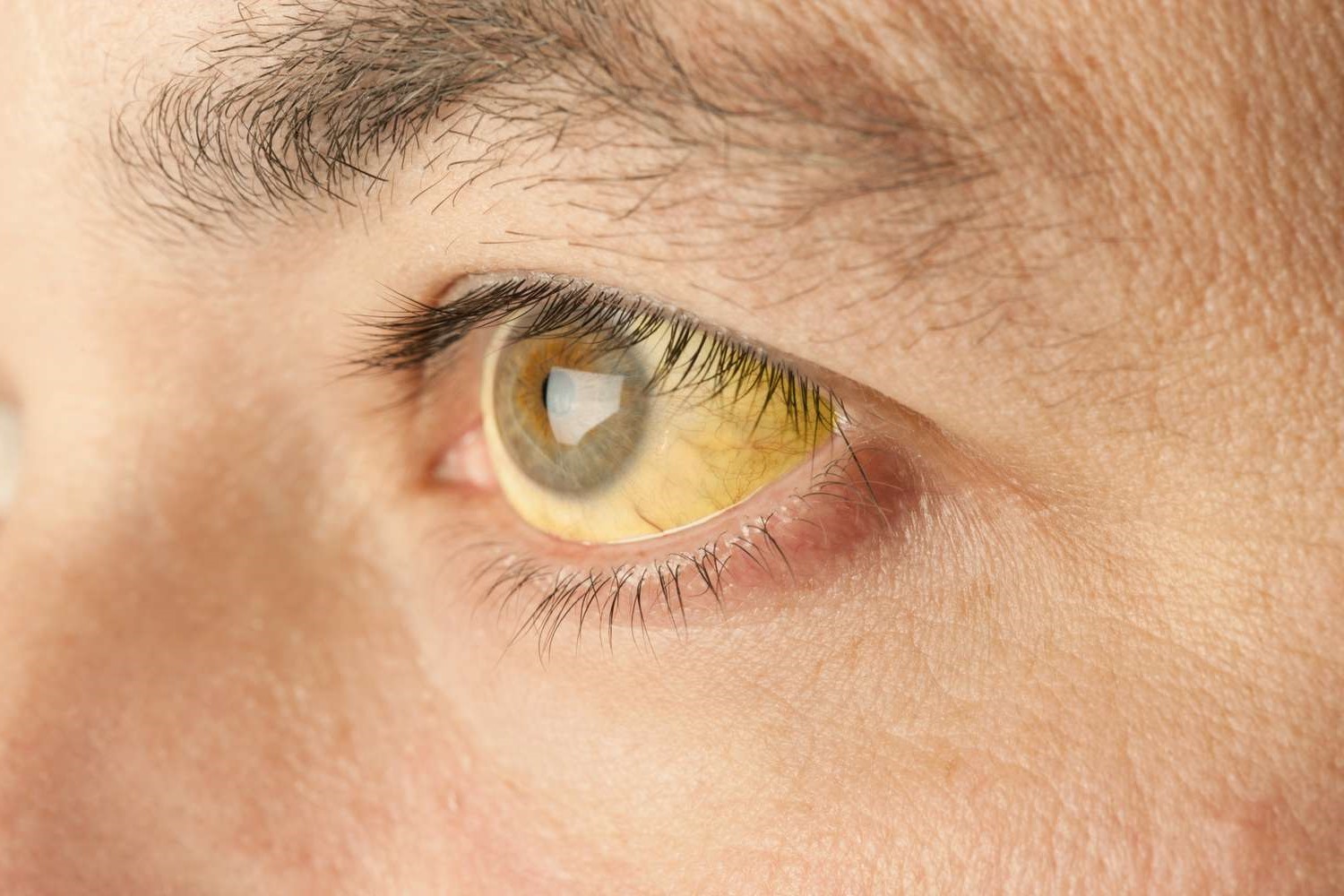
- High levels of bilirubin can cause jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- Newborns often have higher bilirubin levels due to immature liver function.
- Bilirubin is excreted in bile and urine.
- It is a potent antioxidant, protecting cells from damage.
- Bilirubin levels are measured through blood tests.
- Gilbert's syndrome is a common, mild liver disorder that affects bilirubin processing.
- Bilirubin can be toxic at high levels, especially to the brain.
- Phototherapy is used to treat high bilirubin levels in newborns.
Bilirubin in the Body
Understanding how bilirubin functions in the body can help us appreciate its importance and potential issues.
- Bilirubin is formed from the breakdown of hemoglobin in red blood cells.
- The spleen plays a role in breaking down old red blood cells, releasing bilirubin.
- Bilirubin travels to the liver bound to albumin, a protein in the blood.
- In the liver, bilirubin is conjugated with glucuronic acid, making it water-soluble.
- Conjugated bilirubin is excreted into the bile ducts and stored in the gallbladder.
- During digestion, bile is released into the small intestine, aiding in fat digestion.
- In the intestines, bacteria convert bilirubin into urobilinogen.
- Some urobilinogen is reabsorbed into the bloodstream and excreted by the kidneys.
- The rest of the urobilinogen is converted to stercobilin, giving feces its brown color.
- Bilirubin metabolism involves multiple organs, including the liver, spleen, and intestines.
Health Implications of Bilirubin Levels
Bilirubin levels can indicate various health conditions, making it a crucial marker in medical diagnostics.
- Elevated bilirubin levels can indicate liver disease or bile duct obstruction.
- Low bilirubin levels are rare and usually not a cause for concern.
- Chronic high bilirubin levels can lead to kernicterus, a type of brain damage.
- Bilirubin levels can be affected by medications, infections, and genetic conditions.
- Hemolytic anemia, where red blood cells are destroyed faster than they are made, can increase bilirubin levels.
- Liver function tests often include bilirubin measurements.
- Bilirubin levels can fluctuate throughout the day, with higher levels in the afternoon.
- Stress and fasting can temporarily increase bilirubin levels.
- Regular monitoring of bilirubin levels is essential for individuals with liver conditions.
- Bilirubin levels can be managed through diet, medication, and lifestyle changes.
Interesting Facts About Bilirubin
Beyond its medical significance, bilirubin has some intriguing aspects worth noting.
- Bilirubin is responsible for the yellow color of bruises as they heal.
- It contributes to the yellow color of urine.
- Bilirubin can be found in the brain, where it may have a protective role.
- Some animals, like the Greenland shark, have unique ways of processing bilirubin.
- Bilirubin has been studied for its potential anti-inflammatory properties.
- High bilirubin levels can cause itching, a condition known as pruritus.
- Bilirubin levels can be influenced by diet, including the intake of certain fruits and vegetables.
- Alcohol consumption can affect bilirubin metabolism.
- Bilirubin has been used in research to study liver function and disease.
- Some people have naturally higher bilirubin levels without any health issues.
Bilirubin in Newborns
Newborns often experience higher bilirubin levels, leading to a condition known as neonatal jaundice.
- Neonatal jaundice is common and usually harmless.
- The condition occurs because newborns have more red blood cells and immature liver function.
- Breastfeeding can help reduce bilirubin levels in newborns.
- Phototherapy, using blue light, helps break down bilirubin in the skin.
- Severe cases of neonatal jaundice may require a blood transfusion.
- Monitoring bilirubin levels in newborns is crucial to prevent complications.
- Bilirubin levels typically peak around the third to fifth day after birth.
- Premature babies are more likely to develop neonatal jaundice.
- Genetic factors can influence bilirubin levels in newborns.
- Early detection and treatment of high bilirubin levels can prevent serious health issues.
The Final Word on Bilirubin
Bilirubin, a yellow compound found in bile, plays a crucial role in our bodies. It’s produced when red blood cells break down and is processed by the liver. High levels can indicate liver problems or other health issues, while low levels are usually less concerning. Understanding bilirubin helps in diagnosing conditions like jaundice, hepatitis, and gallstones.
Keeping an eye on bilirubin levels through regular check-ups can provide valuable insights into your liver health. If you notice symptoms like yellowing of the skin or eyes, it’s wise to consult a healthcare professional. They can run tests to determine if your bilirubin levels are within a healthy range.
Knowledge about bilirubin empowers you to take proactive steps for better health. Stay informed, stay healthy, and always listen to your body’s signals.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.