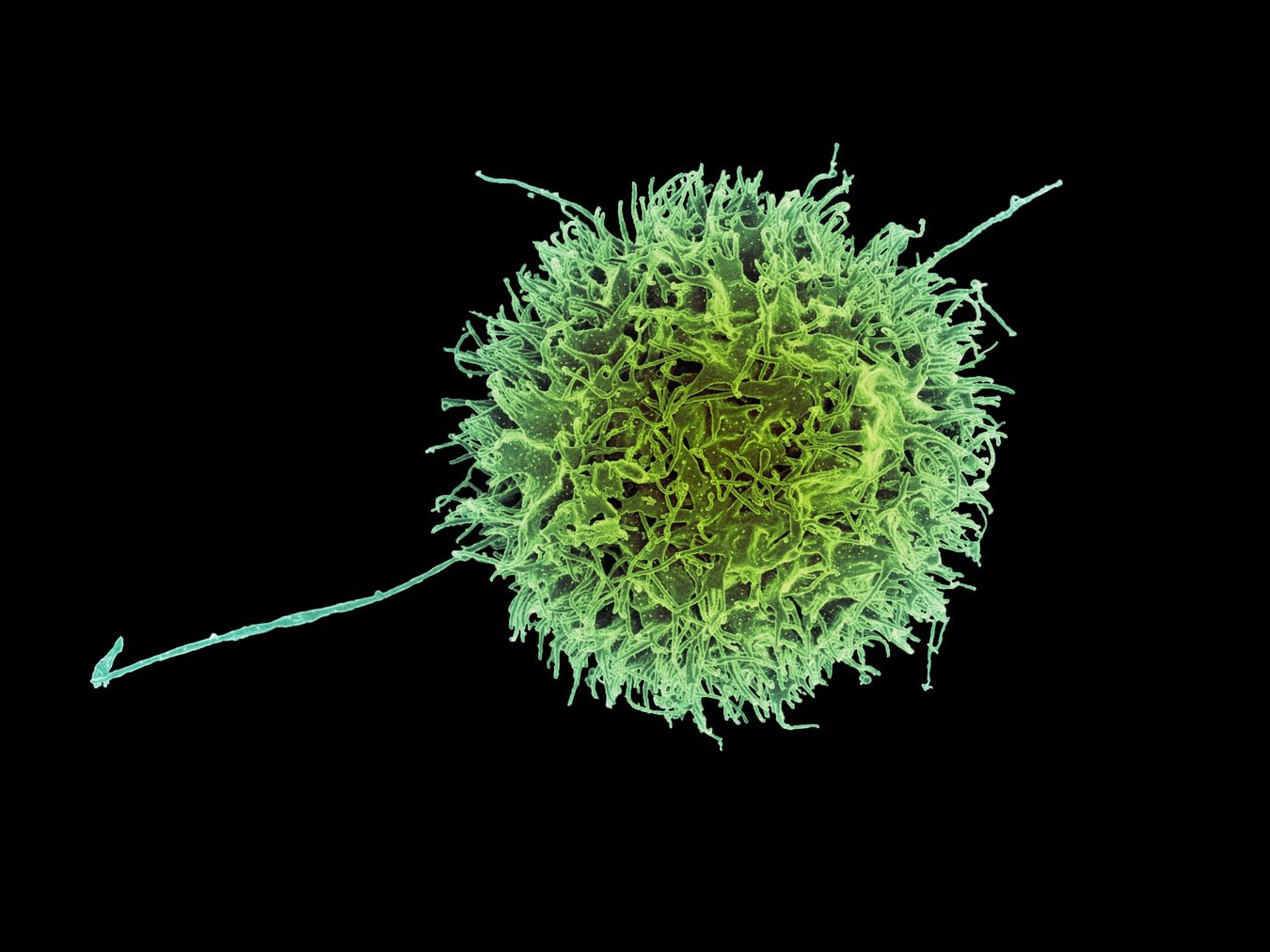
Natural Killer (NK) cells might sound like something out of a sci-fi movie, but they play a crucial role in your immune system. These cells act as the body's first line of defense against infections and cancer. NK cells patrol your body, identifying and destroying harmful invaders without needing prior exposure. Think of them as the immune system's special forces, always ready to spring into action. But how do they work? What makes them so effective? In this post, we'll uncover 40 intriguing facts about these tiny warriors, shedding light on their importance and how they keep you healthy. Get ready to be amazed by the power of NK cells!
Key Takeaways:
- Natural Killer (NK) cells are powerful immune cells that can recognize and destroy infected or cancerous cells without needing prior activation. They play a crucial role in the body's defense against infections and diseases.
- NK cells have potential therapeutic applications in treating cancer, viral infections, and autoimmune diseases. Researchers are exploring ways to enhance their function for medical treatments, offering hope for future breakthroughs in medicine.
What Are Natural Killer (NK) Cells?
Natural Killer (NK) cells are a type of white blood cell that play a crucial role in the body's immune system. They are part of the innate immune system, which means they act as the body's first line of defense against infections and diseases.
- NK cells are a type of lymphocyte, a subset of white blood cells.
- They are called "natural killers" because they do not require prior activation to kill cells that are infected or cancerous.
- NK cells are found in the blood, spleen, liver, and other tissues.
- They make up about 10-15% of the lymphocytes in the human body.
- NK cells can recognize stressed cells in the absence of antibodies and MHC, allowing for a faster immune reaction.
How Do NK Cells Work?
NK cells have unique mechanisms to identify and destroy harmful cells. They use a combination of receptors and signaling pathways to detect abnormalities.
- NK cells use activating and inhibitory receptors to distinguish between healthy and abnormal cells.
- When an NK cell encounters a target cell, it releases cytotoxic granules that contain perforin and granzymes.
- Perforin forms pores in the target cell's membrane, allowing granzymes to enter and induce apoptosis (cell death).
- NK cells also produce cytokines like interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) to enhance the immune response.
- They can kill virus-infected cells without the need for antibodies or antigen presentation.
Importance of NK Cells in Cancer
NK cells play a significant role in controlling and eliminating cancer cells. Their ability to target and destroy tumor cells makes them a focus of cancer research.
- NK cells can recognize and kill cancer cells that have downregulated MHC class I molecules.
- They are involved in the surveillance of tumor cells, preventing the spread of cancer.
- NK cell activity is often reduced in cancer patients, leading to increased tumor growth.
- Researchers are exploring ways to enhance NK cell function for cancer immunotherapy.
- NK cells can be engineered to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) to target specific cancer cells.
NK Cells in Viral Infections
NK cells are essential in the body's defense against viral infections. They can quickly respond to and eliminate virus-infected cells.
- NK cells are among the first responders to viral infections.
- They can recognize and kill cells infected with viruses like influenza, HIV, and hepatitis.
- NK cells produce cytokines that help control viral replication.
- Some viruses have evolved mechanisms to evade NK cell detection.
- Enhancing NK cell activity is a potential strategy for treating viral infections.
Factors Affecting NK Cell Activity
Several factors can influence the activity and effectiveness of NK cells. Understanding these factors can help in developing therapies to boost NK cell function.
- Age can affect NK cell activity, with older individuals often having reduced NK cell function.
- Stress and lack of sleep can weaken NK cell activity.
- Certain medications, like corticosteroids, can suppress NK cell function.
- Regular exercise has been shown to enhance NK cell activity.
- Diet and nutrition, particularly the intake of vitamins and minerals, can impact NK cell function.
Therapeutic Applications of NK Cells
NK cells have potential therapeutic applications in treating various diseases. Researchers are exploring ways to harness their power for medical treatments.
- NK cell-based therapies are being developed for cancer treatment.
- NK cells can be used in adoptive cell transfer therapy, where NK cells are isolated, activated, and infused back into the patient.
- Researchers are investigating the use of NK cells in treating autoimmune diseases.
- NK cells are being studied for their potential in treating viral infections.
- Genetic engineering techniques are being used to enhance NK cell function for therapeutic purposes.
Interesting Facts About NK Cells
NK cells have some fascinating characteristics that make them unique among immune cells. These interesting facts highlight their importance and versatility.
- NK cells can "remember" previous encounters with certain pathogens, a feature traditionally associated with adaptive immunity.
- They can interact with other immune cells, like dendritic cells and macrophages, to coordinate the immune response.
- NK cells can influence the outcome of pregnancy by regulating the immune environment in the uterus.
- They play a role in controlling the body's response to stress and inflammation.
- NK cells can be activated by certain cytokines, like interleukin-2 (IL-2) and interleukin-15 (IL-15).
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is uncovering new insights into NK cells and their potential applications. The future holds exciting possibilities for harnessing NK cells in medicine.
- Researchers are studying the role of NK cells in aging and age-related diseases.
- Advances in genetic engineering are enabling the creation of more effective NK cell therapies.
- Studies are exploring the use of NK cells in combination with other immunotherapies for cancer treatment.
- Researchers are investigating the potential of NK cells in treating chronic infections.
- The development of NK cell-based vaccines is an emerging area of research.
Final Thoughts on NK Cells
Natural Killer (NK) cells are fascinating warriors in our immune system. They play a crucial role in defending against viruses and cancer. Unlike other immune cells, NK cells don't need prior exposure to recognize threats. They act swiftly, making them a first line of defense. Research shows their potential in cancer therapy, offering hope for new treatments. Understanding NK cells better can lead to breakthroughs in medicine. Their ability to distinguish healthy cells from infected ones is remarkable. Scientists continue to study these cells to harness their full potential. NK cells remind us of the body's incredible ability to protect itself. As research progresses, we may see even more innovative uses for these powerful cells. Keep an eye on future developments in immunotherapy and NK cell research. The future looks promising for harnessing the power of NK cells in medicine.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
