C4 plants are fascinating due to their unique photosynthesis process, which sets them apart from other plants. But what exactly makes them special? C4 photosynthesis allows these plants to thrive in hot, dry environments where others struggle. This process is more efficient at capturing carbon dioxide, leading to faster growth and better water use. Corn, sugarcane, and sorghum are some well-known examples of C4 plants. These plants play a crucial role in agriculture and food production. Understanding their unique characteristics can help improve crop yields and sustainability. Ready to learn more? Here are 37 intriguing facts about C4 plants!
What Are C4 Plants?
C4 plants are a group of plants that have a unique way of photosynthesis, allowing them to thrive in hot, dry environments. This adaptation helps them conserve water and efficiently use carbon dioxide. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about these resilient plants.
-
C4 plants use a specialized form of photosynthesis called the C4 pathway. This process helps them capture carbon dioxide more efficiently than C3 plants, especially under high light intensity and temperatures.
-
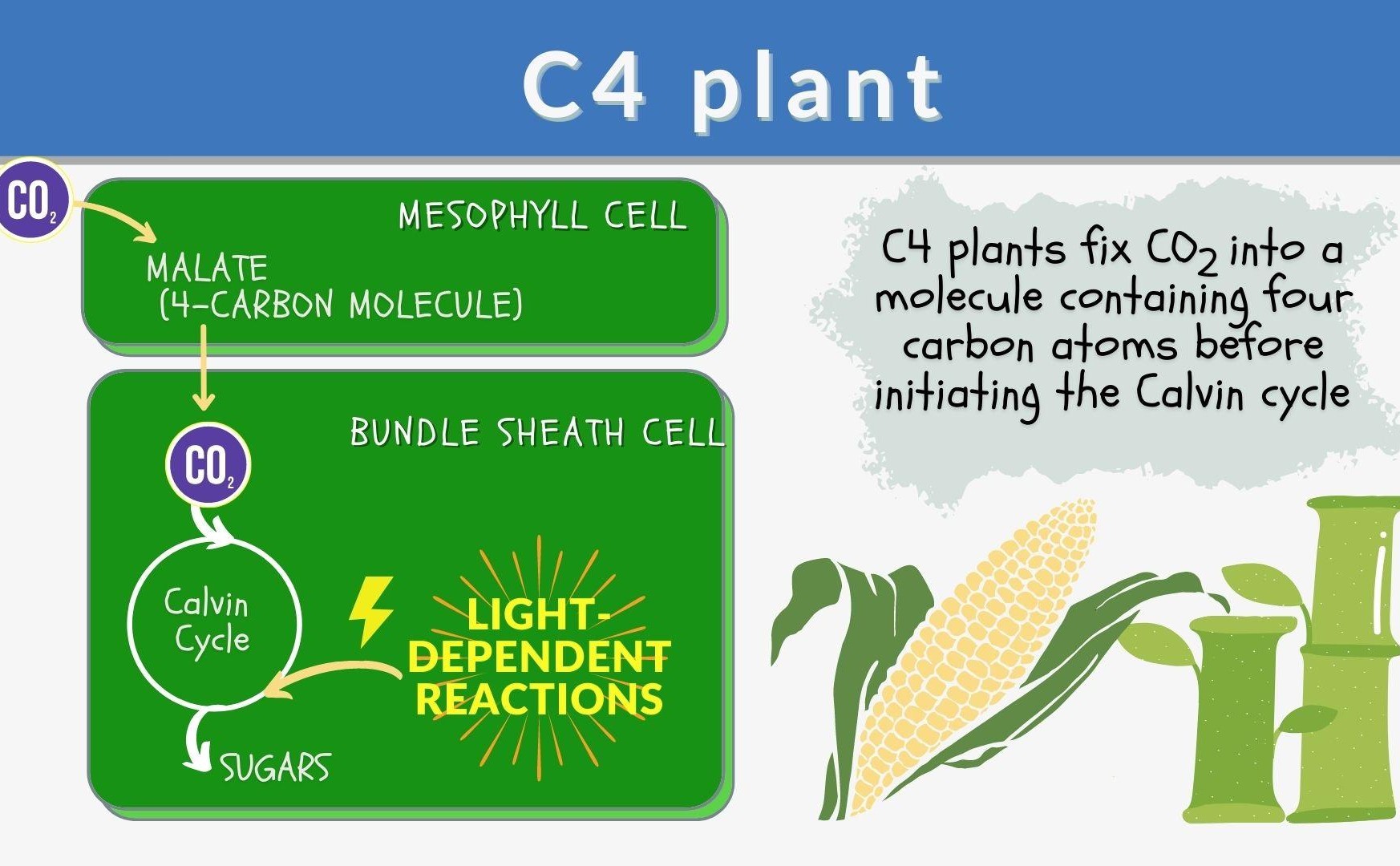
They are named after the four-carbon molecule, oxaloacetate, which is the first product of carbon fixation in these plants. This is different from C3 plants, where the first product is a three-carbon molecule.
-
C4 plants have a unique leaf anatomy known as Kranz anatomy. This structure includes bundle sheath cells surrounding the vascular bundles, which play a crucial role in the C4 pathway.
Examples of C4 Plants
Many common plants fall under the C4 category. These plants are often found in tropical and subtropical regions.
-
Maize (corn) is one of the most well-known C4 plants. It is a staple food crop in many parts of the world and thrives in warm climates.
-
Sugarcane is another important C4 plant. It is widely cultivated for sugar production and biofuel.
-
Sorghum, a drought-resistant grain, is also a C4 plant. It is used for food, animal fodder, and biofuel.
-
Millets, including pearl millet and finger millet, are C4 plants. They are hardy crops that grow well in arid and semi-arid regions.
-
Amaranth, a leafy green vegetable, is a C4 plant. It is known for its high nutritional value and resilience to harsh growing conditions.
Advantages of C4 Photosynthesis
C4 photosynthesis provides several benefits that help these plants survive and thrive in challenging environments.
-
C4 plants are more efficient in photosynthesis under high light and temperature conditions. This efficiency allows them to grow faster and produce more biomass.
-
They have a higher water-use efficiency compared to C3 plants. This means they can produce more biomass with less water, making them ideal for arid regions.
-
C4 plants are better adapted to low carbon dioxide concentrations. This adaptation helps them maintain high rates of photosynthesis even when CO2 levels are low.
-
They can tolerate saline soils better than C3 plants. This tolerance allows them to grow in areas where other crops might struggle.
Evolution of C4 Photosynthesis
The evolution of C4 photosynthesis is a fascinating topic that sheds light on how plants adapt to their environments.
-
C4 photosynthesis evolved independently in multiple plant lineages. This convergent evolution suggests that it is a highly advantageous trait.
-
The C4 pathway likely evolved as a response to declining atmospheric CO2 levels. This adaptation helped plants maintain efficient photosynthesis when CO2 was scarce.
-
C4 plants first appeared around 30 million years ago. This timing coincides with significant changes in global climate and atmospheric composition.
-
There are over 8,000 species of C4 plants. These species are spread across 19 different plant families.
C4 Plants and Agriculture
C4 plants play a significant role in agriculture, providing food, fodder, and biofuel.
-
C4 crops like maize and sugarcane are major sources of food and energy. They are cultivated on millions of hectares worldwide.
-
C4 plants contribute to food security in many developing countries. Their resilience to harsh conditions makes them reliable crops in regions prone to drought.
-
Research is ongoing to improve the yield and stress tolerance of C4 crops. Advances in genetic engineering and breeding techniques hold promise for future agricultural productivity.
-
C4 plants are being studied for their potential to mitigate climate change. Their efficient carbon fixation could help reduce atmospheric CO2 levels.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite their advantages, C4 plants face challenges that researchers are working to overcome.
-
Breeding C4 traits into C3 crops is a major research goal. Success in this area could revolutionize agriculture by making more crops resilient to climate change.
-
Understanding the genetic basis of C4 photosynthesis is crucial for crop improvement. Advances in genomics and biotechnology are helping scientists unravel the complexities of this trait.
-
Climate change poses a threat to C4 plants. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns could impact their growth and productivity.
-
Efforts are underway to develop C4 rice. This ambitious project aims to create a rice variety with the efficiency of C4 photosynthesis, potentially boosting yields and food security.
Interesting Facts About C4 Plants
Here are some more intriguing tidbits about C4 plants that highlight their unique characteristics and importance.
-
C4 plants can fix carbon dioxide at night. This ability helps them conserve water by keeping their stomata closed during the hottest part of the day.
-
They have a higher nitrogen-use efficiency than C3 plants. This means they can grow well in soils with lower nitrogen levels.
-
C4 plants can thrive in nutrient-poor soils. Their efficient photosynthesis and nutrient use make them ideal for marginal lands.
-
Some C4 plants are used in traditional medicine. For example, amaranth has been used for its medicinal properties in various cultures.
-
C4 plants can help combat soil erosion. Their extensive root systems help stabilize the soil and prevent erosion.
-
They play a role in carbon sequestration. By capturing and storing carbon dioxide, C4 plants can help mitigate climate change.
-
C4 plants are often more competitive than C3 plants in warm environments. This competitive edge allows them to dominate in certain ecosystems.
-
They can grow in a wide range of habitats. From grasslands to savannas, C4 plants are found in diverse environments around the world.
-
C4 plants have a unique enzyme called PEP carboxylase. This enzyme helps them capture carbon dioxide more efficiently than C3 plants.
-
They can tolerate high levels of light intensity. This tolerance allows them to thrive in open, sunny areas where other plants might struggle.
-
C4 plants are often used in biofuel production. Their high biomass yield makes them ideal candidates for renewable energy sources.
-
They have a lower photorespiration rate than C3 plants. This means they lose less energy during photosynthesis, making them more efficient.
-
C4 plants are a focus of research for improving crop resilience. Scientists are exploring ways to transfer C4 traits to other crops to enhance their productivity and stress tolerance.
The Final Word on C4 Plants
C4 plants are fascinating. They’ve got a unique way of photosynthesis that helps them thrive in hot, dry climates. This makes them super important for agriculture, especially in regions where water is scarce. Corn, sugarcane, and sorghum are some of the most well-known C4 plants. They’re not just food sources but also key players in biofuel production. Understanding how C4 plants work can help scientists develop crops that are more resilient to climate change. This could be a game-changer for food security worldwide. So, next time you munch on corn or sip on a sugarcane drink, remember the incredible science behind these plants. They’re not just part of our diet; they’re a crucial part of our future.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
