The Law of Independent Assortment is a fundamental principle in genetics, first introduced by Gregor Mendel. This law states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes. But what does this mean for you? It means that the inheritance of one trait generally doesn't affect the inheritance of another. For example, the gene for flower color in peas doesn't influence the gene for plant height. This principle helps explain the genetic variation seen in offspring. Understanding this law is crucial for grasping how traits are passed down through generations. Ready to dive into some intriguing facts about this cornerstone of genetics? Let's get started!
What is the Law of Independent Assortment?
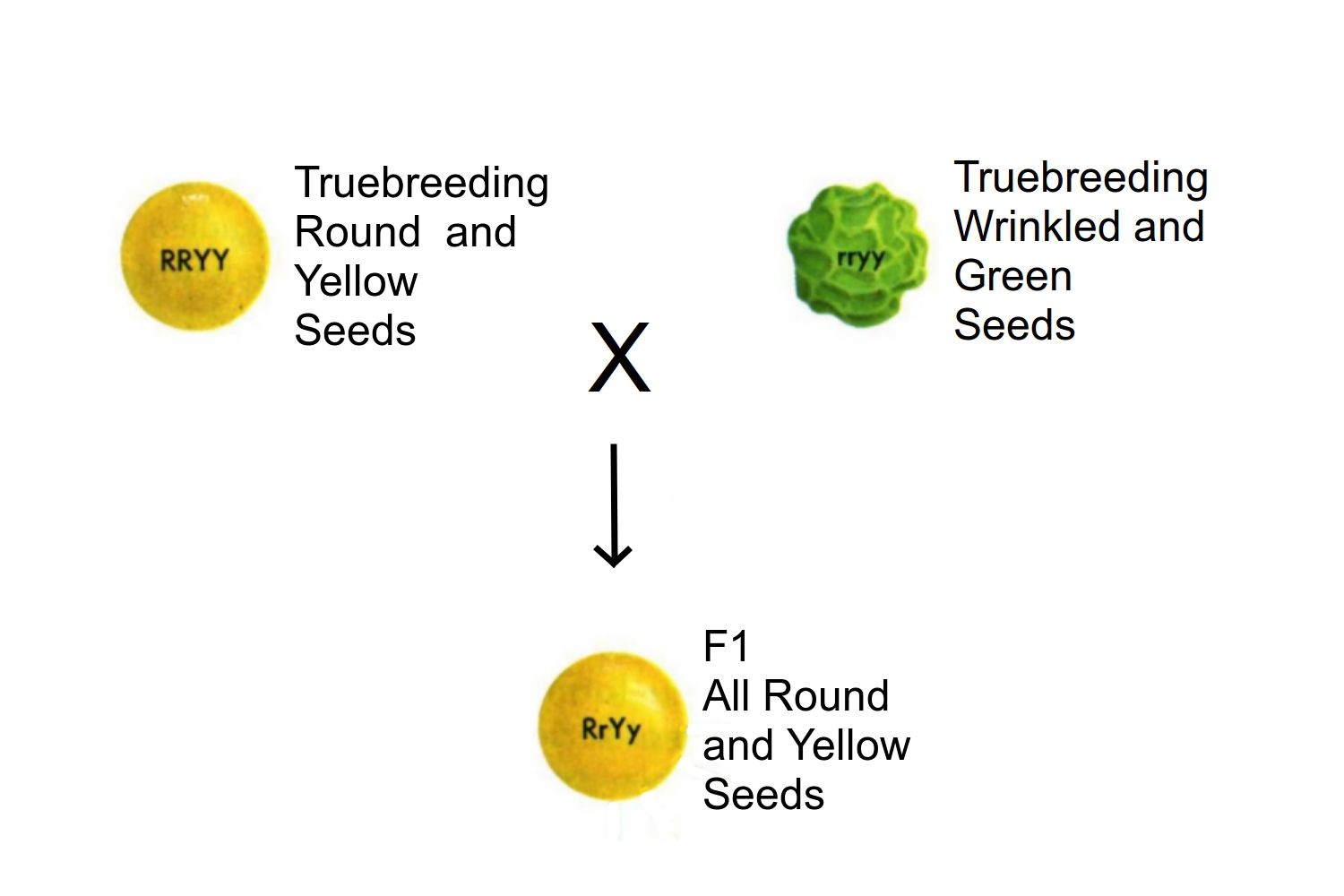
The Law of Independent Assortment is one of Gregor Mendel's foundational principles of genetics. It explains how different genes independently separate from one another when reproductive cells develop. This law plays a crucial role in understanding genetic variation.
- Gregor Mendel formulated the Law of Independent Assortment in the 1860s through his experiments with pea plants.
- This law states that alleles of different genes get distributed independently of one another during gamete formation.
- Mendel's work laid the groundwork for modern genetics, earning him the title "Father of Genetics."
- The law applies to genes located on different chromosomes or those far apart on the same chromosome.
- Independent assortment contributes to genetic diversity by creating new combinations of traits.
How Does Independent Assortment Occur?
Understanding the mechanics behind independent assortment helps grasp how genetic diversity arises. This process occurs during meiosis, a type of cell division that produces gametes.
- During meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up and then separate into different gametes.
- The random orientation of chromosome pairs during metaphase I leads to independent assortment.
- Each gamete receives a random mix of maternal and paternal chromosomes.
- Crossing over, which occurs during prophase I, can further shuffle genes between homologous chromosomes.
- Independent assortment and crossing over together ensure that each gamete is genetically unique.
Why is Independent Assortment Important?
The significance of independent assortment extends beyond just genetic variation. It has profound implications for evolution, agriculture, and medicine.
- Genetic variation produced by independent assortment is essential for natural selection.
- It allows populations to adapt to changing environments over generations.
- In agriculture, breeders use this principle to develop crops with desirable traits.
- Understanding independent assortment aids in predicting genetic disorders and inheritance patterns.
- It also helps in studying complex traits influenced by multiple genes.
Examples of Independent Assortment
Real-world examples can illustrate how the Law of Independent Assortment operates in various organisms.
- In pea plants, Mendel observed that seed shape and seed color assort independently.
- Drosophila melanogaster (fruit flies) exhibit independent assortment of eye color and wing shape genes.
- Human blood type and hair color genes assort independently, leading to diverse combinations.
- In corn, kernel color and texture traits follow the law of independent assortment.
- Independent assortment in dogs results in a wide variety of coat colors and patterns.
Exceptions to the Law of Independent Assortment
While the Law of Independent Assortment is a general rule, there are notable exceptions due to genetic linkage and other factors.
- Genes located close together on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together, a phenomenon known as genetic linkage.
- Linked genes do not assort independently unless crossing over occurs between them.
- Epistasis can also affect the expression of genes, complicating the patterns of inheritance.
- Polygenic traits, influenced by multiple genes, may not follow simple Mendelian inheritance patterns.
- Environmental factors can interact with genetic factors, influencing trait expression.
Modern Applications of Independent Assortment
The principles of independent assortment continue to be relevant in contemporary genetics and biotechnology.
- Genetic counseling uses knowledge of independent assortment to assess the risk of inherited conditions.
- In forensic science, DNA profiling relies on the independent assortment of genetic markers.
- Biotechnology companies use this principle to engineer organisms with specific traits.
- Independent assortment is fundamental to quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping, which identifies genes associated with complex traits.
- It also plays a role in genome-wide association studies (GWAS), linking genetic variants to diseases.
Fun Facts About Independent Assortment
Here are some interesting tidbits that highlight the fascinating aspects of the Law of Independent Assortment.
- Mendel's work was largely ignored during his lifetime and only gained recognition decades later.
- The rediscovery of Mendel's laws in the early 20th century revolutionized biology.
- Independent assortment explains why siblings can have vastly different combinations of traits.
- The principle is not limited to plants and animals; it also applies to fungi, bacteria, and other organisms.
Bringing It All Together
The Law of Independent Assortment is a cornerstone of genetics. It explains how genes for different traits are passed on independently of one another. This principle, discovered by Gregor Mendel, helps us understand genetic variation and inheritance patterns. Knowing this law is crucial for fields like genetics, medicine, and agriculture. It aids in predicting genetic outcomes, improving crop yields, and even understanding genetic disorders.
Whether you're a student, a scientist, or just curious about how traits are inherited, the Law of Independent Assortment offers valuable insights. It’s fascinating to see how something discovered in pea plants has such a wide-reaching impact. Keep exploring, keep questioning, and remember that the world of genetics is vast and ever-evolving. Understanding these basics can open doors to even more exciting discoveries.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
