Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are fascinating components of the immune system. These proteins play a crucial role in recognizing pathogens and activating immune responses. TLRs detect microbial invaders like bacteria, viruses, and fungi, triggering a defense mechanism to protect the body. Found on immune cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, they act as sentinels, scanning for danger. Each type of TLR is specialized to recognize specific molecular patterns associated with different pathogens. Understanding Toll-like receptors helps in developing treatments for infections, autoimmune diseases, and even cancer. Dive into these 32 intriguing facts about TLRs to grasp their importance in maintaining health and fighting diseases.
What Are Toll-like Receptors?
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a type of protein that play a crucial role in the immune system. They help the body recognize and respond to pathogens like bacteria and viruses. Here are some fascinating facts about these important proteins.
-
TLRs are found on the surface of certain immune cells, such as macrophages and dendritic cells.
-
They were first discovered in fruit flies, where they were named "Toll" because of the German word for "amazing" or "great."
-
Humans have 10 different types of TLRs, each recognizing different components of pathogens.
-
TLRs can detect a wide range of microbial molecules, including lipopolysaccharides, flagellin, and nucleic acids.
-
When a TLR recognizes a pathogen, it triggers an immune response to help fight off the infection.
-
TLRs are part of the innate immune system, which provides the body's first line of defense against infections.
How Do Toll-like Receptors Work?
Understanding the mechanism of TLRs can shed light on how our bodies fend off infections. Here are some key points about their function.
-
TLRs recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that are commonly found in microbes but not in human cells.
-
Once a TLR binds to a PAMP, it activates signaling pathways that lead to the production of cytokines and other immune molecules.
-
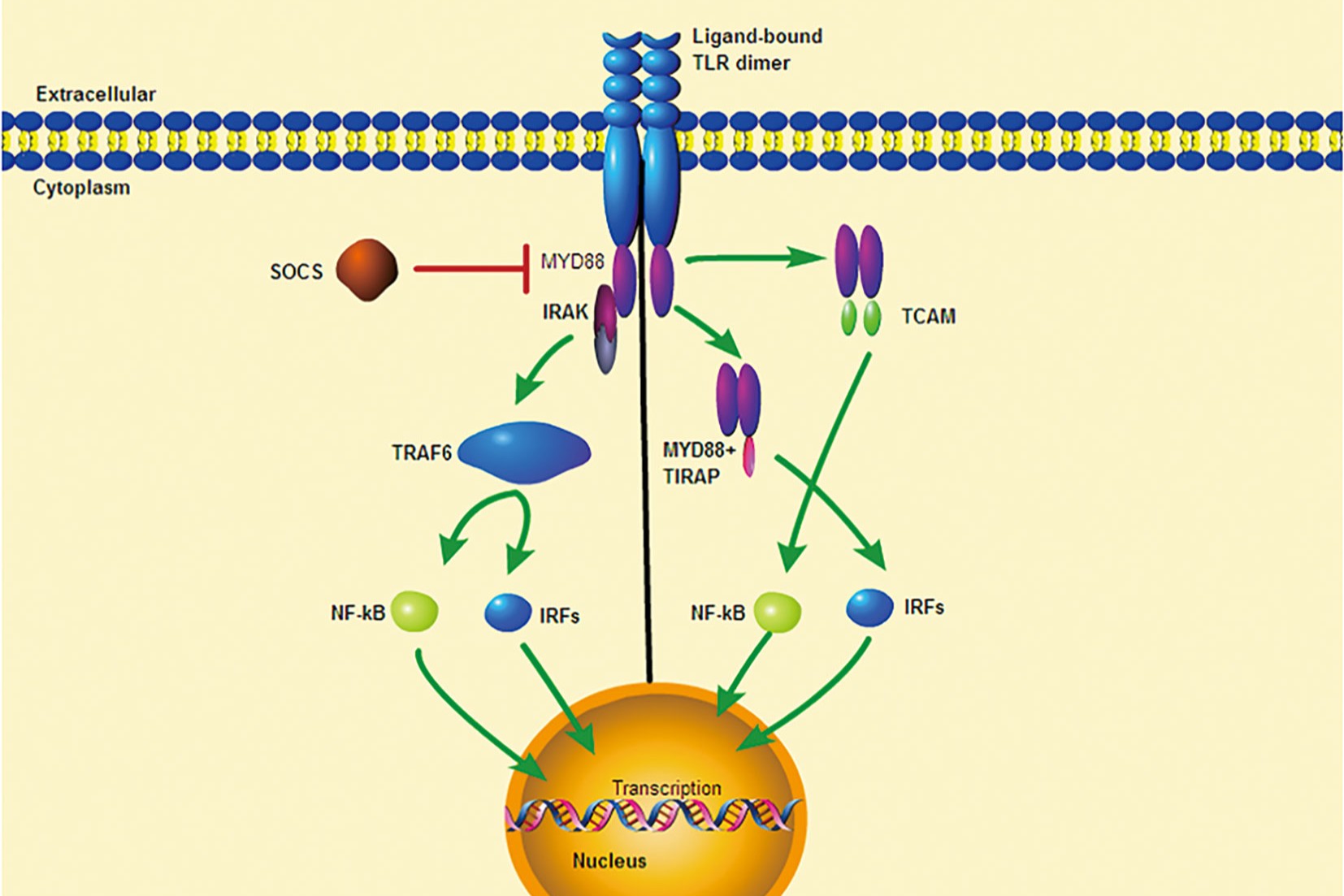
These signaling pathways often involve adaptor proteins like MyD88 and TRIF, which help transmit the signal inside the cell.
-
The activation of TLRs can lead to inflammation, which helps recruit other immune cells to the site of infection.
-
TLRs can also activate the adaptive immune system, which provides a more specific and long-lasting response to pathogens.
-
Some TLRs are located on the cell surface, while others are found in intracellular compartments like endosomes.
The Role of Toll-like Receptors in Disease
TLRs are not only important for fighting infections but also play a role in various diseases. Here are some interesting facts about their involvement in health and disease.
-
Mutations in TLR genes can lead to immune deficiencies, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
-
Overactivation of TLRs can contribute to chronic inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
-
TLRs have been implicated in the development of atherosclerosis, a condition where plaques build up in the arteries.
-
Some cancers can exploit TLR signaling to promote tumor growth and evade the immune system.
-
TLRs are involved in the body's response to vaccines, helping to generate a protective immune response.
-
Researchers are exploring TLR agonists and antagonists as potential therapies for various diseases, including cancer and autoimmune disorders.
Toll-like Receptors in Research and Medicine
TLRs are a hot topic in scientific research, with many studies exploring their potential applications in medicine. Here are some notable points about their role in research.
-
TLRs are used as targets for developing new vaccines, as they can enhance the immune response to the vaccine.
-
Scientists are studying TLRs to better understand how the immune system recognizes and responds to pathogens.
-
TLR agonists are being tested as adjuvants in cancer immunotherapy to boost the body's ability to fight tumors.
-
Some TLR antagonists are being investigated as treatments for inflammatory diseases by blocking excessive TLR activation.
-
TLRs are also being studied in the context of allergies, as they may play a role in the development of allergic reactions.
-
Understanding TLR signaling pathways can help identify new drug targets for treating infectious diseases.
Interesting Tidbits About Toll-like Receptors
Here are some additional fun and lesser-known facts about TLRs that highlight their significance and versatility.
-
The discovery of TLRs in fruit flies earned researchers the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2011.
-
TLRs are named after the Toll gene in fruit flies, which was found to be crucial for their development and immunity.
-
Some TLRs can recognize viral RNA, helping the body detect and respond to viral infections.
-
TLRs can also recognize damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which are molecules released by damaged or dying cells.
-
The study of TLRs has led to a better understanding of how the immune system distinguishes between self and non-self.
-
TLRs are conserved across many species, from insects to humans, highlighting their fundamental role in immunity.
-
Some TLRs can form dimers, meaning they pair up with another TLR to recognize certain PAMPs more effectively.
-
Research on TLRs continues to uncover new insights into their function and potential therapeutic applications.
The Power of Toll-like Receptors
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are like the body's security system, always on the lookout for invaders. They play a crucial role in the immune response by recognizing pathogens and triggering defense mechanisms. Understanding TLRs helps in developing new treatments for infections, autoimmune diseases, and even cancer. These receptors are not just limited to humans; they are found across various species, highlighting their importance in evolution. Research continues to uncover new aspects of TLRs, offering hope for medical advancements. By studying TLRs, scientists aim to create better vaccines and therapies, ultimately improving health outcomes. So, the next time you hear about TLRs, remember their vital role in keeping us safe. They are tiny but mighty warriors in the fight against disease.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
