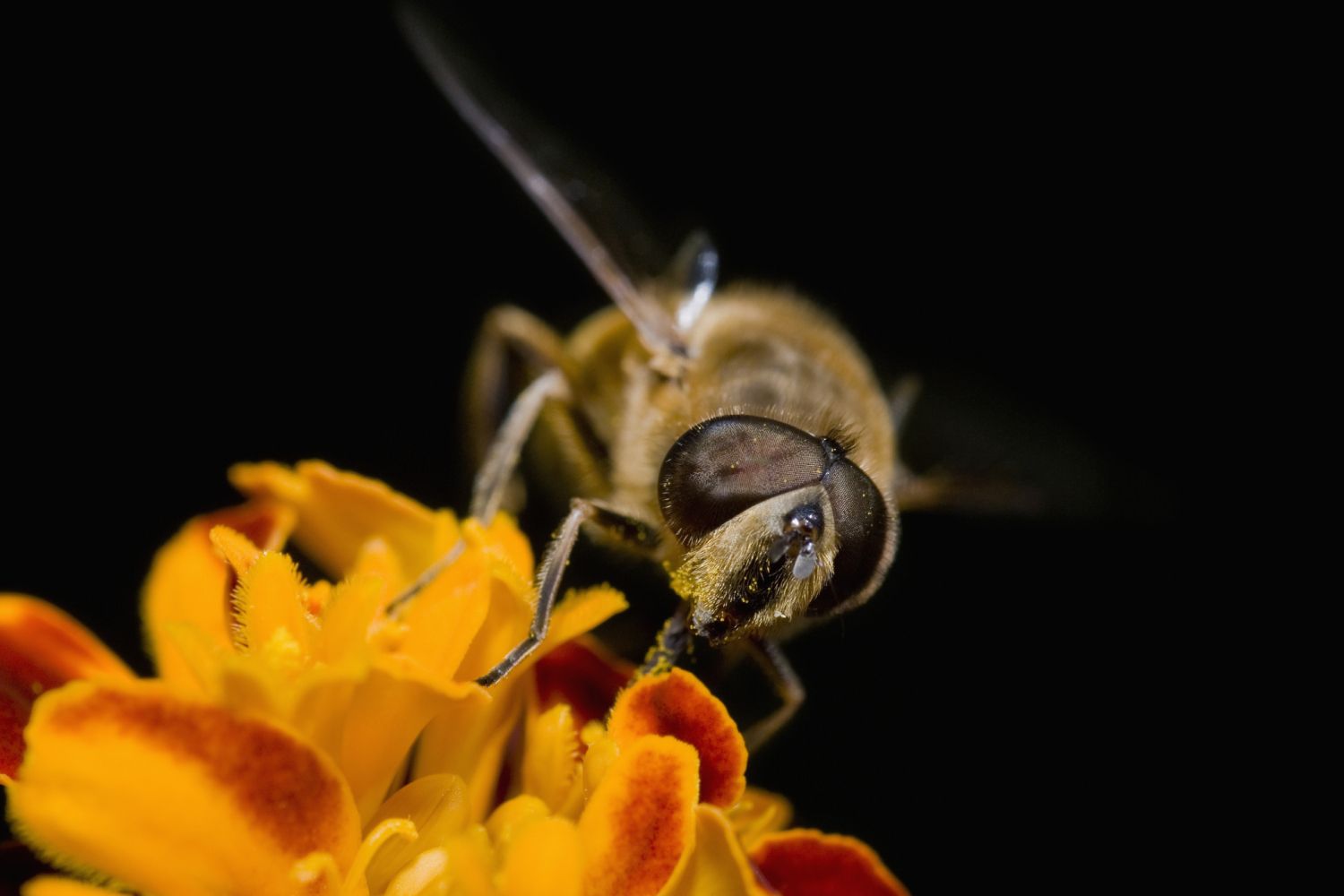
Coevolution is a fascinating process where two or more species influence each other's evolution over time. Imagine a dance where each partner's moves shape the other's steps. This intricate relationship can be seen in nature's most captivating partnerships, like bees and flowers or predators and prey. Coevolution drives diversity, adaptation, and survival in ecosystems. Understanding these interactions helps us appreciate the delicate balance of life on Earth. From the vibrant colors of a butterfly's wings to the sharp claws of a hunting hawk, coevolution showcases nature's creativity and resilience. Ready to dive into 31 amazing facts about this incredible phenomenon? Let's get started!
What is Coevolution?
Coevolution happens when two or more species influence each other's evolution. This process can lead to fascinating adaptations and relationships in nature. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about coevolution.
-
Mutual Influence: Coevolution involves species evolving in response to each other. For example, bees and flowers have coevolved; bees get nectar, while flowers get pollinated.
-
Predator-Prey Dynamics: Predators and prey often coevolve. Faster prey may lead to faster predators, creating an evolutionary arms race.
-
Symbiotic Relationships: Some species develop symbiotic relationships through coevolution. For instance, clownfish and sea anemones protect each other from predators.
-
Mimicry: Certain species mimic others as a result of coevolution. The viceroy butterfly mimics the toxic monarch butterfly to avoid predators.
-
Plant-Herbivore Interactions: Plants and herbivores coevolve. Plants may develop toxins to deter herbivores, while herbivores evolve resistance to these toxins.
Examples of Coevolution in Nature
Nature is full of examples where coevolution has shaped the interactions between species. Here are some notable ones.
-
Acacia Trees and Ants: Acacia trees provide food and shelter for ants, which in return protect the trees from herbivores.
-
Yucca Plants and Yucca Moths: Yucca plants rely on yucca moths for pollination, while the moths lay their eggs in the flowers, ensuring food for their larvae.
-
Cleaner Fish and Host Fish: Cleaner fish eat parasites off host fish, benefiting both species.
-
Figs and Fig Wasps: Fig trees and fig wasps have a mutualistic relationship where wasps pollinate the figs, and in return, the figs provide a place for wasp larvae to develop.
-
Leafcutter Ants and Fungi: Leafcutter ants cultivate fungi, which they eat. The fungi benefit from the ants' care and protection.
Coevolution and Human Impact
Human activities can influence coevolutionary processes, sometimes in unexpected ways.
-
Agriculture: Domesticated plants and animals have coevolved with humans. For example, corn has evolved to be more productive due to human cultivation.
-
Pesticide Resistance: Insects can develop resistance to pesticides, leading to a coevolutionary arms race between pests and pest control methods.
-
Antibiotic Resistance: Bacteria evolve resistance to antibiotics, prompting the development of new drugs.
-
Urban Wildlife: Some animals have adapted to urban environments, showing coevolution with human-made habitats.
-
Climate Change: Changing climates can alter coevolutionary relationships, affecting species interactions and survival.
Coevolution in Microorganisms
Microorganisms also engage in coevolution, often with significant implications for health and disease.
-
Bacteria and Viruses: Bacteria and bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) coevolve, leading to diverse bacterial defenses and viral countermeasures.
-
Human Microbiome: The human gut microbiome coevolves with its host, influencing digestion, immunity, and overall health.
-
Pathogens and Hosts: Pathogens and their hosts coevolve, with hosts developing immune responses and pathogens evolving to evade them.
-
Symbiotic Bacteria: Some bacteria form symbiotic relationships with plants, aiding in nitrogen fixation and benefiting both organisms.
-
Probiotics: Probiotic bacteria coevolve with their hosts, promoting gut health and preventing disease.
Coevolution and Evolutionary Theory
Coevolution plays a crucial role in understanding broader evolutionary principles and theories.
-
Red Queen Hypothesis: This hypothesis suggests that species must constantly evolve to survive against ever-evolving opposing species.
-
Adaptive Radiation: Coevolution can drive adaptive radiation, where species rapidly diversify to fill different ecological niches.
-
Gene-Culture Coevolution: Human culture and genetics coevolve, influencing traits like lactose tolerance and disease resistance.
-
Sexual Selection: Coevolution can influence sexual selection, where traits evolve to attract mates or compete with rivals.
-
Speciation: Coevolution can lead to speciation, where new species arise due to evolving interactions between organisms.
Fascinating Coevolutionary Adaptations
Coevolution leads to some of the most remarkable adaptations in the natural world.
-
Venom and Antivenom: Some animals evolve venom, while their prey or predators evolve resistance or antivenom.
-
Camouflage and Detection: Prey species evolve camouflage to avoid predators, while predators evolve better detection methods.
-
Pollination Syndromes: Flowers evolve specific traits to attract particular pollinators, such as color, scent, and shape.
-
Seed Dispersal: Plants evolve fruit traits to attract animals that will disperse their seeds, aiding in plant reproduction.
-
Defense Mechanisms: Some plants develop physical defenses like thorns, while herbivores evolve ways to bypass these defenses.
-
Mutualistic Networks: Complex networks of mutualistic relationships evolve, involving multiple species that benefit from each other's presence.
The Fascinating Dance of Coevolution
Coevolution shows how interconnected life on Earth really is. From the mutualistic relationships between bees and flowers to the predator-prey dynamics of cheetahs and gazelles, these interactions shape the natural world. Understanding coevolution helps us appreciate the complexity of ecosystems and the delicate balance that sustains them.
This dance of adaptation and counter-adaptation drives biodiversity and innovation in nature. It’s a reminder that every species, no matter how small, plays a role in the grand tapestry of life. By studying these relationships, scientists can uncover new insights into evolutionary processes and conservation strategies.
So next time you see a bee buzzing around a flower or a bird eating a fruit, remember the intricate evolutionary dance that brought them together. Coevolution is a testament to the power of nature and its endless capacity for innovation and adaptation.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.